In this article, I am going to explain the various products offered by the Microsoft Power Platform. Microsoft Power Platform is a group of products offered by Microsoft to develop and build complex business solutions, analyze, and draw data visualizations, automate a business process, or build virtual agents for communication. All these products offer a platform in which no code is required to build the applications. These products are in the form of simple GUI which can be used by any business users or developers, thus helping to reduce the need for IT in the organization.
There are four products under the Microsoft Power Platform:
- Power BI – Used to analyze data from different data sources
- Power Apps – Used to build powerful mobile apps for internal use by the organization
- Power Automate – Used to design automated workflows to reduce manual tasks
- Power Virtual Agents – Used to develop flexible chatbots that can communicate with external customers
Power BI
Power BI is the self-service business analytics tool provided by Microsoft. This is considered a part of the Microsoft Power Platform together with the other tools in the bundle. Power BI has a few offerings starting from the Desktop version to the Power BI Service which is hosted on the cloud. It is usually used to connect to a wide range of data, by designing interactive reports, dashboards, or stories which are supported by compelling visualizations.
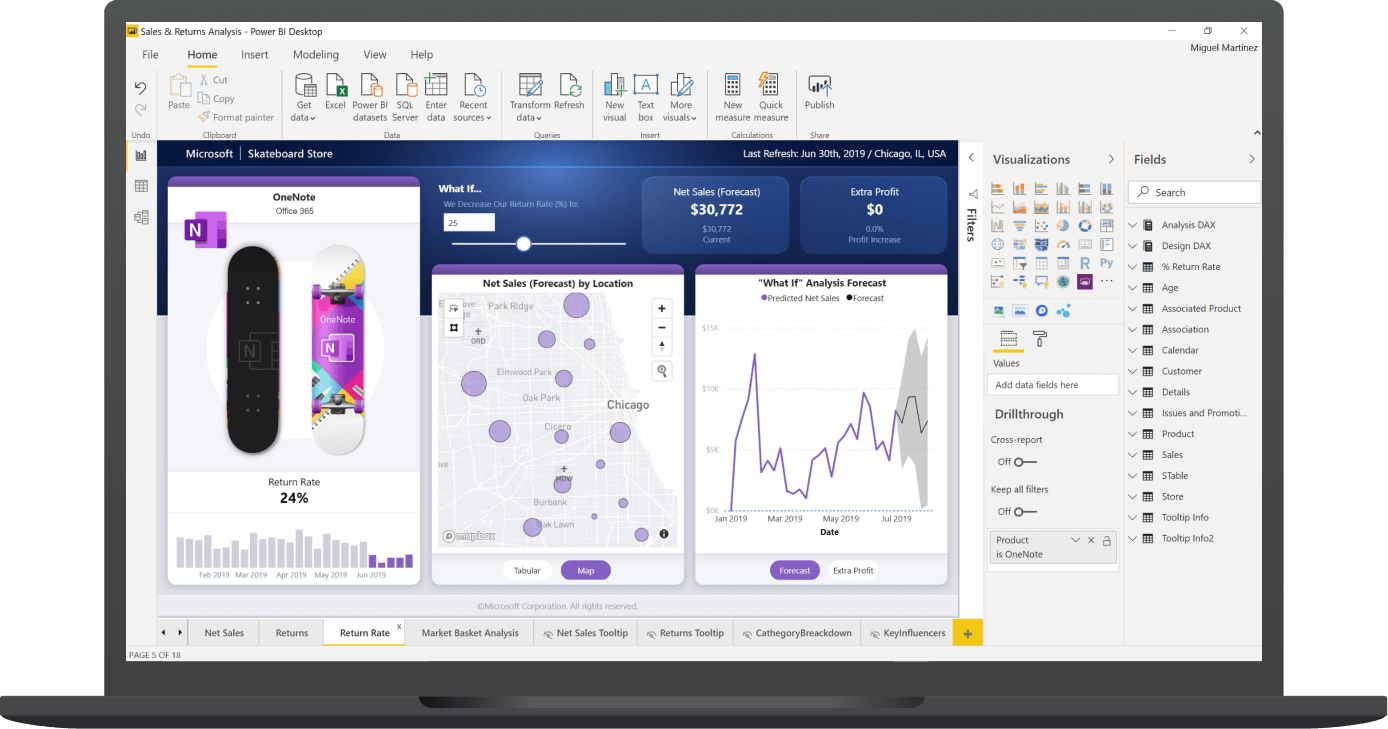
Figure 1 – Power BI Desktop (Source)
Power BI Desktop is available for free download from the Microsoft Store and you can download the application on any Windows machine. At present, Power BI is not available for any other operating systems other than Windows. There is also a mobile application for Power BI, which can be installed on Android and iOS devices. This mobile app is used to visualize reports in a native mobile format rather than the specified desktop view.
