A couple of years ago, Microsoft announced that SQL Server would be available on Open Source (Linux). In this article, we will go through the installation of Microsoft SQL Server on Linux (Ubuntu) and each step in detail.
Read more »
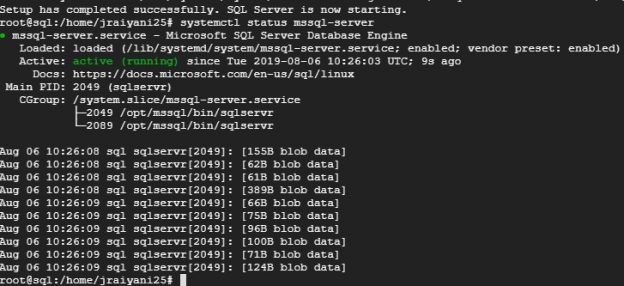


A couple of years ago, Microsoft announced that SQL Server would be available on Open Source (Linux). In this article, we will go through the installation of Microsoft SQL Server on Linux (Ubuntu) and each step in detail.
Read more »
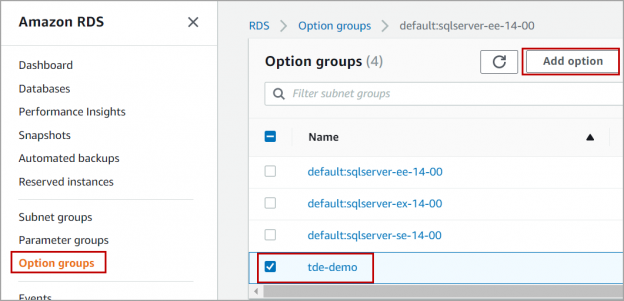
In this article, we will review Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) in AWS RDS SQL Server. AWS RDS supports TDE on SQL Server Enterprise edition of 2012,2014,2016 and 2017 editions.
Read more »
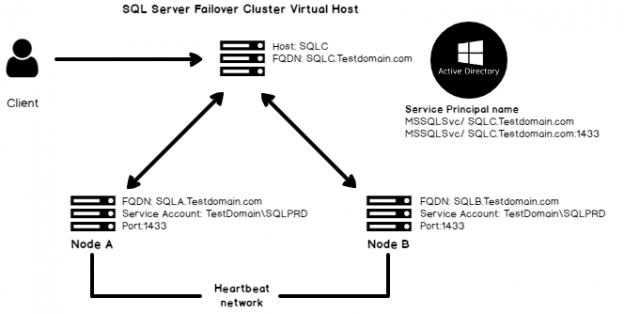
This article gives an overview of Service Principal Name (SPN) for using the Kerberos authentication in SQL Server connections. We use the Kerberos authentication to authenticate windows users securely for providing access to SQL Server.
Read more »
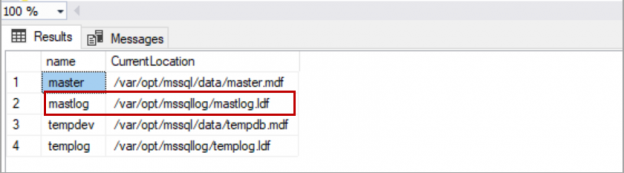
In this article, we will review on managing database files of SQL Server running on Azure Kubernetes service.

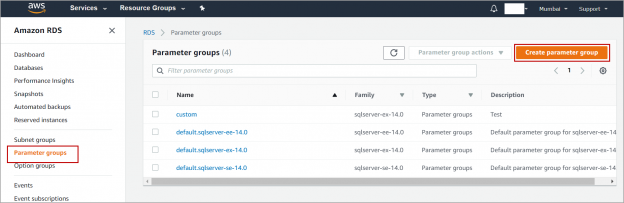
In this article, we will review common database administration tasks for AWS RDS (Relational Database Service) SQL Server instance. RDS does not provide access to some of the system procedures and tables that require advanced privileges. So, we cannot perform all the administration tasks on the RDS SQL Server instance.
