In the 42nd article for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups, we are going to explore lease timeouts and health checks.
Introduction
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups provides resilience for high availability and disaster recovery solution in a multi-node architecture. In the article, Session timeouts in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups, we explained the session timeout configurations to safeguard AG from soft errors.
Suppose you have an availability group configured for automatic failover. In this synchronized availability group, we can have the following types of failover.
- Automatic
- Manual
- You can do forced failover with possible data loss
In the case of automatic failover, the availability group fails over to a synchronized secondary replica without any data loss. However, an automatic failover requires the satisfied conditions defined in the flexible failover policy.
The flexible failover policy depends on the Health-check timeout threshold, Failure-Condition Level and Cluster timeouts.
It is an important aspect to determine the auto-failover causes in a production database environment. The logs are useful factors for monitoring and investigating the failures.
- SQL Server error logs
- Windows cluster logs
- Cluster event logs
- SQL Server failover diagnostics (sp_server_diagnostics) logs
- AlwaysOn_Health extended events output
- System_health extended events
- Application and system logs
The availability group feature requires an underlying Windows Failover Clusters. The cluster requires cluster services on all participating nodes.
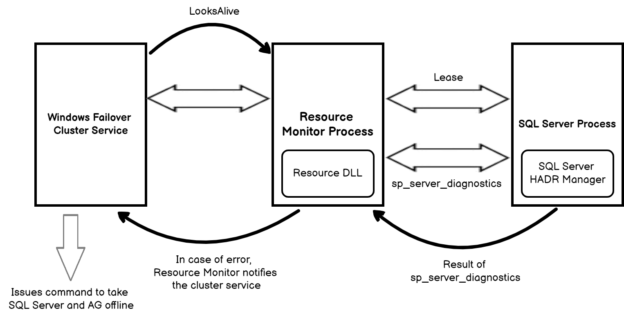
The resource host acts as an interface between the cluster resource and service. SQL Server uses resource DLLs for the resource monitor. These DLLs are responsible for health monitoring and offline-online resource management.
In the below image, we see two levels of monitoring in an AG configuration.
- Looks-Alive
- Is-Alive
Looks-Alive mechanism

In a Windows failover cluster, the cluster service continuously transmits heartbeat to other cluster nodes and waits for the acknowledgment. If it does not receive a heartbeat acknowledgment after a series of heartbeats, it assumes that the corresponding node is down. Subsequently, it broadcasts a message to other cluster nodes, and a node takes over the cluster ownership based on the quorum votes and majority configuration. If due to any reason, the cluster could not determine the quorum majority, all nodes in a cluster go into the resolving state and all cluster resources are taken offline. This process is known as Looks-Alive and runs every 5 seconds. The Windows failover cluster uses the Looks-Alive mechanism for an integration between the cluster resource host and SQL process. On the primary replica, SQL Server uses a dedicated lease worker thread.

Go to Windows Failover Cluster and right-click on the cluster resource. In the properties, you get configured values for LeaseTimeout. By default, it is set to 20000 milliseconds (20 seconds).

The lease worker thread and resource host work circularly, as shown in the below image.

Image reference: Microsoft docs
In the SQL Server logs on the primary replica, you get a message from the lease worker. The lease worker thread and resource host maintains a time-to-leave (TTL), and it gets updated each time threads wait up after a signal from another resource.
If the lease timeout period elapsed while waiting for the signal, the AG resource goes into the resolving state. In the case of AG failover, SQL Server logs another entry to stop the lease renewal.
Is-Alive mechanism
The SQL Server Always on resource DLL uses the sp_server_diagnostics stored procedure for the health of SQL Service. The stored procedure reports the status for the system, resource, IO subsystem, query processing and events. It uses a FAILURE_CONDITION_LEVEL for implementing defining a condition in which automatic failover can happen.
|
Failover Condition Level |
Description |
|
1 |
Automatic failover occurred due to server down or lease expiry. |
|
2 |
No data returned from sp_server_diagnostics. It can be related to the hung server issue. The automatic failover can happen due to SQL Server is not connected to the cluster or due to user-defined health check timeout. |
|
3 (Default level) |
System error ( stack dumps, orphaned spinlocks, serious write-access) |
|
4 |
Resource error (For example- persistent out-of-memory condition) |
|
5 |
Query processing (for example – Scheduler deadlock or unresolvable deadlock) |
A failover condition encompasses conditions lower than configured conditions as well. For example, the default condition 3 also uses condition levels 1 and 2.
You can use the ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP to set a specific failover condition level.
|
1 |
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG1 SET (FAILURE_CONDITION_LEVEL = 1); |
But how long resource DLL with wait for the output from the stored procedure sp_server_diagnostics? The resource DLL uses the timeout properties for this purpose. By default, the timeout is 30,000 milliseconds, i.e. 30 seconds. You can set the value for a timeout from 15 seconds to 4294967 seconds.
You can modify the health check timeout from the following ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP command.
|
1 |
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG1 SET (HEALTH_CHECK_TIMEOUT = 60000); |
We can query sys.dm_xe_session to check the extended events for the sp_server_diagnostics session.
The output of these events is stored in the default log directory. For example, in my environment, these files are available in the C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.INST1\MSSQL\Log directory.
Lease Time out in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
As shown below, the lease timeout is 20 seconds. By default, the Windows failover cluster renewals the lease every 5 seconds, i.e. ¼ time of the lease timeout.

