The SQL database integrity check is one of the most crucial and important tasks of the database administrator. The database integrity task checks the structural integrity and allocation of all database objects and indexes. The integrity checks can be performed by using the DBCC CheckDB command. The CheckDB command is used to identify the corruption in the database. The command performs the following operations on the database.
- Executes the DBCC CHECKTABLE on every table and view
- Executes the DBCC CHECKCATALOG on the databases
- Executes the DBCC CHECKALLOC on the databases
- Validates the service broker data
- Validates the content of indexed views
You can read DBCC CHECKDB (Transact-SQL) to learn more about the DBCC CheckDB command.
Usually, DBAs create custom scripts to identify the corruption in the databases. But, if you are working on multiple databases, it becomes tedious to review the logs generated by the DBCC CheckDB command. So I have created a SQL stored procedure that executes across all databases, and if it finds any consistency errors, it sends the details to the DBA team.
In my previous article, Automate SQL database backups using Windows Task Scheduler, I had explained how we could automate the process to generate a full and differential backup of SQL database restored in SQL server express edition. This article explains how we can automate the consistency check of SQL database created in SQL Server express edition. To demonstrate, I have downloaded a sample database from here. I have installed SQL Server Express edition and restored the database using the following command:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
USE [master] GO RESTORE DATABASE [DemoCorruptMetadata] FROM DISK = N'C:\SQL Backup\DemoCorruptMetadata2008R2.bak' WITH FILE = 1, MOVE N'DemoCorruptMetadata' TO N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.SQLEXPRESS\MSSQL\DATA\DemoCorruptMetadata.mdf', MOVE N'DemoCorruptMetadata_log' TO N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.SQLEXPRESS\MSSQL\DATA\DemoCorruptMetadata_log.ldf', NOUNLOAD, STATS = 5 |
Once a database is restored, let’s run the DBCC CheckDB command to view the errors.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
set nocount on GO use master GO dbcc checkdb (DemoCorruptMetadata) with all_errormsgs, no_infomsgs |
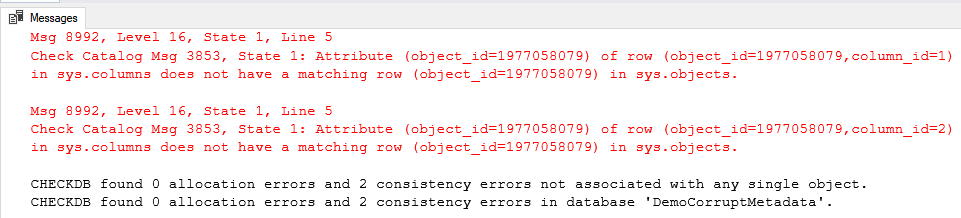
As you can see in the above image, the database is corrupted, and the consistency check command has reported errors. To perform the consistency check, I have created a stored procedure that
- Run the consistency check on all SQL databases, and if it finds any consistency errors, it inserts those errors in a temp table
- Extract the message from the temp table and send the HTML formatted email to the DBA team
The code of the stored procedure is shown below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 |
USE master GO CREATE PROCEDURE Sp_db_integrity_check AS BEGIN DECLARE @DBName VARCHAR(150) DECLARE @dbcccommand NVARCHAR(max) DECLARE @DBcount INT DECLARE @i INT = 0 CREATE TABLE #errormsgs ( error INT NULL, level INT NULL, state INT NULL, messagetext VARCHAR (7000) NULL, repairlevel INT NULL, status INT NULL, dbid INT NULL, dbfragid INT NULL, objectid INT NULL, indexid INT NULL, partitionid INT NULL, allocunitid INT NULL, riddbid INT NULL, ridpruid INT NULL, [file] INT NULL, page INT NULL, slot INT NULL, refdbid INT NULL, refpruid INT NULL, reffile INT NULL, refpage INT NULL, refslot INT NULL, allocation INT NULL, ) CREATE TABLE #userdatabases ( NAME VARCHAR(500) ) INSERT INTO #userdatabases SELECT NAME FROM sys.databases WHERE database_id > 4 SET @DBcount=(SELECT Count(1) FROM #userdatabases) WHILE ( @DBcount > @i ) BEGIN SET @DBName = (SELECT TOP 1 NAME FROM #userdatabases) SET @dbcccommand='dbcc checkdb (' + @DBName + ') with no_infomsgs, all_errormsgs,tableresults' INSERT INTO #errormsgs EXEC ('dbcc checkdb (' +@DBName + ') with no_infomsgs, all_errormsgs,tableresults') DELETE FROM #userdatabases WHERE NAME = @DBName SET @i=@i + 1 END DROP TABLE #userdatabases END --select MessageText from #errormsgs DECLARE @subject NVARCHAR(max) DECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(max) SET @subject = 'Database Consistancy Check report for Server : ' + @@servername SET @tableHTML = ' <html> <Body> <style type="text/css"> table {font-size:9.0pt;font-family:verdana;text-align:left;} tr {text-align:left;} h3 { display: block; font-size: 15.0pt; font-weight: bold; font-family: verdana; text-align:left; } </style> <H3>Summery of Database Consistancy Check on Server ' + @@servername + '</H3>' + N'<table border="1">' + N'<tr><th>MessageText</th><th>Corrupt Database</th></tr>' + Cast((SELECT Isnull(messagetext, '') AS 'TD', '', Isnull( Db_name(dbid), '') AS 'TD', '', Isnull(repairlevel, '') AS 'TD' , '' FROM #errormsgs FOR xml path ( 'tr' ), root) AS NVARCHAR( max)) + N'</table> </html> </Body>' EXEC msdb..Sp_send_dbmail @profile_name = 'DBMailProfile', @recipients = 'ni*********87@outlook.com', @subject = @subject, @importance = 'High', @body = @tableHTML, @body_format = 'HTML'; |
As you know, the SQL Server Express edition does not support database mail, but you can configure the database mail using T-SQL queries. You can read this article, Database Mail configuration in the SQL Server Express edition to understand the process in detail.
