Before going through the main concern of this article, indexing the foreign key columns, let’s take a small trip back to review the SQL Server Indexes and Foreign Key concepts.
Read more »
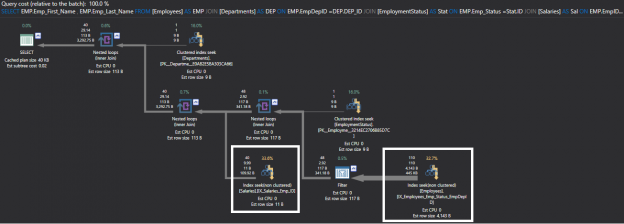


Before going through the main concern of this article, indexing the foreign key columns, let’s take a small trip back to review the SQL Server Indexes and Foreign Key concepts.
Read more »
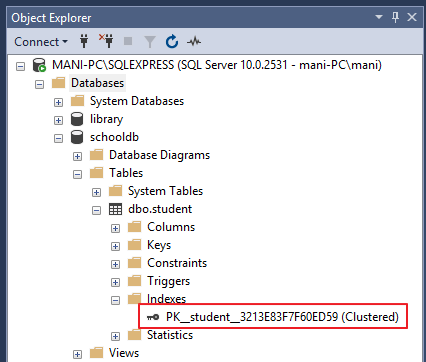
Indexes are used to speed-up query process in SQL Server, resulting in high performance. They are similar to textbook indexes. In textbooks, if you need to go to a particular chapter, you go to the index, find the page number of the chapter and go directly to that page. Without indexes, the process of finding your desired chapter would have been very slow.
Read more »
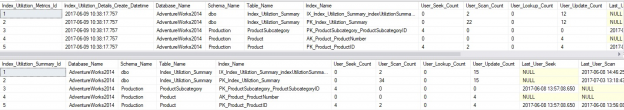
Understanding indexing needs allows us to ensure that important processes run efficiently and that our server hardware is not being over-taxed by poorly performing queries.
Collecting metrics on SQL Server index usage and missing index needs is critical to making smart decisions. To be truly proactive, though, we need to create a framework that allows us to quickly, efficiently, and regularly report on changes in indexing needs. With a system in place that can let us know when changes are needed, we can stay ahead of the optimization game and keep our customers happy!
Read more »
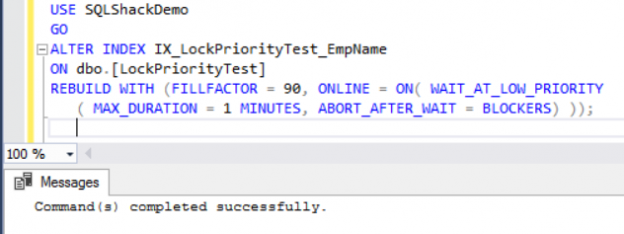
When you perform a SQL Server Online Index Rebuild operation, introduced for the first time in SQL Server 2005, the index will not be taken down. But at a specific point, in which the new index new is built and switched from the old structure of the index, a special kind of lock, Schema Modification (SCH-M), will be granted. This lock may cause blocking if your database server is busy.
Read more »
Indexing is key to efficient query execution. Determining what indexes are needed to satisfy production needs is often a game of cat and mouse in which we are forced to react to performance problems after they are brought to our attention. Being able to proactively monitor index needs and respond effectively before complaints are received can save us immense time while preventing costly performance messes.
Read more »
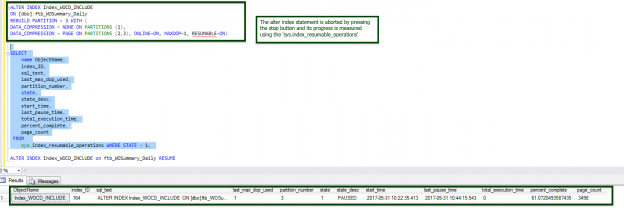
Managing indexes is a critical component of database maintenance but we often don’t think about the indicators behind the index maintenance operations. SQL Server 2017 (CTP 2.0) introduces a very useful index feature, to mitigate the administration overhead of index maintenance which we’ll review and discuss in this article.
