This article will cover SQL Server C2 auditing using C2 audit mode including an introduction, comparison of auditing technologies, configuration and common criteria compliance
Introduction
Auditing is a key aspect of an IT system for many reasons such as compliances, troubleshooting, etc. SQL Server has different possibilities of configuring auditing at different levels. Though there exists different customizable, configurable auditing mechanisms, there needs to have predefined, standard auditing mechanism so that end users need to simply enable the auditing option.
Different Auditing Configurations
As indicated before, there are several options for auditing in SQL Server.
Option | Pros | Cons |
Server and Database Audit | Customizable to any granular level | A lot of configuration is needed |
Triggers | DML/DDL triggers can be implemented for granular level | The performance will be impacted |
System Views | Available out of the box | Limited Auditing options and most of the time it provides the current states only. |
SQL Profiler | Customizable to any granular level | The performance will be impacted. |
Extended Events | Customizable to any granular level | Configurations are needed |
Solution
C2 Auditing and Common Criteria Compliance are two internationally accepted auditing standards.
C2 audit mode is the auditing option that can be used to facilitate auditing standard. By enabling C2 auditing, it allows the administrator to enable a comprehensive type of auditing, logging. This is named as C2 audit mode because it is logging of the form specified by the U.S. Department of Defense regulations to meet the certification at the C2 level of trust. Those regulations were specified in a document called the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria, often referred to as the “Orange Book” in the “Rainbow Series.” The Orange Book is now depreciated in favor of the Common Criteria. Nonetheless, C2 Auditing is still a commonly used term.
C2 audit mode generally means assigning a unique generated audit ID to each group of related processes, starting at login. Thereafter, certain forms of system calls performed by every process are logged with the audit ID.
Configuring C2 Auditing in SQL Server
C2 audit mode feature is available in SQL Server on-premises edition but not in Azure SQL Server Database, Azure SQL Data Warehouse and Parallel Data Warehouse. In the case of Azure, there are separate auditing options are available.
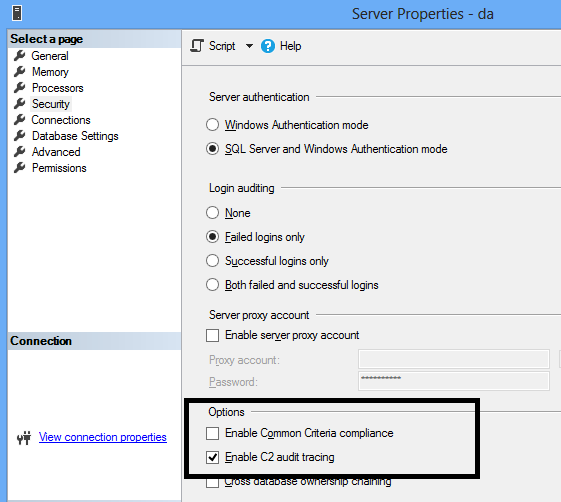
This can be configured in multiple ways. Following is the configuration of C2 Auditing by using the user interface. Under the server properties, in the Security Tab, the following option can be selected to enable C2 audit mode.
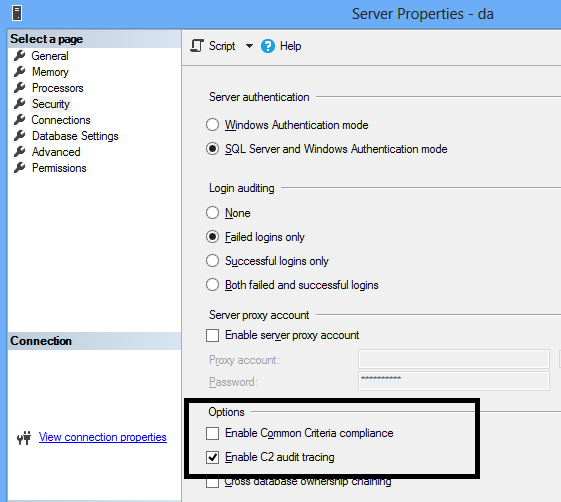
In the above Figure, there is another option, Common Criteria compliance which will be discussed later.