Power BI enables the user to connect to several heterogeneous data sources and fetch the relevant data into the Power BI data model. Once the data is within Power BI, the users can modify, shape and transform this data according to the reporting needs. This transformed data can be then visualized in the form of graphs and charts to get insights upon. These visualizations can be used to support various scenarios like storytelling, what-if analyses, forecasts, and other predictions, etc.
Power BI also has many REST APIs available using which, the developers can automate few administrative tasks, such as refreshing a dataset or adding a new user to a report, etc. This takes the Power BI service to another level which also supports embedding the Power BI Dashboards within another web application. This web application will behave like that of the Power BI service, except the fact that it can now have the user control and other features native to the web application.
There are three different versions of Power BI. Although the Power BI Desktop is free, to use the Power BI Pro Service, the users need to pay a monthly fee of 9.99 USD. And the Power BI Premium cost depends on the number of users and the deployment capacity.
Power Apps
Power Apps is a nice and intuitive platform that provides users with a drag and drop feature to build a user interface for a mobile application. The users can add various controls to the user interface like textboxes, choice fields, etc. It can also allow users to use media devices like the camera, videos, etc. and other features necessary to build a modern mobile application. There is a feature to connect to various data sources using Power Apps and after the development is completed, the users just need to publish the app to be consumed in the organization.