Read more »
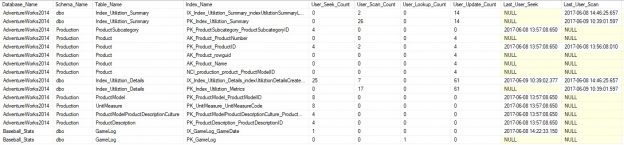
Indexing is key to efficient query execution. Knowing what indexes are unneeded, incorrectly used, or unused can allow us to reduce disk usage and improve write performance at little cost to your organization.
Read more »
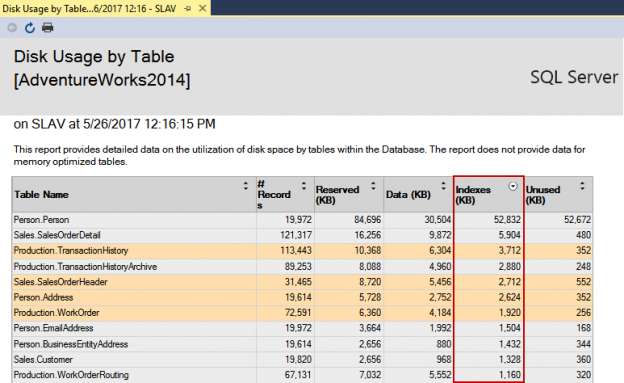
Just like a book index, SQL Server index has a similar purpose, to provide faster searching, gathering and sorting of information from a database, without need to go through all of the objects over and over. Instead, an index provides the gateway between the table rows and query engine, in order to achieve better both database and query performance.
Read more »
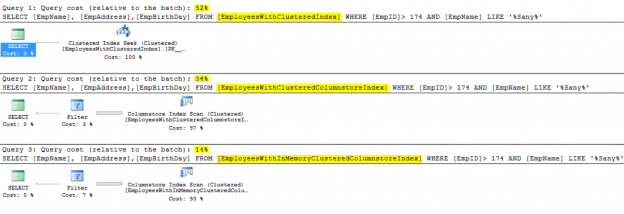
With Microsoft SQL Server, like all Microsoft products, you will enjoy experiencing new features and enhancements to the existing ones, when a new SQL Server version is launched. These SQL Server enhancements concentrate heavily in simplifying and speeding up the data retrieval without consuming excessive resources.
Read more »
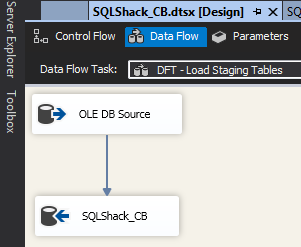
My team and I were recently tasked with refactoring older data marts, particularly those that were created with SQL Server 2008 in mind. As we all know, SQL Server has undergone significant changes since the release of SQL Server 2008. One of those changes relates to the introduction of columnstore as an alternative to the traditional B-tree index (rowstore). Whilst most of the existing documentation relating to columnstore seem to focus on the benefit of columnstore against data warehouse workloads, in this article I argue that the usage of columnstore index should not be limited to facts and dimensions instead let’s introduce it in our data warehouse staging environments too.
Read more »
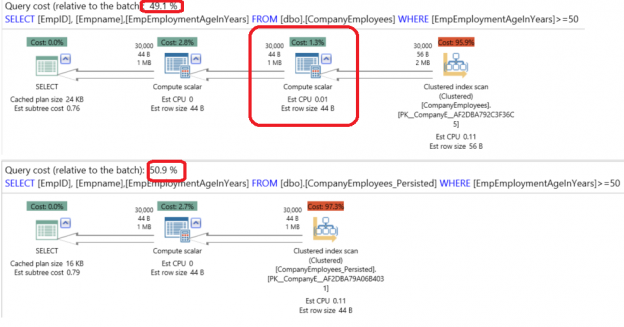
A SQL Server Computed Column is a virtual column that is not stored physically on the table, unless it is previously specified as PERSISTED. A computed Column value is calculated using a specific expression that can be constant, function, data from other columns on the same table or a combination of these types connected together by one or more operators.
