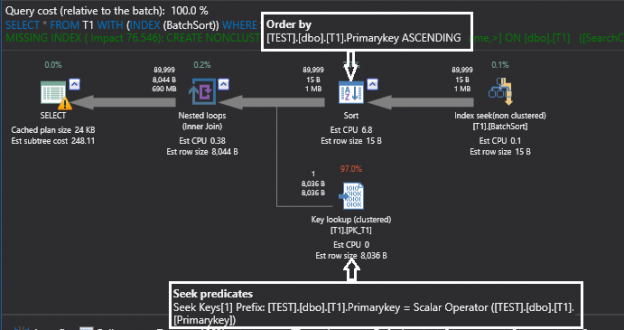
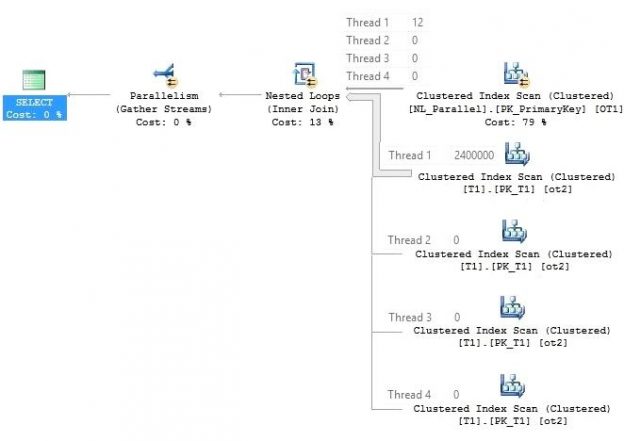
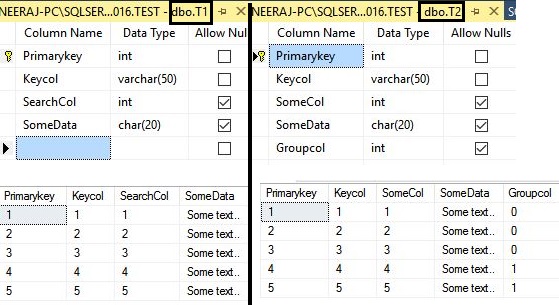
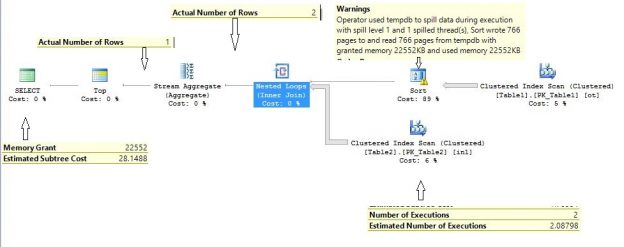
In SQL Server, it`s not always required to fully understand the internal structure, especially for performance and optimization, if the database design is good, because SQL Server is a very powerful Relational Database and, as such, it has many inbuilt optimization processes which assure a response to the users as fast as possible. But it is always beneficial for the SQL Server developers and administrators to understand the internal structure of the SQL Server so that they can understand and fix the problems that slowed the response of the Database.
Read more »