Power Apps is offered more like a platform-as-a-service from the Microsoft Power Platform. This service enables the users to quickly build apps that can be run on any modern web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, etc. and on the native mobile apps using Android, iOS, or Windows. One important thing to note here is that using Power Apps, we can build mobile applications for internal users and not for customers around the world. As this platform is no code, developers won’t be able to control the UI elements or modify the underlying HTML codes to do any tweaking.
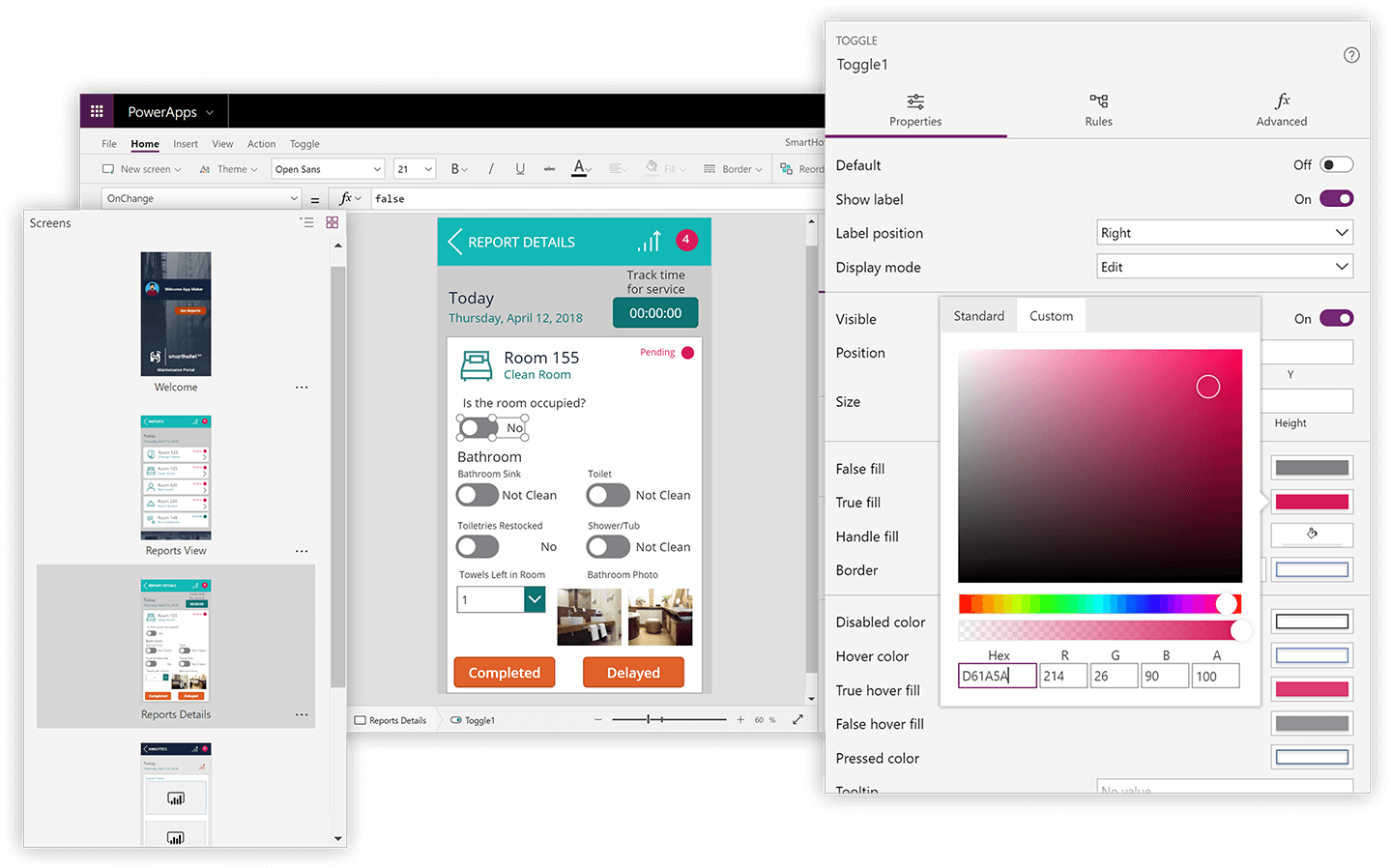
Figure 2 – Microsoft Power App (Source)
Power Apps come with a subscription if you are already using Office 365 Enterprise or anything higher than that. The Power Apps also come with a community plan which can be used as a free development environment and to upskill new talents. For more information about the licensing, please follow the official documentation from Microsoft.
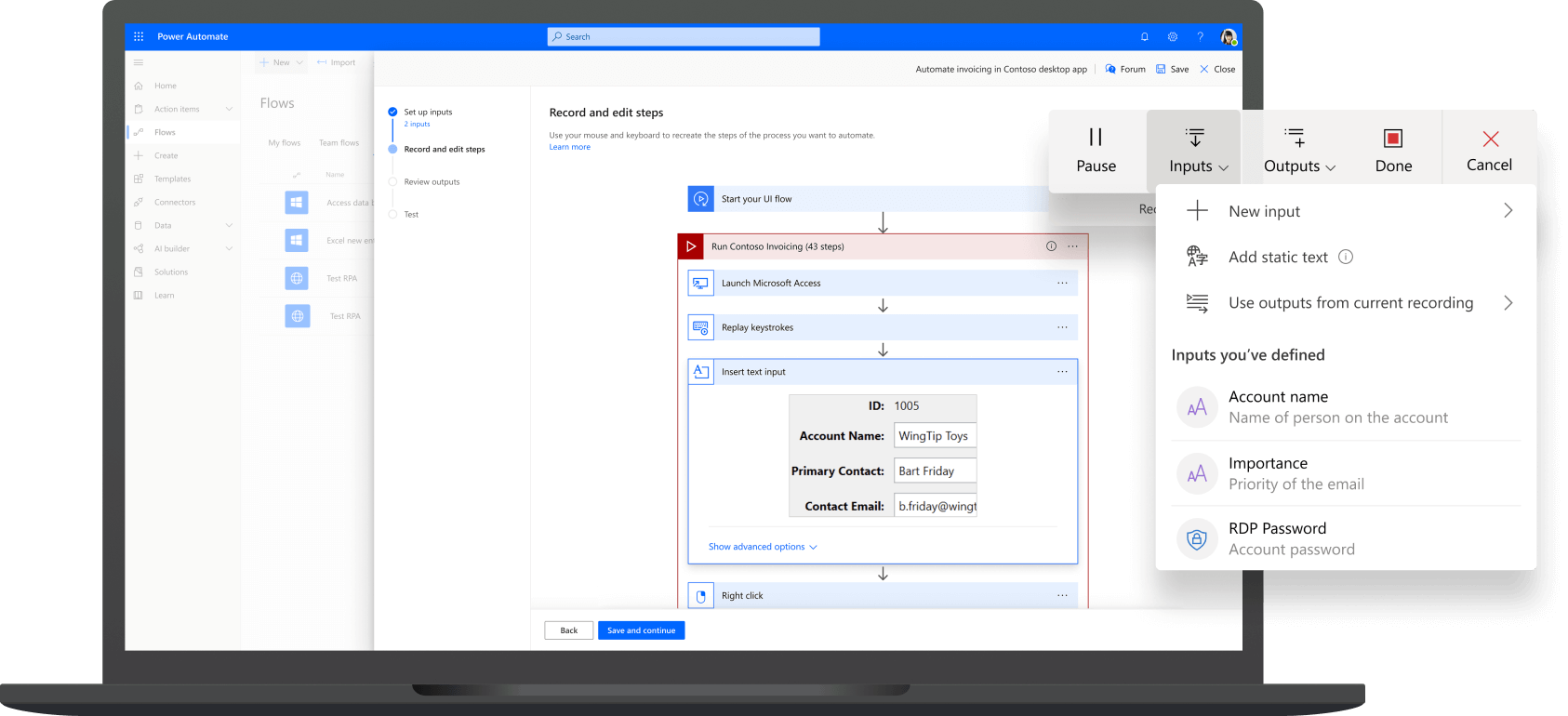
Power Automate
Power Automate, formerly known as Microsoft Flow is a component of the Microsoft Power Platform that allows the business users to automate workflows within the organizations without writing any code for the same. Modern businesses always gearing up for a faster and automated environment to tackle most of the previously handled manual tasks. These tasks can be as simple as automating leave policies within an organization or sending an email once a task is completed in Jira.
Figure 3 – Microsoft Power Automate (Source)