Read more »
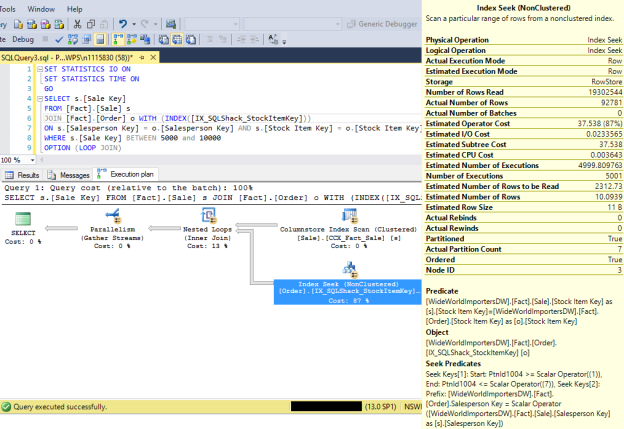
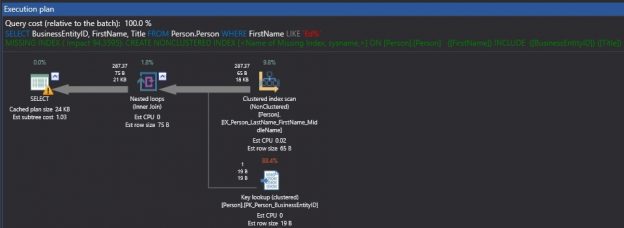
It is common assumption that an Index Seek operation in a query plan is optimal when returning a low number of output rows. In a scenario involving residual predicates, an Index Seek operation could be reading a lot more rows than it needs into the memory, then each row is evaluated and discarded in memory based on the residual predicate and returns low number of output rows.
This article will explain the concept and the impact of Residual Predicates in a SQL Server Index Seek operation.
Read more »
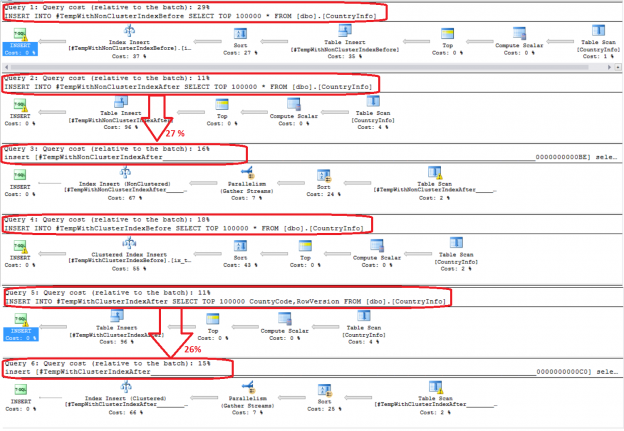
SQL Server temp tables are a special type of tables that are written to the TempDB database and act like regular tables, providing a suitable workplace for intermediate data processing before saving the result to a regular table, as it can live only for the age of the database connection.
Read more »
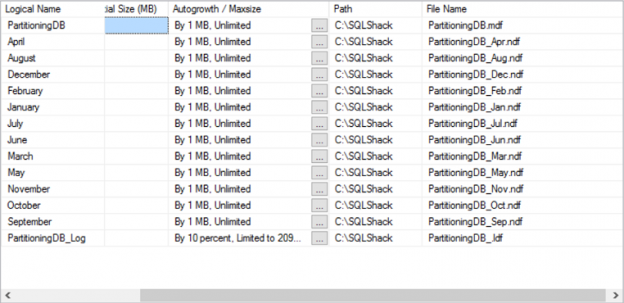
I work for a large, multinational financial institution. Like most companies in this field, ours is conservative and subject to much regulatory oversight. The first has meant that we’re slow to adopt new technologies. We need to be really, really, really sure things won’t break, customer accounts won’t vanish or lose their balances and that the regulators will not raise any red flags. Everything we do is subject to the scrutiny of our internal auditors, even something that seems simple, like rerunning a production job that failed because the host compute was down. I really mean everything!
