In this article, we will configure a SQL Server Always On Availability Group on the Windows Server 2016. We use SQL Server 2019 for configuration.
Introduction
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups offers high availability and disaster recovery solution for mission-critical databases. It also supports to offload some read workloads to the secondary replica. We can also configure database backups from the secondary instance.
Usually, Database Administrators are responsible for configuring availability groups in an organization. Still, they are unaware of the underlying infrastructure creation such as virtual machine, configure an active directory, join virtual servers in the domain, configure a failover cluster, quorum configuration, and storage allocation.
Suppose you do not have any infrastructure set up as of now. You can follow this article series for an end to end guidance on configuration of SQL Server Always On Availability Groups in Windows Server 2016 with SQL Server 2019.
This series combines the following articles:
- A comprehensive guide to SQL Server Always On Availability Groups on Windows Server 2016
- Configure Domain Controller and Active Directory for SQL Server Always On Availability groups
- Configure Failover Cluster, Storage controller, and Quorum configurations for SQL Server always-on availability groups
- Install SQL Server 2019 on Windows Server 2016 with SQL Server always-on availability groups
In this article, we will do the following tasks:
- Oracle VirtualBox installation
- Create Virtual machines with Windows Server 2019
- VM network configurations
Let’s start the journey toward your first SQL Server Always On Availability group.
Configure a Virtual Machine in Oracle VirtualBox
To begin with, we require the following servers.
- Server 1: We require a server for configuring domain controller and active directory
- Server 2: Primary node in the SQL Server Always On Availability group
- Server 3: It acts as a Secondary node for SQL Server Always On Availability group
We will use the Oracle VM VirtualBox in this article to create the virtual machines on my laptop. It is an open-source virtualization software, and you can install Windows, Linux, Unix operating systems on it. In this article, I use Oracle VM VirtualBox 6.1 version.

You can browse this URL, and download the platform-specific software, follow the steps and install it. It is pretty straightforward.
This article uses the term VirtualBox for subsequent sections.
On my laptop, I already have the following two virtual machines configured.
Let’s click on New for a new virtual machine. It asks for the following details.
- Machine name: It is the virtual machine name. It is similar to your laptop hostname
- Machine folder: It is the directory in your local system where VirtualBox stores all relevant files
- Type: Select the required operating system from the drop-down values. I require Microsoft Windows operating system for all VM’s
- Version: Select the version of the operating system. In this article, we will install Windows Server 2016 standard edition

Click Next and configure the RAM for the virtual machine. I would recommend you assign at least 4 GB RAM for testing purposes.

In the next step, add a virtual disk in the new machine. You should consider your database requirements and configure a suitable size of the disk.

Choose the hard disk file type from the following values.
- VDI ( VirtualBox Disk Image)
- VHD(VirtualBox Hard Disk)
- VMDK(Virtual Machine Disk)
We can go ahead with the default hard disk type as VDI. You can refer to VirtualBox documentation for details on hard disk types.

The next step is to configure the static or dynamic disk size. In case of static, if your disk becomes full, you need to expand it to avoid performance issues in the VM.
In the dynamic mode, it automatically grows the hard disk space up to maximum configured values. You should also note that it does not release the space once occupied.

Select the VDI storage file location and size. You should have sufficient space in the drive to avoid any storage issues.

It creates a new virtual machine, as shown below.
Install Windows Server 2016 on Virtual machine
Download Windows Server 2016 ISO for SQL Server Always On Availability Group
Microsoft gives 180 days evaluation copy to use and learn about the Windows Server 2016. It is beneficial to explore new things, especially if you do not have any corporate servers to perform the activity.
Open Microsoft website and start the evaluation version valid up to 180 days. It requires a license to use Windows beyond 180 days. It is enough time for all your testing work or learns new features.

It downloads the Windows Server 2016, depending upon your network bandwidth. Its size is approximately 6.49 GB.
Click on Start in the virtual machine, browse to the directory where we downloaded the Windows Server 2016 ISO, and click Choose.
Note: In the below screenshots, it shows the server name as Windows2k16-1. However, all steps remain the same.