The SQL Server Express edition does not support SQL Server agents, so; we use the Windows task schedular. Windows schedular can execute the batch file, so I have created a batch file that executes a stored procedure using the SQLCMD command. The code of the batch file is the following.
|
1 |
sqlcmd -S Nisarg-PC\SQLExpress -Q "execute sp_DB_Integrity_check" -d DBATools |
Specify the command in the text editor and save the file as *.bat file. Now, let us create a task using windows task schedular. Open Control Panel Open Administrator tools Open Task Scheduler. In the task schedular, Click on Create a basic task. On the first screen, specify the name of the task and description.
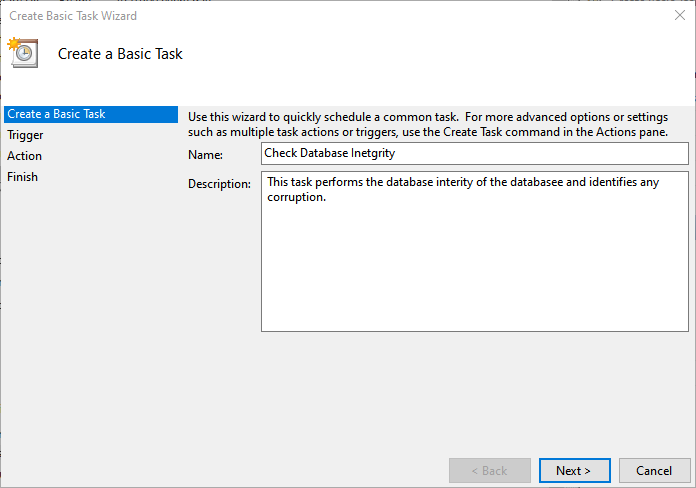
The database consistency check should be performed every week, so specify weekly in the Task Triggers screen.
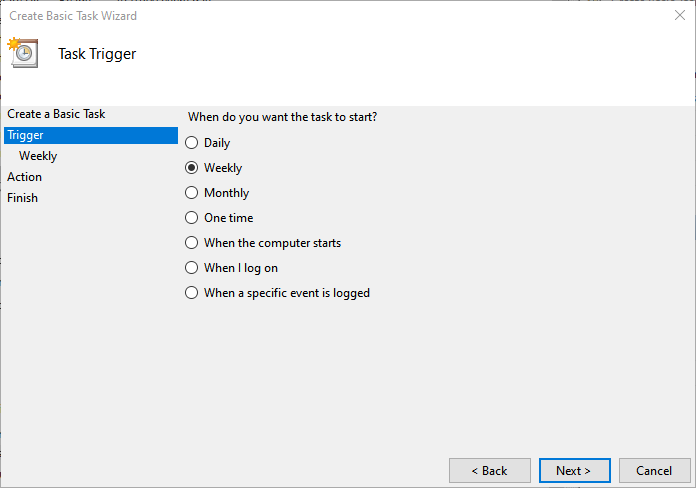
The script should be executed every Sunday at 1:00 AM, so specify 01:00:00 in the Start textbox. The job should be executed one time every week so specify 1 in Recur every textbox. Select Sunday from the list of the days.
We are running a batch script to check the database corruption, so choose the Start a program option on the Action screen.