Also, this can be accomplished by T-SQL as well.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
--Enabling C2 Auditing sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO sp_configure 'c2 audit mode', 1 GO RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE; GO |
The output of this result is followed.
Configuration option ‘show advanced options’ changed from 1 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
Configuration option ‘c2 audit mode’ changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
SQL Server needs to be restarted for this configuration to effect after the configuration is made.
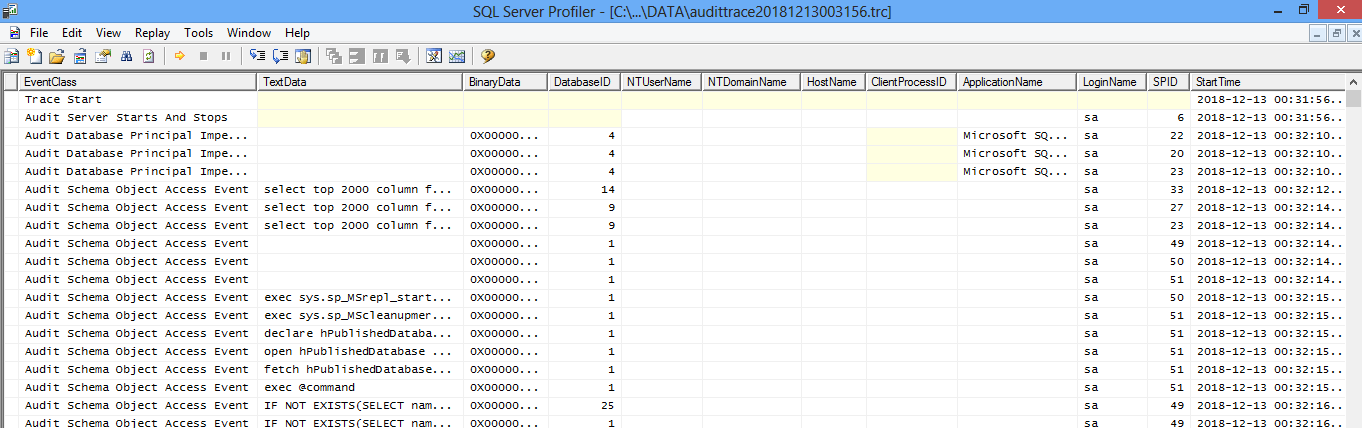
When the SQL Server instance is started, audit log will be written to trace file in the \mssql\data directory for default instances or the \mssql$instancename\data directory for named instances. For example, C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA is the folder name for traces. The trace file name will have the format of as audittrace_yyyymmddhhmmss.trc, where the second part of the name indicates date and time when the trace file was created. Since these logs are created in a folder, windows permissions need to be applied in order to secure audit files.
This trace file can be read from the SQL Profiler tool by opening the profiler tool and opening the trace file.
Also, the following T-SQL query can be used to retrieve the audit data from traces.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
--Retiving C2 Audited Data SELECT * FROM ::fn_trace_gettable( 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\audittrace20181213003156.trc', default ) |
The advantage of this is that the users have the option of joining, filtering or grouping option for better analysis. In case of troubleshooting, it is much better to import traces to a database table. In the case of database tables, you have the option of adding indexes to improve the performance.
The trace file will have a rollover the size of 200 MB which is fixed and after the SQL Server database engine restarts new trace file will be created. It is important to note that C2 auditing can consume a huge amount of disk space on an active system in a short amount of time. This is due to the fact that every auditing option is stored in the trace file. Also, in the case of C2 audit mode is failing, SQL Server instance will be shut down. This means that Auditing has the highest priority over the SQL Server database engine user operations. This means that administrators have to have extra care for the SQL Server systems where C2 auditing is enabled.
