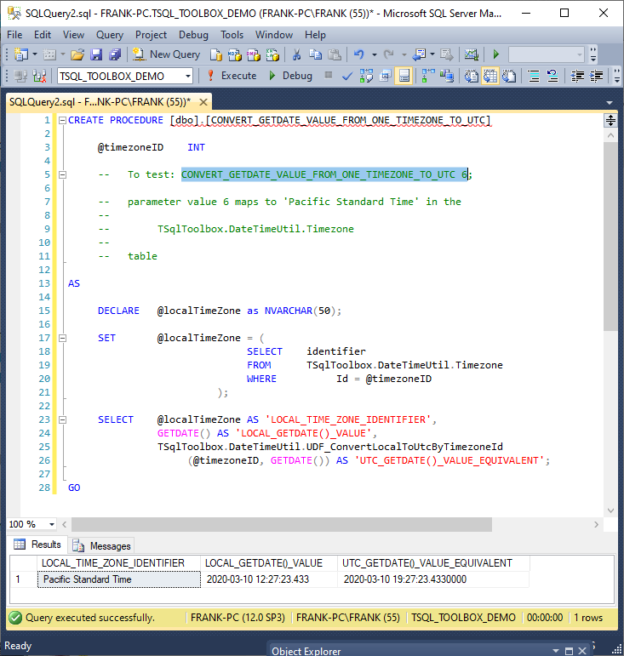
Introduction
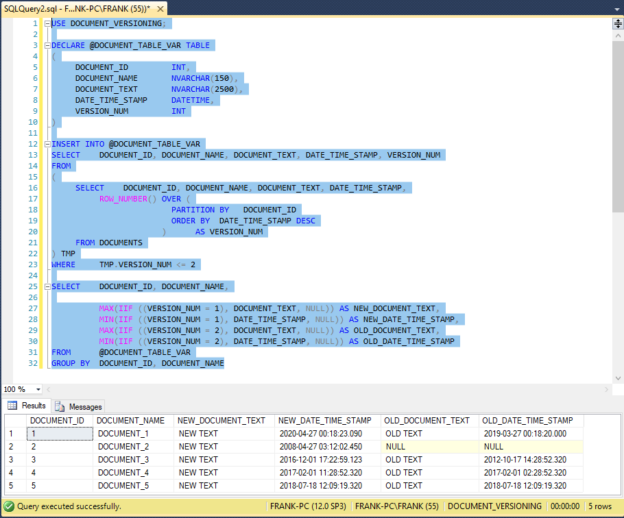
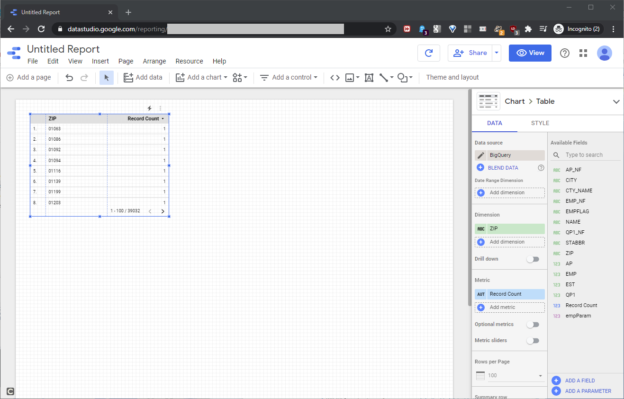
The T-SQL ORDER BY clause sorts SQL Server SELECT
statement result sets, and it becomes important when we build stored procedures. Unfortunately, the syntax offers no flexible way to directly control the ORDER BY clause behavior with argument values. This means we
don’t have an easy way to control the specific column or columns that the ORDER BY clause sorts.
Additionally, SQL Server does not offer a flexible way to directly control the ascending or descending order of any ORDER BY clause column with argument values. Of course, we can certainly hard-code the
ORDER BY clause in a stored procedure, but this approach becomes fixed in stone. We could try a dynamic SQL solution, involving a stored procedure code that dynamically builds and executes SQL
Server statements inside a stored procedure. However, this technique becomes tricky, and it can lead to SQL injection attacks. Other techniques might rely on CASE statements, and their complexity can become overwhelming as the column count grows. This article spotlights a clean, efficient, pinpoint T-SQL stored procedure technique that directly sorts one, some, or all SELECT statement result set columns. The technique avoids dynamic SQL, and it operates directly in a stored procedure. The article also shows how to set the ascending or descending sort order of specific columns.
Read more »