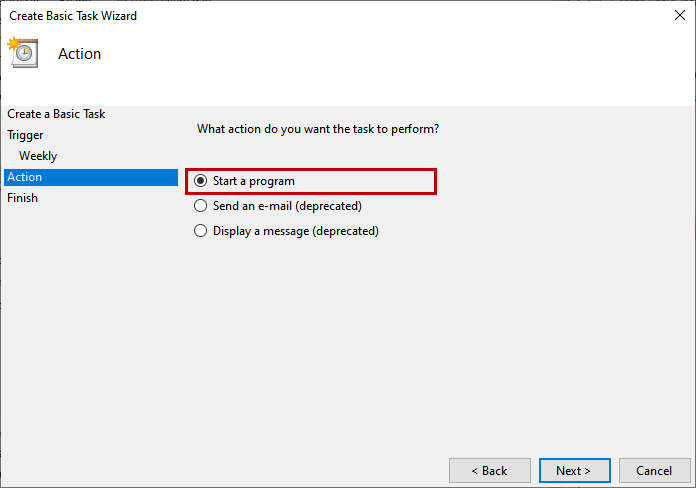
On the Start, a Program screen, specify the full path of the batch file. You can find the file by browsing through the directories. In our case, the batch file has been created in C:\DatabaseScripts, so I have provided the batch file’s full path. Ensure the user who has created the schedule must have read-write access on the directory in which the batch file has been created. Click on Next.
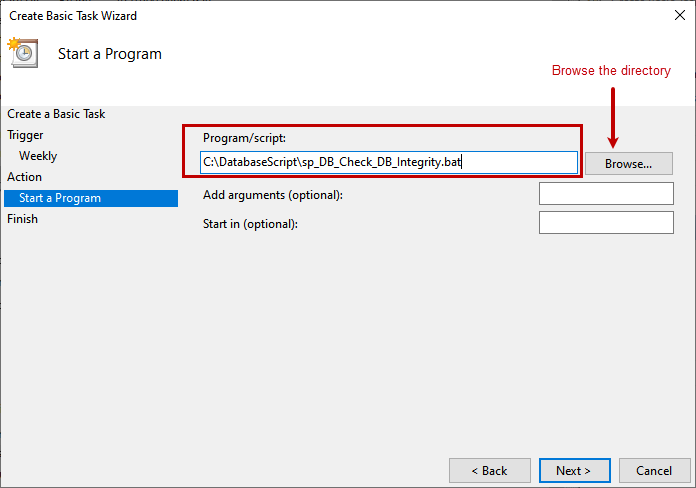
On the Summary screen, you can review the details of created task. Click on Finish.
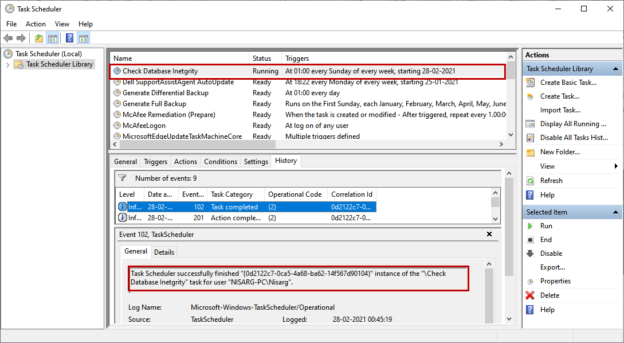
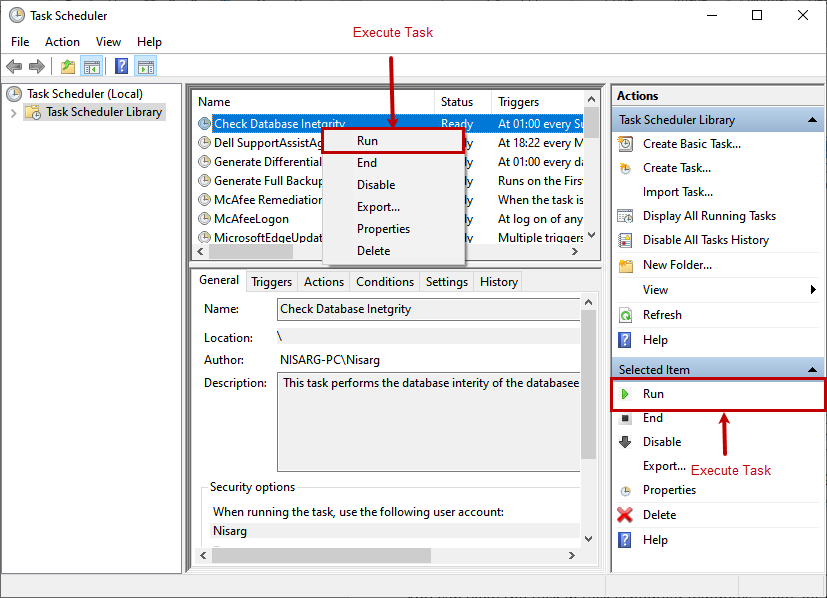
You can view the task in task schedular windows. Now, let us test the configured task. To do that, right-click on Check Database integrity and click on Run. Alternatively, click on the link named Run from the right-pan.
