In this article, we will review how to construct and execute dynamic SQL statements in SQL Server with different examples.
Dynamic SQL is the SQL statement that is constructed and executed at runtime based on input parameters passed. Let us go through some examples using the EXEC command and sp_executesql extended stored procedure.
Executing dynamic SQL using EXEC/ EXECUTE command
EXEC command executes a stored procedure or string passed to it. Please refer to EXEC SQL overview and examples for more details and examples on the EXEC command.
The following example demonstrates constructing the SQL statement using the input variable and executing the SQL statement using the EXEC command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
-- Simple dynamic SQL statement DECLARE @SQL nvarchar(1000) declare @Pid varchar(50) set @pid = '680' SET @SQL = 'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = '+ @Pid EXEC (@SQL) |
There is a possibility of SQL injection when you construct the SQL statement by concatenating strings from user input values. I hope to cover the SQL injection and some methods to prevent SQL Injection in my future articles.
We should take care of null values when concatenating strings from parameters using ‘+’ operator. In the below example, I commented out the statement that sets a value to variable “@pid”.
By default, the variable “@pid” is NULL as we did not set any value. The final statement constructed after concatenation is blank as ‘+’ operator does not handle null values. Please refer to the below image that shows the final value of “@SQL” variable is blank.

In this case, use the ISNULL function to construct a proper SQL statement while concatenating strings using ‘+’ operator.
EXEC command does not re-use the compiled plan stored in the plan cache. Execute the following query and check for the cached plans.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
DECLARE @SQL nvarchar(1000) declare @Pid varchar(50) set @pid = '689' SET @SQL = 'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = '+ @Pid EXEC (@SQL) GO DECLARE @SQL nvarchar(1000) declare @Pid varchar(50) set @pid = '681' SET @SQL = 'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = '+ @Pid EXEC (@SQL) |
Please refer to the below image that shows two separate plans created when the above query is executed for two different parameters.

Executing dynamic SQL using sp_executesql
sp_executesql is an extended stored procedure that can be used to execute dynamic SQL statements in SQL Server. we need to pass the SQL statement and definition of the parameters used in the SQL statement and finally set the values to the parameters used in the query.
Following is the syntax of executing dynamic SQL statements using sp_executesql extended stored procedure.
|
1 |
sp_executesql @stmt, N'@parameter_name data_type' , @param1 = 'value1' |
Below example demonstrates executing dynamic SQL statement by passing parameters to sp_executesql extended stored procedure.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
EXECUTE sp_executesql N'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = @Pid and ProductNumber=@PNumber', N'@Pid varchar(50),@PNumber varchar(50)', @pid = '680',@PNumber='FR-R92B-58'; |

sp_executesql reuses the compiled plan when the statement is executed for different parameters. Execute the following query and check for the cached plan.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
EXECUTE sp_executesql N'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = @Pid and ProductNumber=@PNumber', N'@Pid varchar(50),@PNumber varchar(50)', @pid = '680',@PNumber='FR-R92B-58'; EXECUTE sp_executesql N'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = @Pid and ProductNumber=@PNumber', N'@Pid varchar(50),@PNumber varchar(50)', @pid = '681',@PNumber='FR-R92B-58'; EXECUTE sp_executesql N'SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = @Pid and ProductNumber=@PNumber', N'@Pid varchar(50),@PNumber varchar(50)', @pid = '682',@PNumber='FR-R92B-58'; |
Please refer to the below image that shows the same plan is being used when the statement is executed with different parameters.
Using dynamic SQL inside stored procedures
Following is the example of using dynamic SQL inside a stored procedure. For demo purpose, I used the Product table from the AdventureWorksLT database. This stored procedure is used to search for products based on different columns like name, color, productid, and the product number. The dynamic SQL statement is constructed based on the input parameters passed to the stored procedure and is executed by the EXEC command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 |
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_SearchProducts] ( @ProductID NVARCHAR(50) = NULL ,@Name NVARCHAR(100) = NULL ,@ProductNumber NVARCHAR(100) = NULL ,@Color NVARCHAR(100) = NULL ) AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; DECLARE @SQL VARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE @ProductIDFilter VARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE @NameFilter VARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE @ProductNumberFilter VARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE @ColorFilter VARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE @all VARCHAR(2) = '-1' SET @ProductIDFilter = CASE WHEN @ProductID IS NULL OR @ProductID = 0 THEN '''' + @all + ''' = ''' + @all + '''' ELSE 'ProductID = ''' + @ProductID + '''' END SET @NameFilter = CASE WHEN @Name IS NULL OR @Name = '' THEN '''' + @all + ''' = ''' + @all + '''' ELSE 'Name like ''%' + @Name + '%''' END SET @ProductNumberFilter = CASE WHEN @ProductNumber IS NULL OR @ProductNumber = '' THEN '''' + @all + ''' = ''' + @all + '''' ELSE 'ProductNumber like ''%' + @ProductNumber + '%''' END SET @ColorFilter = CASE WHEN @Color IS NULL OR @Color = '' THEN '''' + @all + ''' = ''' + @all + '''' ELSE 'Color like ''' + @Color + '''' END SET @SQL = 'SELECT ProductID ,Name ,ProductNumber ,Color ,StandardCost ,Size ,Weight FROM SalesLT.Product WHERE ' + @ProductIDFilter + ' AND ' + @NameFilter + '' + ' AND ' + @ProductNumberFilter + '' + ' AND ' + @ColorFilter + '' PRINT (@sql) EXEC(@sql) END |
When we execute the stored procedure with input parameter productid only, the SQL statement is constructed as shown in the below image.