If lease timeout occurs ( >20 seconds), the rhs.exe reports an error in the Windows cluster, and it starts taking preventive action.
You can get the following error messages for a least timeout issues:
|
1 2 3 |
select message_id,text from sys.messages where message_id in(19407,19419,19421,19422) and language_id=1033 |
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups Health Check timeout
SQL Server Always On Availability Group performs a health check of the primary replica using the sp_server_diagnostics stored procedure. The sp_server_diagnostics executes every 10 seconds. The health check timeout is 30 seconds.
Therefore, the stored procedure returns the result on 1/3 * health checks current threshold. If the SP does not return any results, AG refers to the previous state for determining the instance health until the health-check timeout threshold. The next Is-Alive determines that the primary replica is unresponsive, and it initiates the automatic failover.
- Note:
- The sp_server_diagnostics does not perform health checks at the database level
- It does not consider DB level health detection until we explicitly enabled it. Refer to the article, Database-level health detection in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for more details
WSFC configuration and cluster timeouts for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
In a Windows failover cluster, the following parameters control the cluster timeout values:
- SameSubnetDelay
- SameSubnetThreshold
- CrossSubnetDelay
- CrossSubnetThreshold
You can check these parameter values using the Windows PowerShell cmdlet get-cluster().

In my lab environment, the servers are located in the same subnets. Therefore, the following table shows the default values for Windows Server 2012 and 2016.
|
Parameter |
Windows Server 2012 R2 |
Windows Server 2016 |
|
SameSubnetDelay |
1 second |
1 Second |
|
SameSubnetThreshold |
5 heartbeats |
10 heartbeats |
The SameSubnetDelay defines the wait time between the heartbeats. It is 1 second for both Windows Server 2012 and 2016.
The SameSubnetThreshold defines the number of missing heartbeats a cluster can tolerate, and if it does not receive the acknowledgement, the target node is declared dead.
Recap of LeaseTimeout, Session-Timeout and Health check timeouts
- Lease timeout:
- Default value: 20000 milliseconds, i.e. 20 seconds
- It is required to prevent a split-brain scenario in the Windows failover cluster
- It can trigger an AG failover or offline-online
- It is used in both Is-Alive and the Looks-alive mechanism
- Session Timeout:
- It is used to safeguard against soft errors between AG replicas
- default value: 10000 milliseconds or 10 seconds
- It is not part of the Is-Alive or the Looks-alive mechanism
- Secondary replica becomes DISCONNECTED status due to session timeout
- You can configure the session timeouts in the availability group properties from the primary replica instance
- Health Check timeout
- Default value: 30000 milliseconds, i.e. 30 seconds
- It is the timeout if the sp_server_diagnostics does not return any data or reports errors in the health check
- It is used in both Is-Alive and the Looks-alive mechanism
- It also depends on the failover condition levels defined from 1-5, as explained earlier. The default configuration is level 3
Conclusion
In this article, we figured SQL Server Always On Availability Groups flexible failover policy using the lease, health check timeout and Failover Condition Levels. You should review the logs to determine the scenarios where the automatic failover occurred or failed.
Table of contents
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023