Read more »
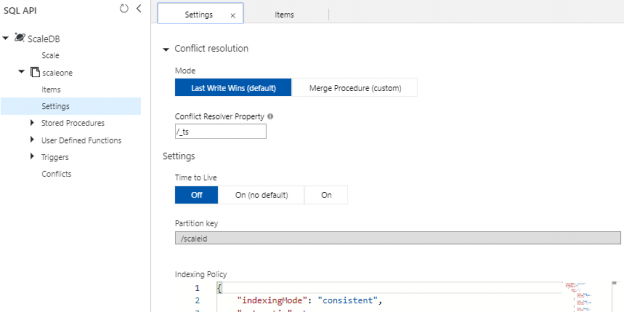
In many situations, we will develop, test or prove new concepts by horizontally scaling new SQL API containers in Azure Cosmos DB over possibly using existing containers. As we’ve seen in previous tips, we can create and remove Cosmos database accounts and databases by using the Azure Portal or PowerShell’s Az module along with making some updates to the configuration, such as the RUs for performance reasons. Similarly, we can create and remove a container through the Azure Portal along with creating and removing the container with PowerShell’s Az module.
Read more »
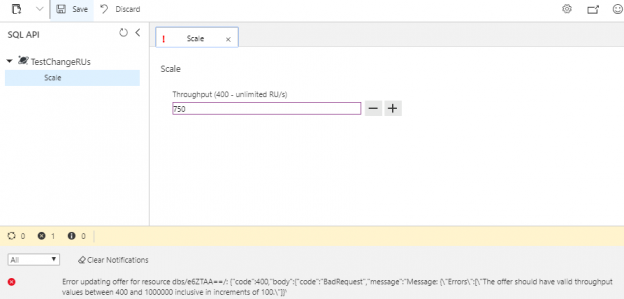
Now that we can create and remove an Azure Cosmos DB and databases that we can use for automation purposes, along with obtaining some information about these accounts, we’ll look at making some changes to these accounts for contexts related to performance. It’s possible that our unit and security testing or development with proof-of-concepts may face performance problems where we need to upgrade the settings of our database account. In this tip, we’ll be working with the SQL API database layer in a Cosmos database account by building on our get, create and remove automation to update its performance.
Read more »
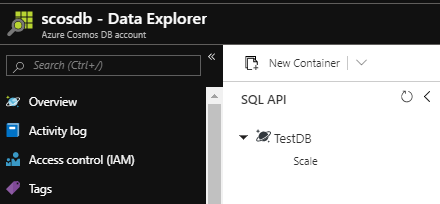
Our testing or development may call for dynamic creation on the database level for Azure Cosmos DB rather than the account level. As we’ve seen with dynamically working with a Cosmos database account using PowerShell, we can create, remove, and obtain properties of the account. Identically, we can do this on the database level as well and we may use this in testing if we need the same Cosmos database account for other testing purposes. Development situations may also involve use cases where we want to test a concept and dynamically create a database within our Cosmos database account. In this tip, we’ll look at working with our Azure Cosmos database account on the database object level where we do nothing to manipulate the account itself, only add databases to the account once it’s been setup.
Read more »
In this article, we will review how to create a Kubernetes cluster in AWS using KOPS, provision Elastic Block Store (EBS) as persistent volume to store the database files and deploy SQL Server in the K8s cluster.
Read more »
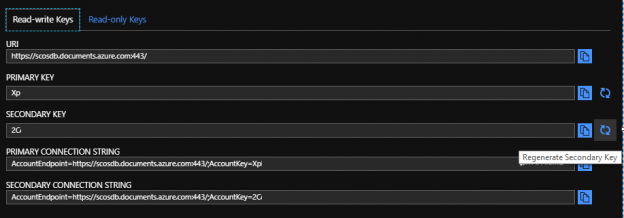
After we set up our Azure Cosmos DB, we may want to get, add to, or update existing properties. We may use some of the get functionality that PowerShell provides to dynamically save values to encrypted configuration files or tables that we use for application purposes and this functionality could be added to the creation of the Cosmos database account, or a separate step in addition to the creation. In secure contexts, this ensures security without the properties after passing through human eyes since they are saved directly to an encrypted location. In the same manner, we may want to regenerate the keys for the account and save the connection strings with the new keys.
