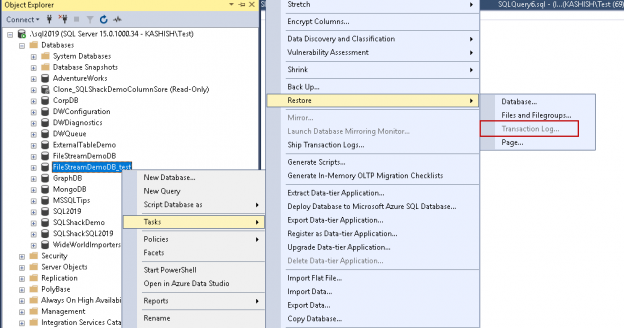
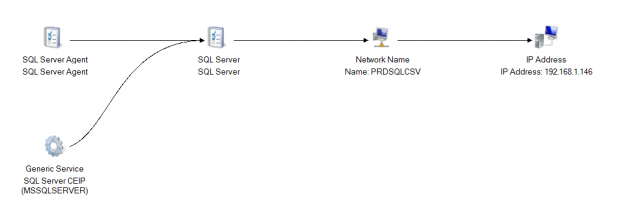
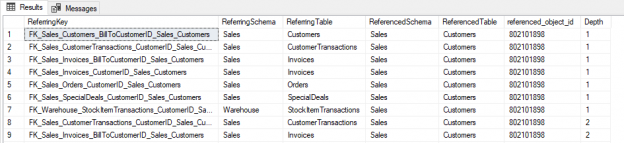
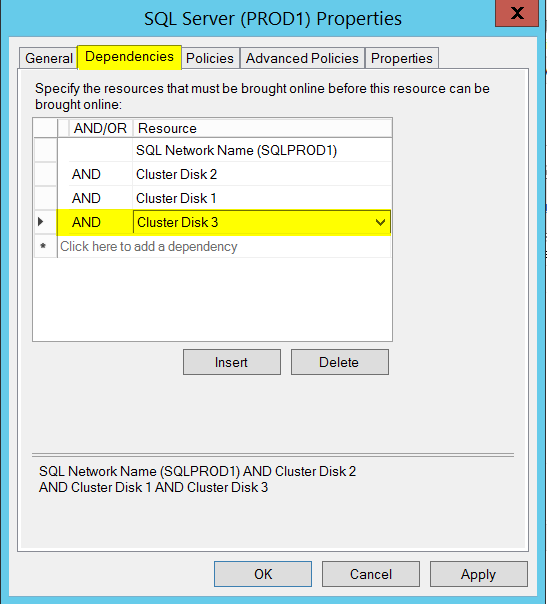
Microsoft SQL Server provides us with a wide variety of solutions to architect High availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) solutions for mission-critical workloads. In this article, let’s just focus on HA, specifically Failover Clustering. Failover clustering is probably the most mature, robust and stable high availability solution which Windows Server Operating system offers. It’s been there around for few decades now and did evolve over time along with SQL Server. In this article Let’s see a hidden feature of windows server failover cluster which helps in making our already highly available SQL Server Failover clustered instances even more highly available. The new feature which we are going to talk about is Cluster Shared Volumes, AKA CSVs. Considering windows server 2019 is around the corner, I say CSVs are not a new concept in clustering, it’s been there for almost a decade now. Microsoft introduced CSVs in windows server 2008R2, but at that time SQL Server was not supported on CSVs. Well, CSVs were originally designed for Hyper-V workloads and later on enhanced for File servers and eventually landed into SQL Server beginning version 2014.
Read more »