This article will explain the impact of TDE (Transparent Data Encryption) on one of the crucial system databases, tempdb. Everybody wants to secure their data to prevent unauthorized access and use. SQL Server is a very popular enterprise RDBMS system that is used to store client’s data inside their databases. It also offers multiple features to secure the data stored in the databases. TDE (Transparent Data Encryption) is one of those features which is used to secure SQL Server databases by encrypting their database files. TDE protects data by applying encryption using a certificate which is also protected by the master key.
Enabling encryption for user databases seems to be a very easy and straightforward step. The influence of this enablement might have some adverse impacts on other databases operations if you have not done careful planning. I have already covered one of such impacts on Instant File Initialization in my last article. You must read this article, Understanding Instant File Initialization after enabling TDE on SQL Server Databases, to understand how TDE enablement disables IFI (Instant File Initialization) feature for TDE enabled databases.
Today, I will discuss one more impact of enabling TDE on tempdb and on other user databases hosted on your SQL Server instance.
Relation between Transparent Data Encryption and Tempdb
Tempdb is a system database designed to be used by all SQL Server connections for their temporary operations like sorting, row versions, temp tables, etc. You can read more about tempdb here. Database tempdb is very critical for SQL Server instance to run in a healthy state, even poor sizing of these database files can affect the performance of the whole SQL Server instance.
I always suggest having careful planning of TDE enablement because if we enable TDE for any SQL Server user database, the tempdb database will automatically be encrypted. This is by design and seems logical as well. We know tempdb is used by all SQL Server connections so there might be a possibility that some of the data from the database which is encrypted using TDE will present in tempdb for some temporary activities. To prevent this expose, Microsoft has designed to encrypt the tempdb database the moment you encrypt any user database on that SQL Server instance.
As tempdb will be encrypted post enabling transparent data encryption for any user database and we know all SQL Server connections from other non-encrypted databases also use tempdb for their various temporary activities. You will see some negative performance impact on your transactions despite the fact you have not encrypted your very own database because every transaction must use some additional CPU cycles for encryption and decryption activities in tempdb.
One more fact about the relationship between transparent data encryption and tempdb is when you will remove TDE from the user database, you will not see this removed and decrypted for the tempdb database. If you access the sys.databases system object and see the value of tempdb database under is_encrypted column, it will still be showing 1 i.e. encrypted. You need to restart the SQL Server service to unencrypt tempdb completely. If you are running with older versions like SQL Server 2016 or 204 then you might observe tempdb as encrypted even after restarting the SQL Server service post removing TDE from all user databases.
I will show you a proof of concept about this relation between TDE and Tempdb in the below sections of this article. Below are the high-level steps I will perform to demonstrate this POC (proof of concept).
- Enable TDE on a user database and validate tempdb encryption state
- Remove TDE from the user database and capture tempdb encryption state
Let’s start with the first bullet in the below section.
Enable TDE on a user database and validate tempdb encryption state
I used SQL Server 2019 for this demonstration. I have created a database named “Test_DB” and enabled TDE by executing the below set of T-SQL statements. I am not covering detailed steps on how to enable transparent data encryption on a user database. I generally used the below set of scripts as a template for TDE enablement. You can also use it for your testing and learning. You can execute these statements in one shot to create a master key, certificate, database encryption key, and enabling encryption on the database.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
--Create master key USE master; GO CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD='$ql$h@ck@12'; GO --Create Certificate using above master key CREATE CERTIFICATE Test_DB_TDECert WITH SUBJECT='Test_DB_Encryption'; GO --Create a database encryption key USE Test_DB GO CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE Test_DB_TDECert; GO --Enable encryption ALTER DATABASE Test_DB SET ENCRYPTION ON; GO |
I am not showing any screenshot of the above execution as it is not needed in this article. Now, we have enabled transparent data encryption for user database “Test_DB” by executing the above statements. Let’s check what is tempdb encryption state post enabling TDE for this database. Run below T-SQL to validate encryption for user database as well as tempdb.
|
1 2 3 4 |
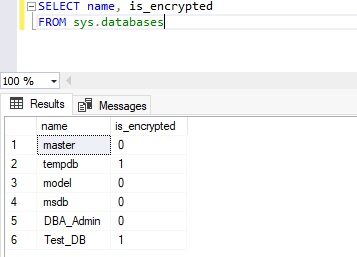
--Check TDE for tempdb and user database SELECT name, is_encrypted FROM sys.databases Go |
The output of the above T-SQL statement is showing that transparent data encryption is enabled for both databases (Test_DB and tempdb) as is_encrypted value for both databases is showing as 1.