Power Automate already comes in with several pre-defined templates to choose a workflow and start working with. Users can pick up any of these workflows from the templates or can also start building their own workflow from scratch. All these workflows can be further divided into three main types which are based on the trigger of any workflow as follows:
- Automated Workflow – These types of workflows are triggered based on some other action. For example, send a mail when a task is completed
- Scheduled Workflow – These workflows are scheduled to execute at specific times of the day, week, or month
- Button Workflow – These workflows are triggered by the click of the button
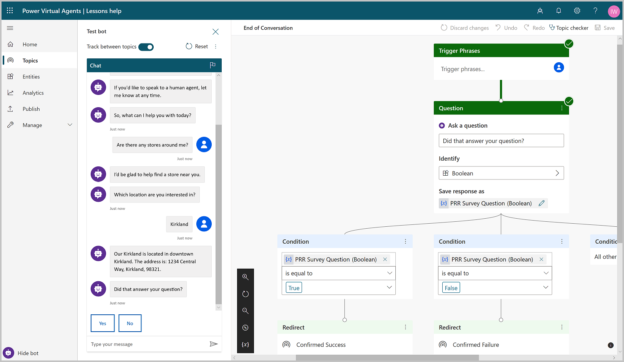
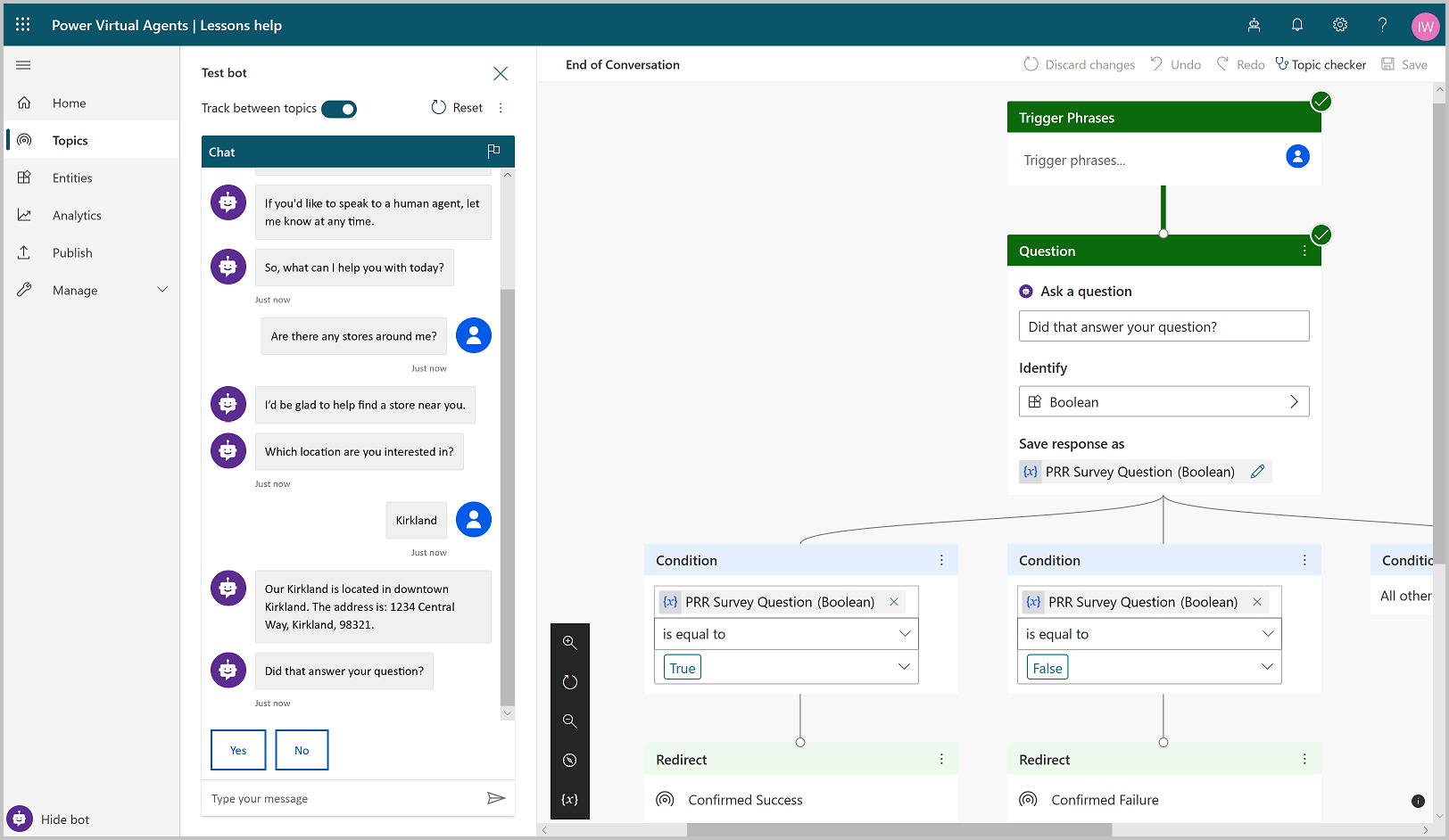
Power Virtual Agents
This is a new addition to the Microsoft Power Platform. Virtual Agents are the bot building services provided by Microsoft for business users. Using this, the users can build a virtual chat agent from scratch without having to write a single line of code. All the integration and logics can be implemented in the graphical user interface of the Power Virtual Agents portal.
Figure 4 – Microsoft Power Virtual Agent (Source)
Power Virtual Agents can handle the entire chatbot development life cycle, starting from the dialog creation to the deployment of the virtual agent to a channel like Slack, Skype, Teams, etc. This service is also integrated with the other tools within the Microsoft Power Platform such as Power Automate. Based on the user’s replies, the virtual agents are capable to trigger any workflow from the Power Automate and get the job done as intended.