Please refer to the below image that shows a different SQL statement constructed when productid and product number are passed as input parameters to the stored procedure.

Let us re-write the stored procedure to form dynamic SQL and execute it using sp_executesql extended stored procedure. Please refer to the below sample script.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 |
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[usp_SearchProducts2] ( @ProductID NVARCHAR(50) = NULL ,@Name NVARCHAR(100) = NULL ,@ProductNumber NVARCHAR(100) = NULL ,@Color NVARCHAR(100) = NULL ) AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; DECLARE @SQL NVARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE @ParameterDef NVARCHAR(500) SET @ParameterDef = '@ProductID NVARCHAR(50), @Name NVARCHAR(100), @ProductNumber NVARCHAR(100), @Color NVARCHAR(100)' SET @SQL = 'SELECT ProductID ,Name ,ProductNumber ,Color ,StandardCost ,Size ,Weight FROM SalesLT.Product WHERE -1=-1 ' IF @ProductID IS NOT NULL AND @ProductID <> 0 SET @SQL = @SQL+ ' AND ProductID = @ProductID' IF @Name IS NOT NULL AND @Name <> '' SET @SQL = @SQL+ ' AND Name like ''%'' + @Name + ''%''' IF @ProductNumber IS NOT NULL AND @ProductNumber <>'' SET @SQL = @SQL+ ' AND ProductNumber like ''%'' + @ProductNumber + ''%''' IF @Color IS NOT NULL AND @Color <>'' SET @SQL = @SQL+ ' AND Color like ''%'' + @Color + ''%''' EXEC sp_Executesql @SQL, @ParameterDef, @ProductID=@ProductID,@Name=@Name,@ProductNumber=@ProductNumber,@Color=@Color END GO |
Let us execute below sample thread that will retrieve all the products that are red.
|
1 |
[usp_SearchProducts2] @ProductID=0,@Name='',@ProductNumber='',@Color = 'red' |

OUTPUT parameter in sp_executesql
sp_executesql extended stored procedure supports the output parameter to store the value returned by the select query and use the output variable in another statement.
Following is the example script which shows the usage of the output variable in sp_executesql.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
DECLARE @ProdNumber nvarchar(50) EXECUTE sp_executesql N' SELECT @ProdNumberOUT= ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = @Pid' ,N'@Pid varchar(50) ,@ProdNumberOUT nvarchar(25) OUTPUT' ,@pid = '680' , @ProdNumberOUT = @ProdNumber OUTPUT select @ProdNumber as ProductNumber |
Temp tables in dynamic SQL
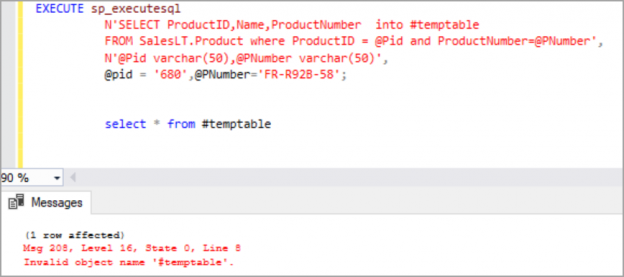
The local temp table created by executing dynamic SQL cannot be accessed outside the execution of dynamic SQL. It throws invalid object error as shown in the below image.

A workaround for this is to create the local temp table outside and use it in the dynamic SQL. Following is the example that demonstrates this scenario.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
CREATE TABLE #temptable ( ProductID VARCHAR(50) ,Name VARCHAR(100) ,ProductNumber VARCHAR(100) ) EXECUTE sp_executesql N' INSERT INTO #temptable SELECT ProductID,Name,ProductNumber FROM SalesLT.Product where ProductID = @Pid and ProductNumber=@PNumber' ,N'@Pid varchar(50),@PNumber varchar(50)' ,@pid = '680' ,@PNumber = 'FR-R92B-58'; SELECT * FROM #temptable |
Please refer to the below image. we can see that the data is inserted in the temp table and can be accessed again.

Comparison of EXEC command and sp_executesql extended stored procedure
|
sp_executesql |
EXEC Command |
|
Reuses the cached plan |
Generates multiple plans when executed with different parameters |
|
Less prone to SQL Injection |
Prone to SQL injection |
|
Supports parameterization |
Does not support parameterization |
|
Supports output variable |
Output variable is not supported |
Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to construct and execute dynamic SQL in SQL Server using the EXEC command and sp_executesql extended stored procedure with different examples. In case you have any questions, please feel free to ask in the comment section below.
- Geo Replication on Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) enabled Azure SQL databases - October 24, 2019
- Overview of the Collate SQL command - October 22, 2019
- Recover a lost SA password - September 20, 2019