Read more »

As a DBA, I am often asked why is something performing slow, what and why statistics need to be updated or what will cause them to be “off”. My initial question to clients when they pose these questions to me is what changed on your end? Did the data change significantly and did the rebuild or reorganize index job run? Before I get into the answers to these questions from my clients, let me give you some background. So, just to clarify, for most of my clients, I work as a remote part-time DBA, that being said, I manage their database from every aspect including setting up servers, backups/restore, troubleshooting, managing their index’s, etc. and again remotely. So normally, I have setup jobs that will manage their index’s ranging from a weekly rebuild or even sometimes I use one that I’ve designed that makes a choice to either rebuild or reorganize an index based on fragmentation level. The “general rule of thumb” is reorganizing the index for fragmentation from 5% to 29% and rebuild when 30% plus. Those are pretty standard numbers I did not make them up.
Read more »
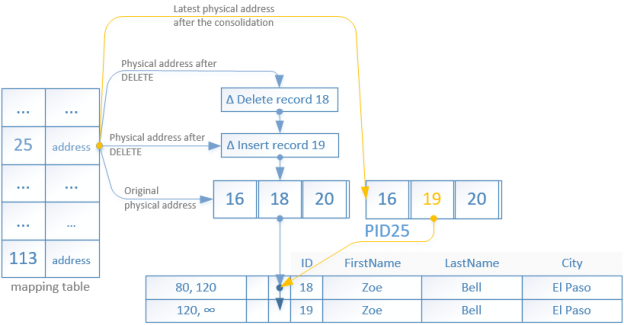
With the introduction of Microsoft’s new In-Memory OLTP engine* (code name Hekaton) a new type of nonclustered index was introduced to help you search the in-memory tables based on a range of values. Although the name is similar it does differ from the one we have in the traditional disk tables.
Read more »
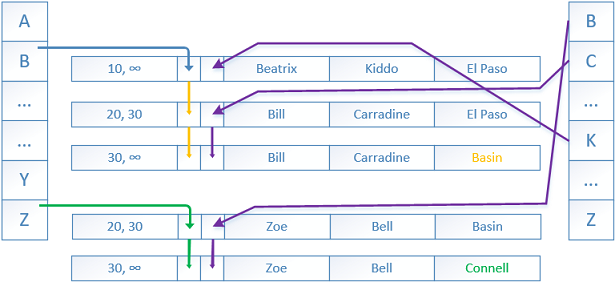
With the introduction of Microsoft’s new In-Memory OLTP engine (code name Hekaton) the familiar B-Tree indexes were not always the optimal solution. The target of the Hekaton project was to achieve 100 (hundred) times faster OLTP processing, and to help this a new index was introduced – the hash index.
Read more »
The Index Create Memory setting is an advanced SQL Server configuration setting which the SQL Server database engine uses to control the amount of maximum memory which can be allocated towards the creation of an index. In this article, we will take a look at the steps to resolve the below mentioned error message.
Read more »
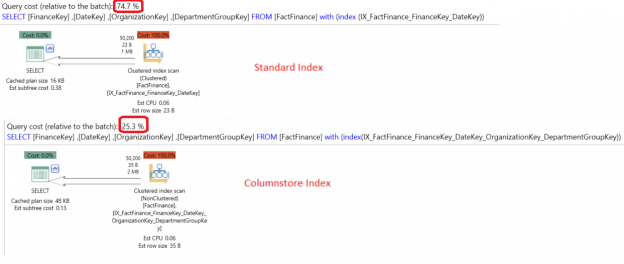
By default, SQL Server stores data logically in the tables as rows and columns, which appear in the result grid while retrieving data from any table and physically in the disk in the row-store format inside the data pages. A new data store mechanism introduced in SQL Server 2012, based on xVelocity in-memory technology, in which the data is stored in the column-store data format. This data store mechanism called the Columnstore index.