Read more »
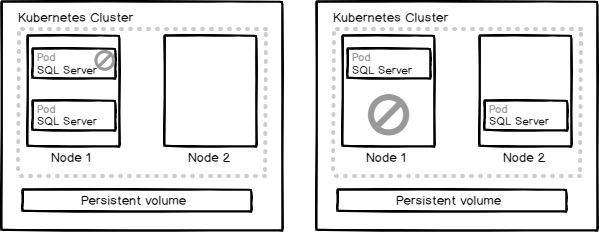
In this article, we will review how to create a Kubernetes cluster in Azure Kubernetes Service, provision the persistent volume to store the database files and deploy SQL server on Kubernetes cluster.
Read more »
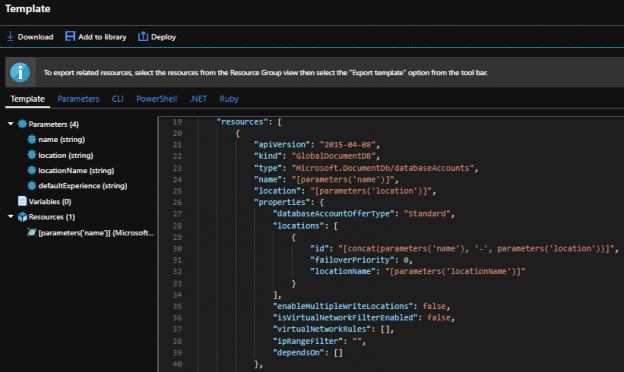
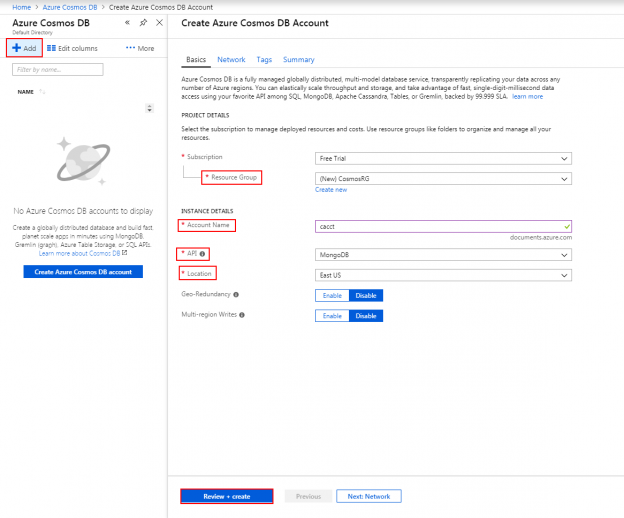
When managing Azure Cosmos DB, we can use the Azure portal and create resources through the interface or use the command line in the portal and create resources. PowerShell also supports some functionality for creating and managing these resources, which can help development teams automate the creation of these databases for quick creations, unit and security tests, removals if the resources aren’t required following the tests. We can also use these scripts for creating templates that we may use in multi-scaling creations (like databases in a group designed for horizontal scale). Generally, in one-off situations, the Azure Portal will suffice for deployments if there is a cost to develop automation that is not required. In this tip, we’ll look at the process of creating a blank and removing the same Azure Cosmos DB.
Read more »
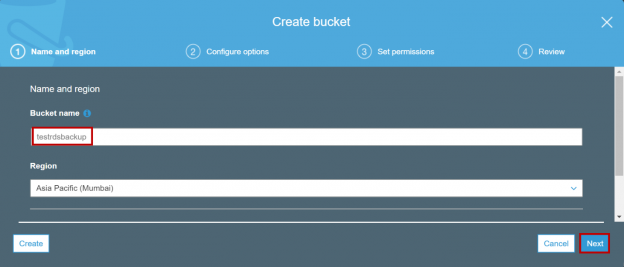
In this article, we will review how to migrate database from on-premises SQL Server instance to AWS RDS SQL Server instance and between AWS RDS instances using native backup, restore and amazon simple storage service(S3).