Now let’s check their encryption state using another DMV sys.dm_database_encryption_keys which is more descriptive. Run below T-SQL statements to get the output.
|
1 2 3 4 |
--Check TDE for Tempdb and user database SELECT DB_Name(database_id) As [DB Name, encryption_state, encryption_state_desc FROM sys.dm_database_encryption_keys Go |
This DMV sys.dm_database_encryption_keys returns details about encrypted databases and their associated keys. You can get much useful information using this DMV like create dates, modify dates, the algorithm used for keys, encryption type, encryption scan state, etc. We can see the state of both databases is showing as 3 which means these databases are encrypted. Here is the description of other encryption states.
- 0 = No database encryption key present, no encryption
- 1 = Unencrypted
- 2 = Encryption in progress
- 3 = Encrypted
- 4 = Key change in progress
- 5 = Decryption in progress
- 6 = Protection changes in progress
Have a look at the below image to see the details.

When you enable transparent data encryption, it will be logged in the SQL Server error log file with its internal encryption scanning details. You will not see any logs for this feature enablement for the tempdb database. This is because when you run ALTER DATABASE statement to enable encryption, it starts encrypting all existing pages and contents of data and log files using a scan operation whereas this scan is not performed on the existing content of the tempdb database, and it encrypts only upcoming and future contents inside tempdb.
Remove TDE from the user database and validate tempdb encryption State
I would suggest you follow another article where I have written step by step process in detail for TDE removal on a user database. Run below set of statements in the same sequence in which it is given to remove encryption from user database “Test_DB”.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
--Turn OFF TDE ALTER DATABASE Test_DB SET ENCRYPTION OFF Go --Remove database encryption key USE Test_DB GO DROP DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY GO --Remove certificate USE master GO DROP CERTIFICATE TEST_DB_TDECert --Remove master key USE master GO DROP MASTER KEY GO |
Remember to execute the above statements in the same sequence to avoid any issues. Now, I will again check the encryption state for both databases. You can only turn off TDE and carry one with the remaining steps to understand its behavior with tempdb, but I have removed everything related to transparent data encryption to clean all TDE related components.
We can see, there is only one entry in DMV and that is for tempdb, Test_DB is not there because we have removed all keys, certificates, and encryption for this database. If you only turn off TDE and keep keys and certificates, then you can see another entry for database Test_DB with its state as unencrypted.
Both statements are showing that tempdb encryption is still there after removing transparent data encryption from the user database. We will restart SQL Server and check the tempdb encryption state again to see its value.
You can see the below image which is taken after restarting the SQL Server service. Here, the output from both T-SQL statements is showing that tempdb is not encrypted anymore. DMV is not showing any entry whereas the is_encrypted column of sys.databases system object is showing its value as 0 which is for “Not Encrypted”.

The encryption from the tempdb database will be removed after restarting the SQL Server service but this might not be the case for other SQL Server versions like SQL Server 2016 or SQL Server 2014. Note, I have used SQL Server 2019 for this demo and POC.
Microsoft has addressed this behavior for SQL Server 2016 and 2014 and released a KB article KB4042788 which I have attached here and you should also consider applying these patch levels If you are using SQL Server 2014 or SQL Server 2016 and have this product defect.
Conclusion
We have learned that tempdb is impacted after enabling or disabling Transparent Data Encryption from any user databases. I have also explained how TDE secures your data in SQL Server to prevent any unauthorized access even for its temporary transactions in the tempdb database. Data will be secured in the tempdb database while having its transactions in this system database.
Please share this article and comment your feedback in the comment section so that we can improve in a better way.
See more
Be sure to check out ApexSQL Decrypt, add-in that decrypts SQL Server database objects directly from SSMS

- Configure backup storage redundancy for Azure Cosmos DB account - May 15, 2024
- Difference between SQL SELECT UNIQUE and SELECT DISTINCT - January 16, 2024
- How to do a group by clause - April 12, 2023