In this 38th article for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups, we will explore Windows PowerShell scripts to configure it.
Introduction
Windows PowerShell is a scripting language that offers useful modules for database professionals (Developer and DBA). Usually, we use SQL Server Management Studio to perform administrative tasks using the interactive windows. In the previous articles, we used SSMS for all AG configurations. If we go through AG configuration consoles, do the configuration and generate scripts, you get scripts in SQLCMD mode.
In this article, let’s explore how you can use Windows PowerShell for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
A quick overview of SQL Server PowerShell
We have two SQL Server PowerShell Modules – SqlServer and SQLPS.
- SQLPS: It is available with SQL Server installation and useful for backward compatibility. Microsoft does not update this module
- SqlServer: The SqlServer PowerShell module has cmdlets for the latest SQL Server features. You can install this module from the PowerShell gallery
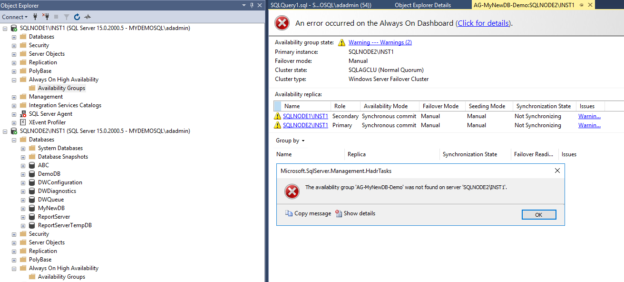
Connect to your primary AG replica in SSMS, right-click on the availability group and Launch Windows PowerShell. You get the following error message because the SqlServer module is not installed on the replica.
To install the SqlServer module, run the following command in the Windows PowerShell with administrative command.
|
1 |
>Install-Module SqlServer |
It downloads the required package and installs it on your primary AG replica.
PowerShell drives for SQL Server
Windows PowerShell scripts uses the virtual drives so that users can traverse different modules, functions similar to a drive. These drives are also known as PowerShell drives.
To understand these PowerShell drives, import the SqlServer module and access the virtual drive using the following command.
|
1 2 |
> Import-Module sqlserver >cd sqlserver:\SQL |
You can access the PowerShell drive now. As you see, the drive appears as SQLServer:\SQL>

Now, use the dir command to check the existing directories. It gives you a server name (in my case SQLNode1). Here, the instance name appears as a folder.
Let’s enter into the folder (SQLNode1) and use the dir command to check its contents. It gives you the instance name and its properties.
The instance name for my primary replica is INST1.
|
1 2 |
PS SQLServer:\SQL CD SQLNode1 PS SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode1 Dir |
Now, enter into the instance folder, and it returns the folders for the different SQL features such as Audit, databases, Logins, Roles, Mail, Triggers.
|
1 2 |
PS SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode1> cd INST1 PS SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode1> dir |
In this list, you also have a folder for AvailabilityGroups. Let’s enter into this folder, and it should return the availability group name.
|
1 |
PS SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1> cd AvailabilityGroups |

You get the following values from this directory.
- Availability Group Name: [AG-MyNewDB-Demo]
- Primary Replica Instance: SQLNode2\INST1

In the availability group, you further get the path for different AG configurations.
- Availability databases
- Availability Group Listeners
- Availability Replicas
- Database Replica states
|
1 2 |
PS SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1\AvailabilityGroups> cd Ag-MyNewDB-Demo PS SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\Ag-MyNewDB-Demo dir |

We can enter into the respective folder, and it returns the corresponding details. For example, cd Availabilitydatabases give you the following details.
- Availability database name
- Synchronization status
- Suspend status: If your AG database synchronization is suspended, it shows True value in the IsSuspended column
- Join status
You should be familiar with the PowerShell Virtual drives for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups. Let’s start the AG configurations with the Windows PowerShell cmdlets.
In my demo environment, the availability group is already configured with the following configuration.
- Primary replica: SQLNode2\INST1
- Secondary replica: SQLNode1\INST1
- AG database: MyNewDB
To begin with the Windows PowerShell, we use the following approach:
- Remove an availability database from the primary replica
- Delete availability group
- disable AG configuration for SQL Service
- Stop and Start SQL Services
- Enable AG configuration for SQL Service
- Configure the availability group and database in the synchronous mode
- Configure the SQL Server Listener
Windows PowerShell Scripts to remove an availability database from the primary replica
Suppose we want to remove a database from the availability group. In Windows PowerShell, we use the Remove-SqlAvailabiltyDatabase cmdlet in the SqlServer module. In the path, you need to be in the availability group folder.
|
1 2 |
> Remove-SqlAvailabiltyDatabase -path SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\availabilitydatabases\MyNewDB |
Launch the AG dashboard. The dashboard does not look healthy because there is no database in the availability group for synchronization.
In the below screenshot, we see the AG database after removing it from the availability group.
- Primary replica SQLNode2: MyNewDB in the online status
- Secondary replica SQLNode1: MyNewDB in the restoring status