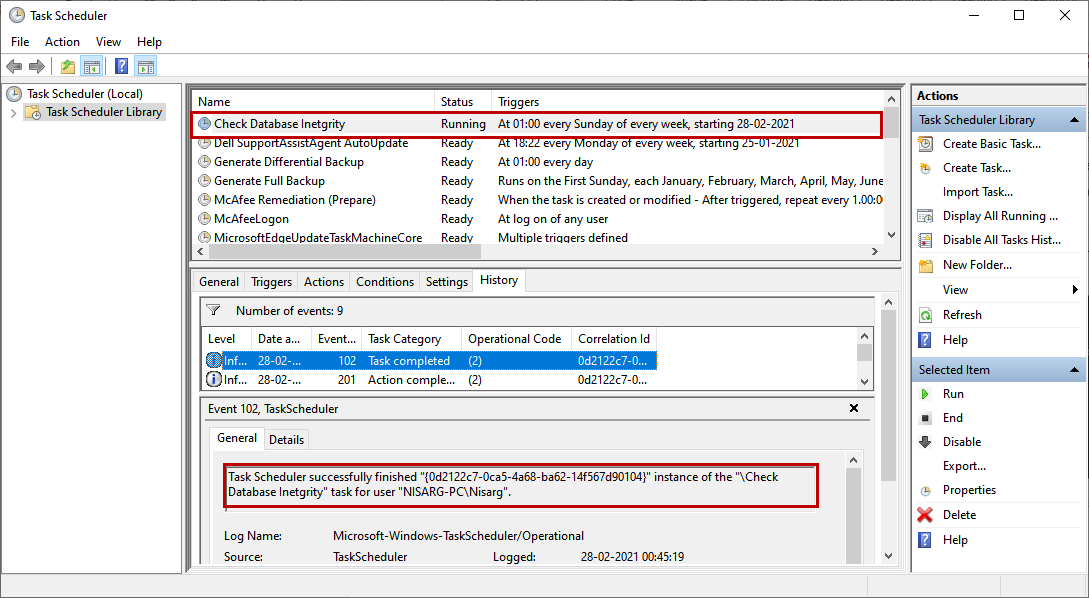
The consistency check process begins.
The process was completed successfully. You can verify the details from the Task History tab of the task schedular.
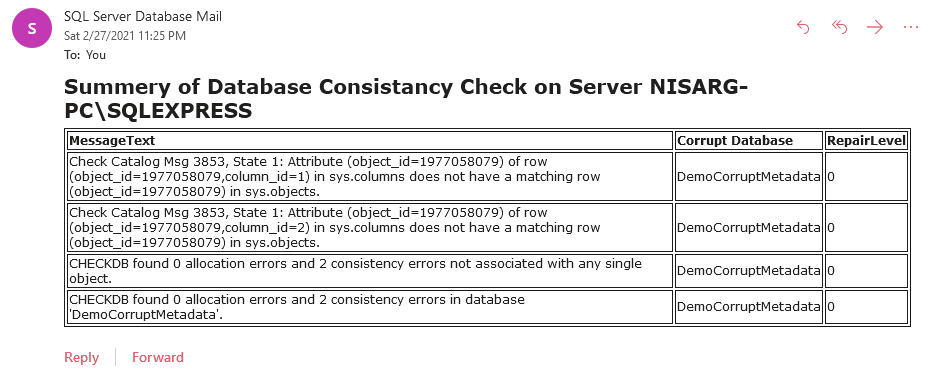
We have restored a corrupted SQL database, so we have received an email with the database consistency errors. The email looks like the following image.
Summary
This article explained how we can identify database corruption using a batch script that has been scheduled in the Windows task schedular. This article can be useful to the entry-level database administrators who want to automate the database maintenance tasks of SQL database created or restored in SQL server express edition. In my next article, we will learn how we can automate the index maintenance of SQL database created in SQL Server express edition using Windows task scheduler. Stay tuned!
- Different ways to identify and change compatibility levels in SQL Server - July 22, 2024
- Copy SQL Databases between Windows 10 and CentOS using SQL Server data tools - October 19, 2022
- Changing the location of FILESTREAM data files in SQL Database - October 14, 2022