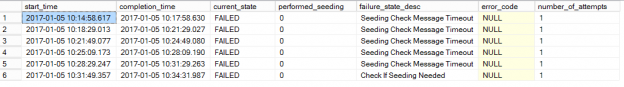
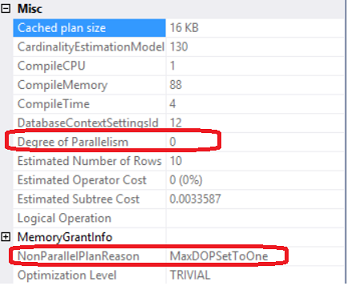
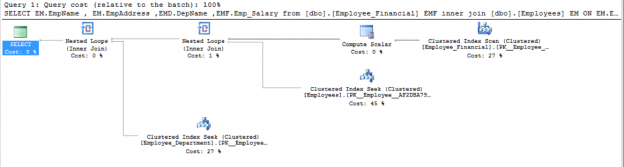
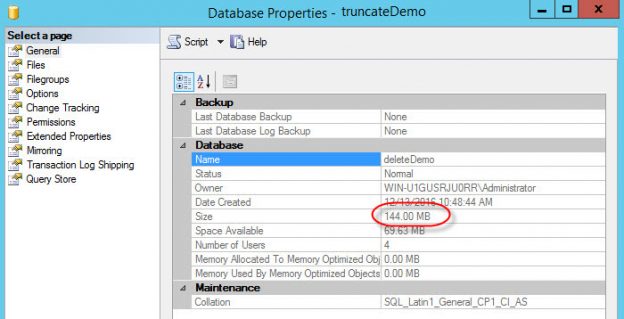
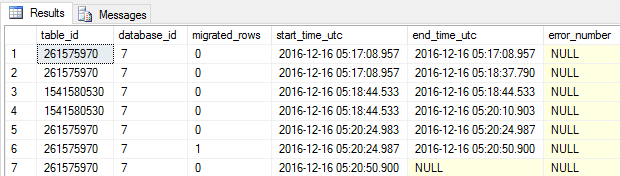
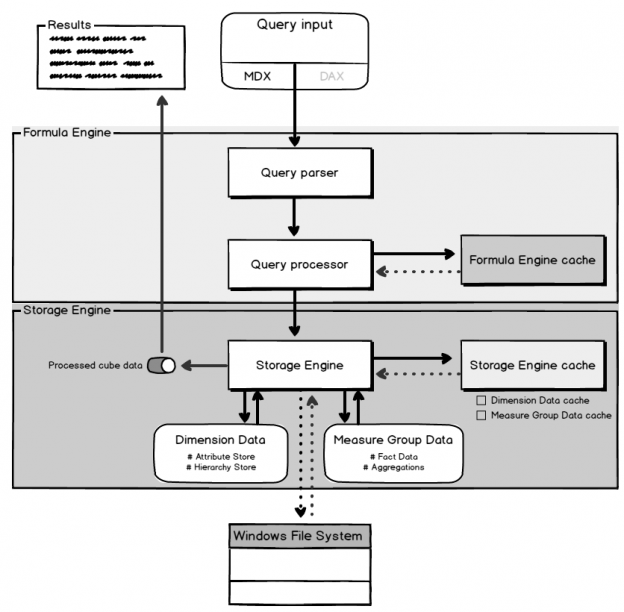
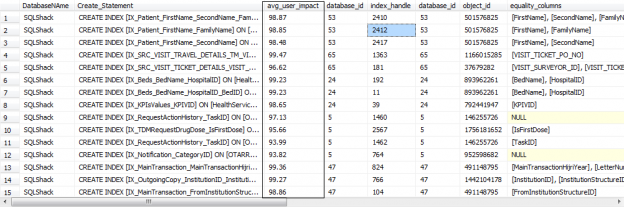
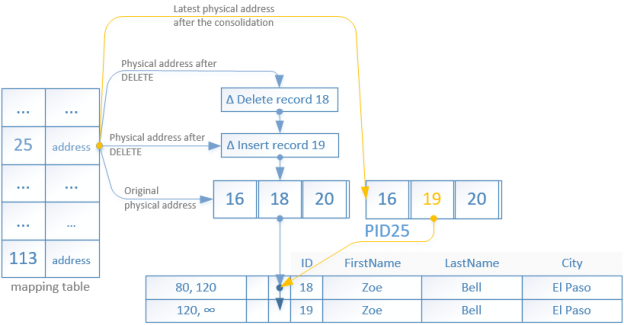
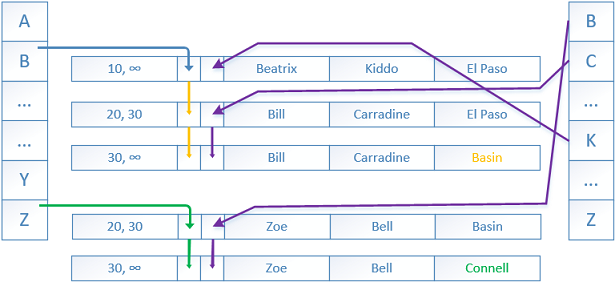
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups are an enterprise-level high-availability and disaster-recovery feature introduced the first time in SQL Server 2012as an alternative to database mirroring. A set of user databases that fail over together forms the availability group. These availability databases are hosted by the availability replicas and can be readable- writable at the primary replica and up to eight sets of secondary replica databases that can be configured to be read-only databases. The availability groups fail over due to the availability replica’s level issues and not the ones caused due to database level issues such as data loss or database corruption.
Read more »