Windows PowerShell Scripts to delete availability groups
To remove an availability group, connect to the primary replica in SSMS, right-click on the availability group and Remove the availability group.
In Windows PowerShell, we use Remove-SqlAvailabilityGroup cmdlet. In the path, you should be in the availability group folder.
|
1 2 |
> Remove-SqlAvailabilityGroup -path SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\Ag-MyNewDB-Demo\ |
If the availability group dashboard is already opened, try to refresh it. You get the error because we have removed the SQL Server Always On availability group.
In the object explorer, you do not see any configured availability groups.
Windows PowerShell Scripts to disable AG configuration for SQL Service
As you know, to use the SQL Server Always On Availability Group features, we enable the feature from the SQL Server Configuration Manager on all AG replicas.
You can verify it from the SQL Server Configuration Manager as per the following screenshot.

Suppose, we want to disable the SQL Always On feature. Using the PowerShell, we use Disable-SqlAlwaysOn cmdlet. In the path, you should be in the instance folder, as shown below.
|
1 |
> Disable-SqlAlwaysOn -Path SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1 -NoServiceRestart |
Now, if you open SQL Server properties, you see it removed the tick from the AG feature checkbox.

We require to restart the SQL service to make the configuration effective. To start the SQL Service, run the following command.
|
1 |
>Stop-Service -InputObject $(Get-Service | Where {$_.name –eq 'MSSQL$INST1' }) -Force |
It stops the SQL Services for the INST1 instance.
To start the SQL service, it uses the start-service PowerShell cmdlet. Run the following command, and it starts the database engine service for SQL Server.
|
1 |
>start-service -Inputobject $(Get-Service | where {$.name -eq 'MSSQL$INST1'}) |
You can validate the SQL Service status in the SQL Server Configuration Manager.
Windows PowerShell Scripts to enable AG configuration for SQL Service
Previously, we disabled the AG configuration from the SQL Services. We need to enable the SQL Server Always On Availability Group configuration, run the following command.
|
1 |
Enable-SqlAlwaysOn -Path SQLServer:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1 -NoServiceRestart |
You can verify from the SQL Server Configuration Manager, and you get a check on the Always On Availability Group as shown below.