Read more »
Why is my database so slow? This query used to be so much faster. Why does it take so long to rebuild my index? How come it was fine last month? Every day I am asked these types of questions by clients. Every day! A lot of database developers and application developers do not realize that indexes are ever changing entities within your database or rather they need to be monitored closely and managed periodically to remain efficient. I cannot even count the times someone tells me “but we have index’s on this or that column and it was fine last month” and so on. All while they fail to realize or even tell me that the database just took on, updated or deleted 1,000,000 records for example, which would definitely change the footprint of the data, making the index’s unsound or in need of help. Even adding 50 new users that use the data differently could require new indexes. That being said, I decided to automate a quick and easy data gathering and reporting job that helps to answer these questions. Most of the time query performance questions can be answered by determining the fragmentation levels of index’s, if there are missing index’s, duplicate index’s, unused index’s and what are the heavy hitters in regards to queries and are queries running in memory or to disk and how many executions. My favorite thing to do with SQL Server is automate, automate and automate the tasks that are asked of me over and over.
Read more »
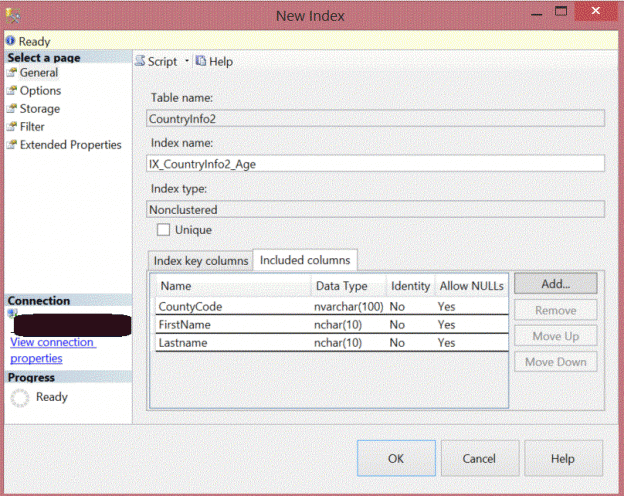
SQL Server indexes are created to speed up the retrieval of data from the database table or view. The index contains one or more columns from your table. The structure of these keys are in the shape of B-tree distribution, enabling SQL Server to find the data quickly.
Read more »
Database maintenance is very important, a critical part of our database administrators’ daily tasks. However, this aspect is frequently underestimated which could lead to performance problems and respectively angry, unhappy customers. In this article, we will take a look at the different maintenance operations we have in SQL Server and how we can optimize them and take the maximum out of each.
Read more »
Filtered indexes are well documented, as they have been around in SQL Server for almost six years now. Despite their longevity and usefulness, discussions of them tend to be very simple overviews using simple queries and not digging too deeply into more precise costs and benefits. This article is inspired by a production problem that cropped up recently involving a filtered index that illustrated that general knowledge of their function was not as complete as it should have been.
Read more »
In a previous chapter, we learned how to use the Tuning Advisor to analyze queries and receive recommendations about indexes, partitions and statistics. In this new chapter, we will learn how to use the command line tool called DTA. The DTA is the command line of the Tuning Advisor.
The DTA is a very powerful tool that can be used to automate some tuning tasks. It can be used combined with the SQL Agent, SSIS, or customized and external tools like programs made in C# or Java.
In this article, we will show how to use this tool.
Read more »
The indexes in many cases are great solutions to solve performance problems. For some problems, they are magical and very cheap solutions. In this chapter, we will show a demo of the SQL Server Tuning Advisor, which is a tool that comes with the SQL Server Installation. We will also use the SQL Server Profiler to generate the information for the Tuning Advisor.
Read more »© Quest Software Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. | GDPR | Terms of Use | Privacy