It shows up the start disk to configure the virtual machine.

Click Start, and it starts to create the process of the virtual machine.

Choose the language, Time & currency format, and keyboard type. By default, it takes the input as per your system configuration. You can change these values if required.

Click Next and Install now to begin Windows configuration for SQL Server Always On Availability group.

Windows Server 2016 ISO involves the following operating systems.
- Windows Server 2016 standard evaluation edition
- Windows Server 2016 standard evaluation edition (desktop experience)
- Windows Server 2016 datacenter evaluation edition
- Windows Server 2016 datacenter evaluation edition(desktop experience)
If we choose edition without desktop edition, it comes without a GUI. You can connect with command-line tools such as CMD, PowerShell to perform your stuff on it. You should be good with the PowerShell or scripting in this case.
For this article, we install Windows Server 2016 standard edition with the desktop experience.
Accept notice and license terms.

Select the installation type.
- Upgrade: Install Windows. Keep files, applications, and settings
- Custom: Install Windows only
We require a fresh Windows installation; therefore, select the second option and proceed.

Select the root operating system directory. In our case, we have a single drive in the virtual machine. By default, it is available for all installation.

Click Next, and it starts the Windows operating system, with default programs and features.

After the Windows installation, it automatically reboots the virtual machine.

After reboot, once it comes up, it asks you to configure a password for the default administrator user. We do not have any domain for this virtual machine. Therefore, we will use this user to login to the system.

Finish the installation process and login with the administrator user credentials set above.

It configures your Windows systems for the first time startup. You can see that VM is part of a workgroup. We will add the domain for this server later.
Open the command prompt and check the IP configuration of this server using the ipconfig command.
Follow the above steps and prepare the below specified virtual machines.
SQLNode1: It is the first node for SQL Server Always On Availability group

SQLNode2: It is the second node for SQL Server Always On Availability group

VDITest3(DC): This server serves as a domain controller and active directory

Network configurations for the Virtual machine in VirtualBox
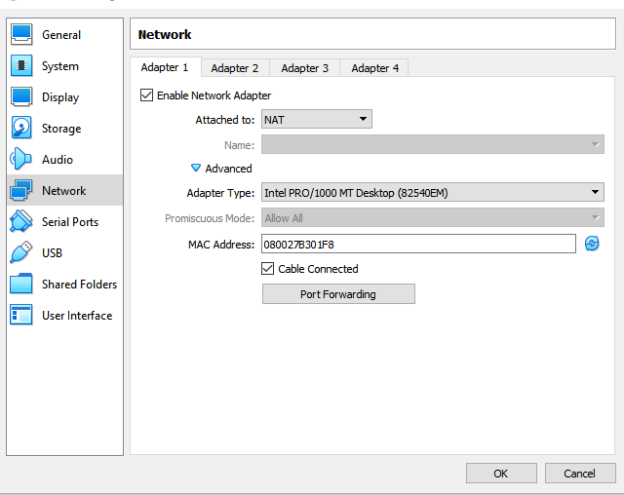
By default, a virtual machine is configured for the Network Address Translation (NAT). In a NAT configuration, usually, a firewall assigns a public address to the VM inside the private network. To view the network configuration, go to the VirtualBox, right-click on it and view Settings -> Network.

Modify the network adapter from NAT to Bridged adapter. In the bridged adapter, select the ethernet adapter.

You can also configure multiple network adapters in a VM. For example, in my case, I have an internet connection using Wi-fi. To use the internet on VM as well, I configured the second adapter for all VM’s as shown below.

Conclusion
In this article, we configured Oracle Virtual machine and prepared three VM’s. We will use these VM’s in the subsequent articles for configuration of SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Table of contents
See more
Check out SpotLight, a free, cloud based SQL Server monitoring tool to easily detect, monitor, and solve SQL Server performance problems on any device

- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023