You need to restart SQL Service before configuring SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Windows PowerShell scripts to configure availability groups, add database in the synchronous mode and create a SQL listener
In this step, we configure the availability group between primary and secondary replica in synchronous mode. The overall script for the AG implementation is as below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
Import-Module SQLServer Restore-SqlDatabase -Database "MyNewDB" -BackupFile "C:\SQL\MyNewDB.bak" -ServerInstance "SQLNode1\INST1" -RestoreAction database -NoRecovery $primaryServer = Get-Item "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1" $secondaryServer = Get-Item "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1" $primaryReplica = New-SqlAvailabilityReplica -Name "SQLNode2\INST1" ` -EndpointUrl "TCP://SQLNode2.mydemosql.com:5022" -FailoverMode Automatic ` -AvailabilityMode "SynchronousCommit" -AsTemplate -Version ($primaryServer.Version) ` $secondaryReplica = New-SqlAvailabilityReplica -Name "SQLNode1\INST1" ` -EndpointUrl "TCP://SQLNode1.mydemosql.com:5022" -FailoverMode ` "Automatic" -AvailabilityMode "SynchronousCommit" ` -AsTemplate -Version ($secondaryServer.Version) New-SqlAvailabilityGroup -Name "AGusingPowerShell" ` -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1" ` -AvailabilityReplica @($primaryReplica,$secondaryReplica) -Database "MyNewDB" Join-SqlAvailabilityGroup -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1" -Name "AGusingPowerShell" Add-SqlAvailabilityDatabase -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\AGusingPowerShell" -Database "MyNewDB" New-SqlAvailabilityGroupListener -Name AGusingPowerShell ` -StaticIp '10.0.2.25/255.255.255.0' -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\AGusingPowerShell" ` -Port 3333 |
Let’s understand the script before implanting it.
-
Import the SqlServer module in your Windows PowerShell
1Import-Module SQLServer -
Restore database MyNewDB on the secondary replica in the NORECOVERY mode from the specified backup file. Here, we prepare our secondary replica with the AG database from a primary replica database copy
1Restore-SqlDatabase -Database "MyNewDB" -BackupFile "C:\SQL\MyNewDB.bak" -ServerInstance "SQLNode1\INST1" -RestoreAction database -NoRecovery -
The below scripts does the following tasks for us:
- Define the primary and secondary replica PowerShell drive path and stored it into the $PrimaryServer and $SecondaryServer variables
-
We use the cmdlet New-SqlAvailabilityReplica to create the primary and secondary
replica. It is similar to the AG wizard where we add all replicas and defines their availability mode,
failover mode and endpoint URL
- EndpointURL: Specify the endpoint in the format – TCP://[ServerName]:[PortNumber]
- FailoverMode: Specify whether you require automatic or manual failover. For asynchronous mode, we can use only manual failover
- AvailabilityMode: Specify whether you require synchronous or asynchronous AG mode
123456789101112$primaryServer = Get-Item "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1"$secondaryServer = Get-Item "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1"$primaryReplica = New-SqlAvailabilityReplica -Name "SQLNode2\INST1" `-EndpointUrl "TCP://SQLNode2.mydemosql.com:5022" -FailoverMode Automatic `-AvailabilityMode "SynchronousCommit" -AsTemplate -Version ($primaryServer.Version) `$secondaryReplica = New-SqlAvailabilityReplica -Name "SQLNode1\INST1" `-EndpointUrl "TCP://SQLNode1.mydemosql.com:5022" -FailoverMode `"Automatic" -AvailabilityMode "SynchronousCommit" `-AsTemplate -Version ($secondaryServer.Version) -
The below script uses the cmdlet New-SqlAvailabilityGroup for creating an availability group. Use the variable $PrimaryReplica, $SecondaryReplica in the AvailabiltyReplica parameter
123New-SqlAvailabilityGroup -Name "AGusingPowerShell" `-Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1" `-AvailabilityReplica @($primaryReplica,$secondaryReplica) -Database "MyNewDB" -
The Join-SqlAvailabilityGroup joins the secondary replica to the availability group. You need to specify the availability group name created using the above script
1Join-SqlAvailabilityGroup -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1" -Name "AGusingPowerShell" -
The Add-SqlAvailabilityDatabase cmdlet adds the secondary database to the availability group. In the path, specify the path for the availability group of the secondary replica
1Add-SqlAvailabilityDatabase -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode1\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\AGusingPowerShell" -Database "MyNewDB" -
In this part of the script, we use the New-SqlAvailabilityGroupListener cmdlet for configuring the availability
group listener. For the listener, we require a static IP address, subnet mask and the listener port
- StaticIP: In this parameter, we specify both the static IP address and its subnet mask
- Port: Specify the listener port. Make sure the port is opened in the Windows firewall
123New-SqlAvailabilityGroupListener -Name AGusingPowerShell `-StaticIp '10.0.2.25/255.255.255.0' -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\SQLNode2\INST1\AvailabilityGroups\AGusingPowerShell" `-Port 3333
Now, it’s time to execute the PowerShell Script for creating the SQL Server Always On Availability Group. In the output, it logs the commands in the console.
You can see the configured availability group [AGusingPowerShell] and its primary replica [SQLNode2\INST1].
You can connect to the primary replica, launch the AG dashboard. Everything looks good.
Conclusion
In this article, we configured the SQL Server Always On Availability Group using Windows PowerShell scripts. You can use Windows PowerShell Scripts for automatically implementing an availability group based on the supplied inputs.
Table of contents
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023