Read more »

In this article, we will review how to migrate database from on-premise SQL Server instance to AWS RDS SQL Server instance using AWS Database migration service. There are different ways to migrate the database to the AWS RDS instance:
Read more »
In this article let’s see how to install a SQL Server Instance using a Docker container in Windows server 2016.
Read more »
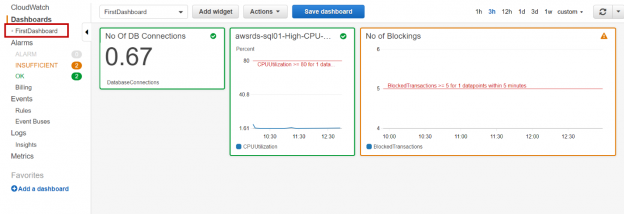
In this article, we will review how to monitor AWS RDS SQL Server database instances and setup email notifications using event subscriptions and CloudWatch alarms.

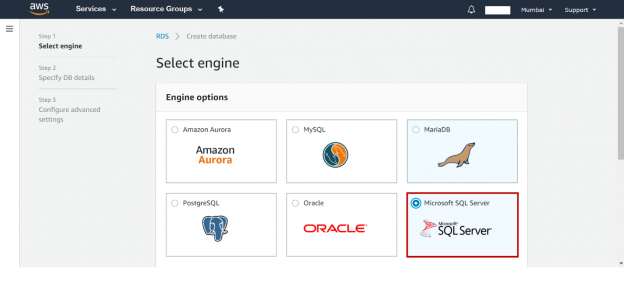
This article will review on how to launch an AWS RDS SQL Server instance and how to connect the instance and modify the properties of database instance.
Read more »
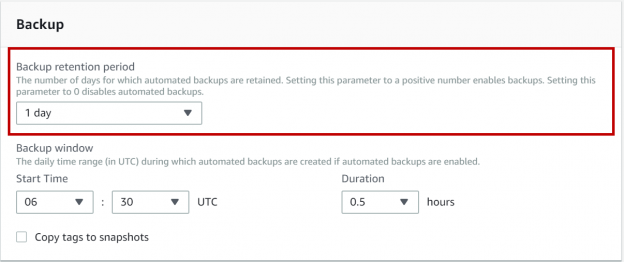
This article will review about the recovery models backups and restore options in available AWS RDS SQL Server.
Read more »
This guide is all about provisioning SQL Server 2019 using Azure Container Instance (ACI), including the installation and configuration. In this article, we talk about the Azure Container Instance (ACI), the Azure PowerShell module, installation and configuration of SQL Server using the Azure PowerShell module, and automation of installation and deployment using templates.
Read more »

As we’ve worked with Azure Cosmos DB, we’ve seen that we can store data within fields and the fields of each document don’t always have to match – though we still want some organization for querying. The fields and values storage becomes useful when working with object-oriented languages as these fields can be keys that we use with values that we extract as properties. For an example, the below PowerShell line creates a JSON document in an object and we can see that we can extract the values of these keys in the JSON object.
Read more »
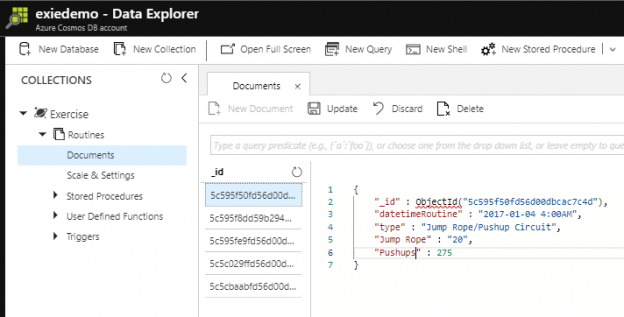
Since we will sometimes require removing documents in Azure Cosmos DB, we’ll want to be able to specify the documents for removal. In some cases, this will be as simple as specifying a field for removal, such as removing one type of workout in our temporary database we’ve created. In other delete situations, we’ll want to remove if the value of the field isn’t what we expect – such as greater than what we want. This applies to updates as well – we may want to drill into a specific value range for an update. In this tip, we’ll look at using operators with strings, numeric types and dates.