Also, to disable the C2 audit mode for a temporary basis, you need to restart SQL Server with the –f flag. If SQL Server shut down due to the failure of C2 Auditing, disable C2 audit mode temporary, then disable the C2 auditing after restarting the SQL Server instance.
A major disadvantage of the C2 audit mode is the performance impact to the SQL Server instance apart from the huge storage it requires. An advantage of the C2 Auditing is that data is saved in the trace files where backups can be taken. However, since these traces files are stored outside of SQL Server, security needs to be applied in order to protect the trace files.
Common Criteria Compliance
C2 auditing has been deprecated by the Common Criteria specification which was developed by the European Union. Common Criteria Compliance is internationally recognized set of guidelines for security for information technology products. This is applied to operating systems, Databases, Network Devices and Smart cards etc. Common criteria certified products have been rigorously evaluated by accredited third party security labs.
This option is available same versions as C2 Audit but Common Criteria Compliance is available in Enterprise and Data Center editions of SQL Server 2008 R2 and after versions. However, with respect to the SQL Server, if you are complying with either C2 or common criteria, the audit result is similar. In the case of Common Criteria Compliance, audited data can be viewed from system views which is more secure than the C2 audit mode.
Similar to C2 Auditing, Common Criteria Compliance can be enabled using the same option of the Security tab of the Server Properties dialog as shown below.
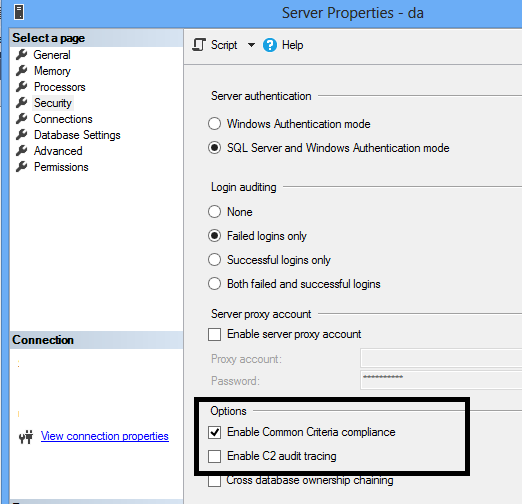
This can be done from T-SQL as shown below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
--Enabling common criteria compliance sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO EXEC sys.sp_configure N'common criteria compliance enabled', N'1' GO RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE GO |
As for C2 Audit, SQL Server needs to be restarted for this configuration to effect after the configuration is made.
Common Criteria Compliance allows the following to occur:
- Residual Information Protection (RIP)
- The ability to view login statistics
- That column GRANT should not override table DENY
These login statistics can be viewed by querying the sys.dm_exec_sessions dynamic management view. Last login date time and last unsuccessful login date time are available in sys.dm_exec_sessions but is not recorded unless Common Criteria Compliance is enabled.
Following are the Criteria Compliance related columns in the sys.dm_exec_sessions DMV.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
SELECT session_id, login_name, last_successful_logon, last_unsuccessful_logon, unsuccessful_logons FROM sys.dm_exec_sessions |
In Common Criteria Compliance, the major advantage is that the auditing data is stored in the database instance itself. However, in Common Criteria Compliance workaround should be applied to keep the historical data as dm_exec_sessions DMV does not store the historical data.
Summary
In case of any auditing mechanism, there will be an impact on the performance of the system. By considering the performance, Common Criteria Compliance is better than C2 audit mode. Also, feature-wise C2 Auditing is better than Common Criteria Compliance.
In case of SQL Server, administrators has the options of enabling both C2 audit mode and Common Criterial Compliance.
- Testing Type 2 Slowly Changing Dimensions in a Data Warehouse - May 30, 2022
- Incremental Data Extraction for ETL using Database Snapshots - January 10, 2022
- Use Replication to improve the ETL process in SQL Server - November 4, 2021