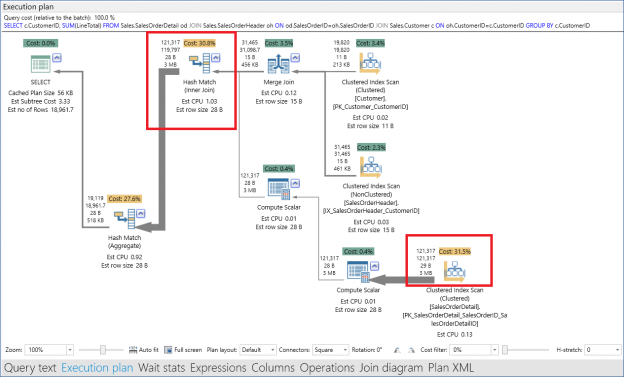
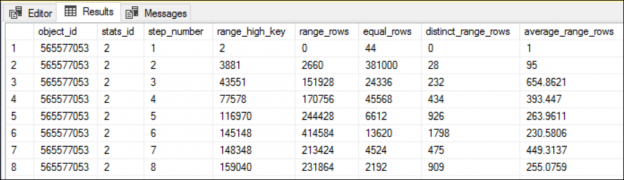
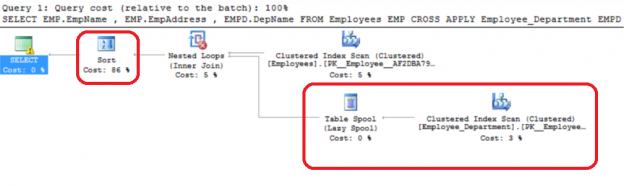
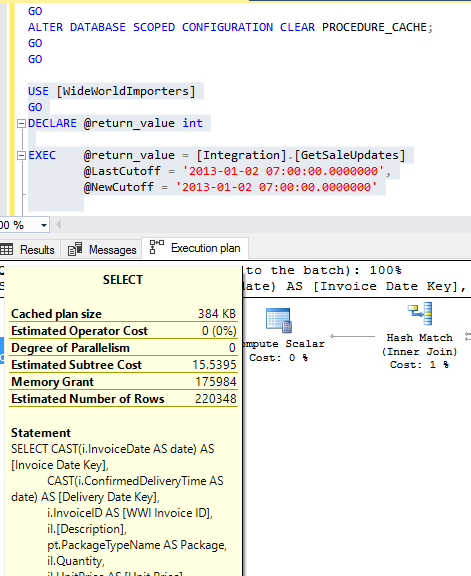
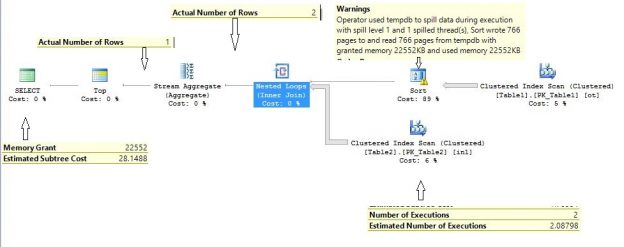
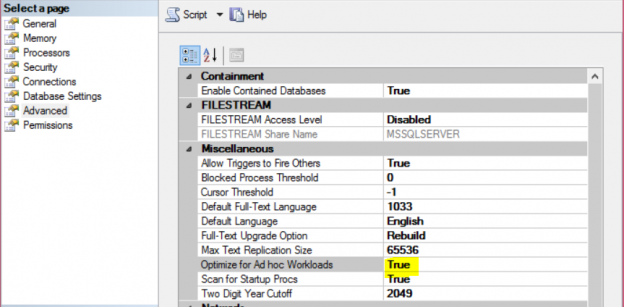
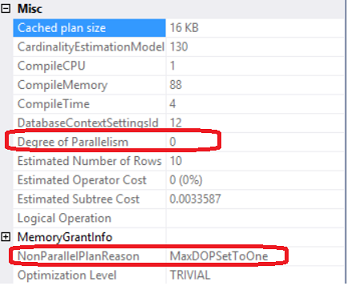
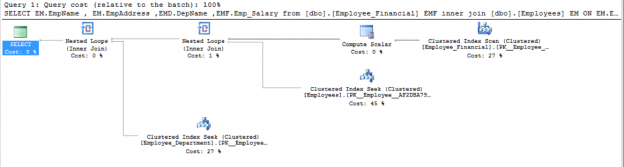
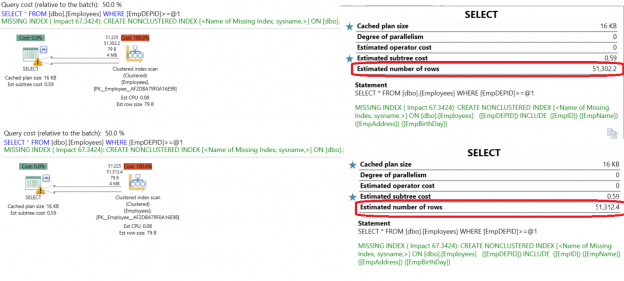
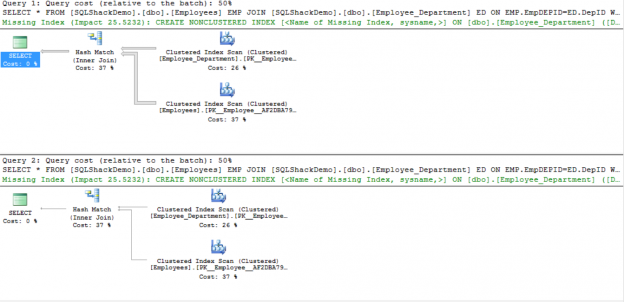
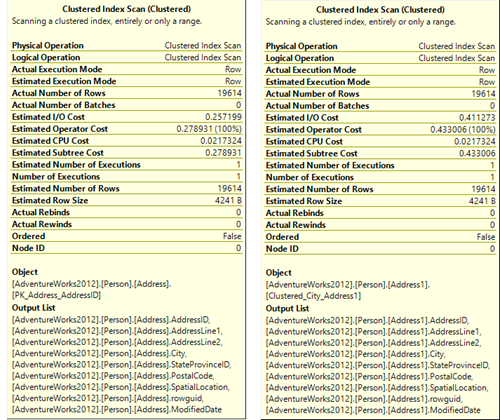
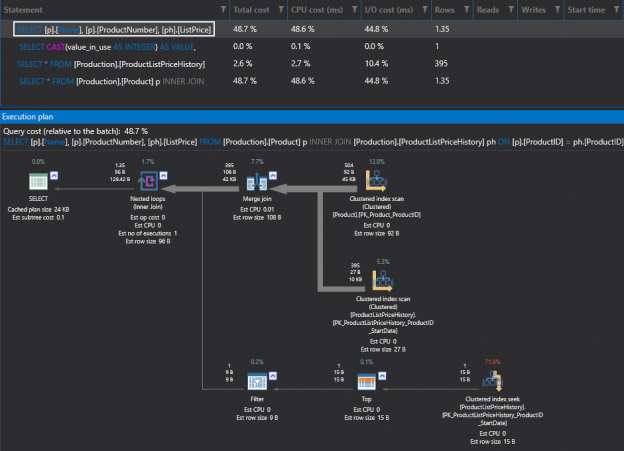
When you run a query in SQL Server, the SQL Server Query Optimizer will draw the road map for that query, specifying the optimal way to execute it, which is called the query execution plan.
Generating the execution plan will take few milliseconds from the CPU cycles, which is negligible for one query or small load, but it will be considerable for a very heavy transactional workload. Because of this, SQL Server caches these generated plans in a special type of memory called the Plan Cache to eliminate the overhead generated by the query plan if the same query is executed again. When you submit your query to the SQL Server Engine, it will search in the plan cache if there is any existing execution plan that can be reused, if an available execution plan is found in the plan cache, the plan will be used to execute that query, otherwise, the SQL Server Query Optimizer will create a new plan and keep it in the plan cache for future use.
Read more »