Read more »
In the first part of this series Getting Started with Azure Cosmos DB, we looked at using Azure Cosmos DB for saving an individual’s fitness routine and why this database structure is better for this data than a SQL database while also showing that we still have to organize our structure like a file system organizes files. In this part of our series, we’ll begin looking at the terminology translation between NoSQL and SQL along with running updates for our documents and queries with filters that return some fields in our document, but not other fields.

In the past two years, we’ve seen an explosion in growth with document-oriented databases like Azure Cosmos DB. MongoDB – one of the major document databases – went live on the Nasdaq and attracted some attention in the past year as well. While more developers are using the document structure for some appropriate data models, less than 10 years ago, some in the industry were predicting that document databases were unnecessary and wouldn’t last because all data could be flattened to fit the SQL model. I took the opposite approach, being an early adopter of MongoDB along with continuing to use SQL databases as I saw opportunities in both SQL and NoSQL for various data structures. While some data do fit the SQL model and SQL will continue to exist, some data are best for document databases, like Azure Cosmos DB. In this series, we’ll be looking at the why and how of document databases.

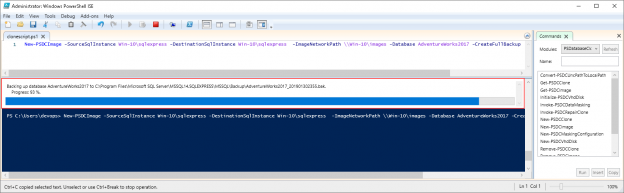
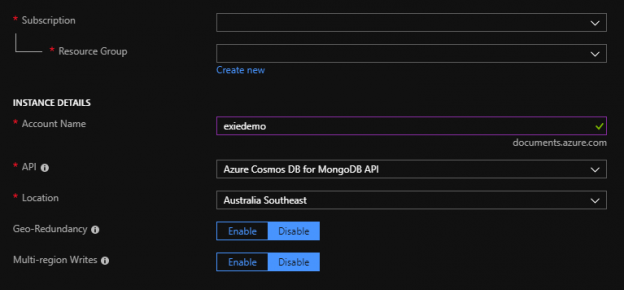
With the complex SQL database development and production infrastructure there comes an issue with database provisioning. The issue implies that all development and testing instances should have proper version of a database in the proper environments. So that means that database development teams, client application teams, QA and testing teams need to work on proper database version which is usually the one in production but naturally cannot work on the production database itself. This is why those environments have to have a provisioned database and there comes the problem for database DevOps teams how to perform database provisioning, which is repetitive task, with optimal time invested.
Read more »
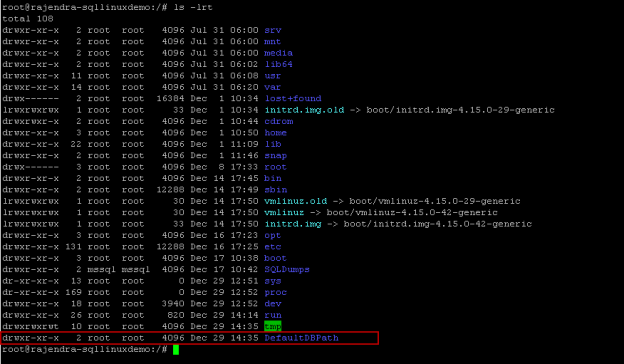
In a previous article, we explored the process to change default SQL dump file location in SQL Server. In this article, we will view the process to change the default database files and backup locations in SQL Server on Linux.
Read more »© Quest Software Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. | GDPR | Terms of Use | Privacy