In this 17h article of the SQL Server Always On Availability Group series, we are going to explore the SQL Server replication for the distribution database in the availability group.
Introduction
In the earlier article (see TOC at the bottom), we explored how you can add the publisher and subscriber database in a high availability configuration using SQL Server Always On Availability Groups. It used a remote distributor for transactional replication.
Suppose the publisher and subscriber databases are on [SQLAG1\INST1] node, and failover happens to the node [SQLAG2\INST2]. In this case, the transactional replication works fine without any issues. It provided high resilience for the publisher and subscriber database.
What about the distribution database? Can we add it to the availability group? In this article, let’s explore the steps required for the distribution database AG.
Overview of the distribution database in the SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
We can add the replication distribution database in the availability group for high availability starting from SQL Server 2017 CU6 and SQL Server 2016 SP2-CU3. It requires special considerations for adding the distribution database.
- You must use a SQL listener for the distribution configuration
- It creates SQL jobs with the listener’s name
- It creates a new job to monitor the status of the distribution database in primary or secondary AG
- SQL Server automatically disables and enables the jobs based on the primary replica. For example, if the distribution database is on the SQLAG1, jobs are enabled on the SQLAG1 instance. In the case of DB failover, jobs got disabled on the SQLAG1 and enabled on the SQLAG2 instance
- The publisher and distributor database cannot exist in an instance
- We cannot use merge, Peer-To-Peer replication
- All replication databases (publisher, subscriber, and distributor) should be a minimum of SQL Server 2017 CU6 and SQL Server 2016 SP2-CU3
- We can use both synchronous and asynchronous data synchronization for the distribution database
- We cannot use the SSMS wizard for the distribution database AG configuration. It needs to set up using the scripts
- We cannot use an existing distribution database for the AG configuration. If the replication is already configured, we need to break the replication first and configure it using the scripts for AG configuration
- The secondary replica of the distribution database should allow read-only connections
- You should use the same domain account in all replica of the distribution database AG
Environmental details
In this article, we use the following environment.
Existing AG configuration:
We configure the distribution database in a new availability group on the following replicas.
- Primary Replica: SQLAG1\INST1
- Secondary Replica: SQLAG2\INST2
- Existing AG database: DBARepository
For this article, we use a standalone instance for the publisher and subscriber.
Publisher and Subscriber: SQLNode3\INST3
Therefore, the overall configuration in terms of the SQL Server replication topology is as below.:
- Publication Server: SQLNode3\INST3
- Subscription Server: SQLNode3\INST3
- Distribution Server: AG replica ( SQLAG1\INST1 & SQLAG2\INST2)
You can use the previous articles in the series to prepare a similar environment.
Steps to configure SQL Server replication distribution database in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Note: You can find the script attached at the bottom of the article.
Step 1: Configure the AG nodes for the distribution DB nodes
In this step, we connect to both the AG replica instances and configure for the distribution. It registers both replica servers as a distributor.
We use the stored procedure sp_adddistributor for this purpose. You should specify the same password for both the servers.

Step 2: Configure the distribution database on the primary replica in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
In this step, we do the following tasks.
- Create the distribution database on the primary replica and install the relevant schema. In the query, we run the stored procedure sp_adddistributiondb in the master database
- Modify the recovery model of the distribution database as FULL
- Take a full backup of the distribution database so that it becomes eligible for an AG group
In the sp_adddistributiondb output, we can see the database objects it creates for the distribution database.
Refresh the object explorer, and you see the [DistributionDB] under the system databases.

Step 3: Verify the endpoints for an availability Group
We already have a database configured on the availability group for both replicas. Therefore, the endpoint [HADR_ENDPOINT] exists. You can navigate to Server Objects -> Endpoints-> Database Mirroring-> script Hadr_endpoint.
Similarly, verify the endpoint on the secondary replica node as well. In case of a new configuration, you should create the endpoint.
Step 4: Add the distribution database in an existing SQL Server Always On Availability Group
Let’s try to add the distribution database in the existing availability group. If you launch the add database to the availability group wizard, it does not display the distribution database in the list. It only shows the user databases in this list.

As stated earlier, we cannot use the SSMS wizard for the AG configuration of the distribution database. Create a new availability group and specify both replicas, their endpoint in the script. You can note here that we used the automatic seeding for the initial database synchronization.

Step 5: Add the secondary replica in the SQL Server Always On Availability Group
In this step, connect to the secondary replica and join it for the new availability group. We also permit to create a new database because of the direct seeding configuration in the previous step. SQL Server automatically creates the distribution database in the secondary replica and synchronizes it.