In addition to the above, the Power Virtual Agents are also able to leverage the Microsoft LUIS service to enhance the user experience by introducing natural language understand features into the virtual agents. You can also build a FAQ bot by using the QnA Maker and deploy your bots to any channels that you need. Finally, we can also use adaptive cards in the bot to make the user interface more intuiting and easier to understand. The license cost of Power Virtual Agents is 1000 USD per month for every 2000 sessions. For more information on licensing, please visit https://powervirtualagents.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/.
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen the overview of the Microsoft Power Platform and the essential tools that are provided in this bundle. In a nutshell, the Power Platform provides four different tools under the umbrella. To build business solutions, users can leverage the Microsoft PowerApps whereas to automate specific business processes we can use the Microsoft Power Automate. Using the Microsoft Power BI, we can analyze data and build visualizations from a vast number of data sources. Finally, to set up a virtual agent for communication, you can use the Microsoft Power Virtual Agents to build a chatbot without much coding.
See more
To boost SQL coding productivity, check out these SQL tools for SSMS and Visual Studio including T-SQL formatting, refactoring, auto-complete, text and data search, snippets and auto-replacements, SQL code and object comparison, multi-db script comparison, object decryption and more

- Getting started with PostgreSQL on Docker - August 12, 2022
- Getting started with Spatial Data in PostgreSQL - January 13, 2022
- An overview of Power BI Incremental Refresh - December 6, 2021