Step 6: Create the SQL Listener for the distribution database availability group
In this step, create a new SQL listener for the distribution database availability group. Now, create the listener on the primary replica. You need to specify the listener IP address and the port. This port should be allowed within your firewall.

Refresh the object explorer on the primary replica, and you see a new availability group, availability database (DistributionDB), and its listener.

Step 7: Enable the secondary SQL Server Always On Availability Group replica for the distributor
Connect to the secondary replica and use the stored procedure sp_adddistributiondb to create it on the secondary AG replica.

Step 8: Configure the publisher to use the distribution database in SQL Server Always On Availability Group
Connect to both AG replica and use the stored procedure sp_adddistpublisher. You should specify a shared directory accessible from both replicas and distributor instances in the @working_directory argument.

Step 9: Configure the publisher server for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Connect to the publisher instance and execute the sp_addDistributor stored procedure. In the @distributor argument, you must specify the SQL Listener of the distribution database availability group.

Step 10: Create a local publication in SQL Server replication
At this step, create a local publication in the SQLNode3\INST3 instance. You can follow the previous article for the detailed step.
Here, you can see my publication SQLPub_AG configured on the SQLNode3 instance.

Step 11: Create a linked server on the primary and secondary replica
On both AG replicas, create a linked server, and it should point to the subscriber instance. In my case, both the publisher and subscriber database are in the same SQL instance.

Step 12: Create a local subscription for SQL Server Always On Availability Group
On the subscription server, right-click on the local subscription and create a new subscription.
In the new subscription wizard, select the publication created earlier.

In the distribution agent location, select the first option – Run all the agents at the distributor. Here, you can note that it shows the SQL Listener name for push subscriptions.

In the subscribers, select the existing subscription database or create a new database.

Use the SQL agent account or any appropriate account for the distribution agent security.

We can have continuous synchronization or at a fixed schedule. Let’s go with the default option – Run continuously.

Initialize the subscription with a snapshot of the publication data, as shown below.

Create the subscription with the configurations we have done so far.

It created the subscription successfully, as shown below.

Launch the SQL Server replication monitor and view the replication status. It shows failed below because my distribution SQL service account does not have permission to connect to the publisher.
Assign the permissions to the service account, and it quickly synchronizes the publisher and the subscriber.
It shows excellent performance with minimum latency.
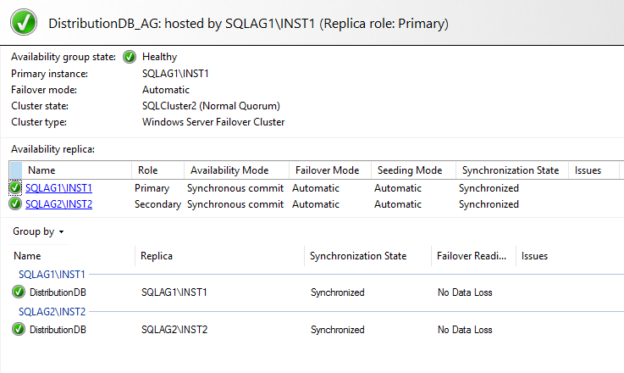
You should review the health of the availability group dashboard. We can verify that the DistributionDB database is in the availability group configuration.

Failover the distribution database and monitor SQL Server replication
Let’s perform failover for the [DistributionDB] database from the SQLAG1\INST1 to the SQLAG2\INST2. It should not break the SQL Server replication because the distribution database will be available from the new primary replica in SQL Server Always On Availability Group.

The failover is successful, as shown below.

Refresh the object explorer of the previous secondary replica (SQLAG1\INST1), and here, you see two availability groups.
- DistributionDB_AG: Secondary replica
- SQLDRAG: Primary

Launch the AG dashboard from the new primary replica SQLAG2\INST2. AG dashboard looks good.

Verify the SQL Server replication status. We can verify here that the transaction replication is working fine after the distribution database failover as well.
Verify the records should be the same in both publisher and subscriber database.

Conclusion
In this article, we explored the process of adding a distribution database in the SQL Server Always On Availability Group configuration. It provides high availability for publication, subscription, and the distribution database for the SQL Server replication.
Table of contents
See more
Check out SpotLight, a free, cloud based SQL Server monitoring tool to easily detect, monitor, and solve SQL Server performance problems on any device

- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023