This is the 25th article in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups series. In this article, we will explore the high availability configuration for reporting services databases.
Configure SQL Server Reporting Services for standalone databases
SQL Server Reporting Services (commonly known as SSRS) is a service to deploy paginated reports for web and mobile. Data representation is an art, and SSRS helps you to visualize the data in an informative way using various graphs, charts, KPI, matrix.

Image Source: Microsoft docs
Until SQL Server 2016, the reporting services comes with the SQL Server installation. If we choose the reporting services feature, it installs the reporting services and configures its databases in the local instance.
Starting from SQL Server 2017, Microsoft separated the reporting services from the standard SQL Server installation. It is a standalone application that you can download, install, upgrade independently.
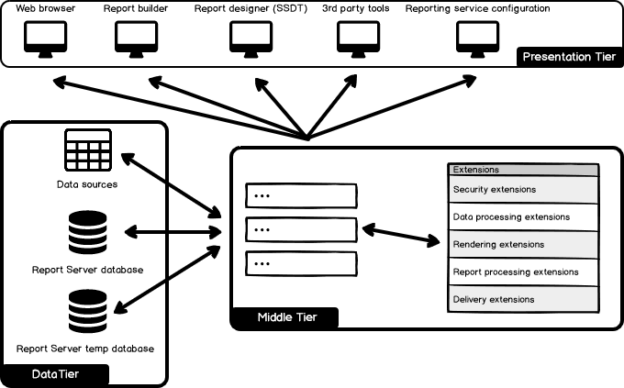
In the below image, you see the SSRS architecture diagram with various components involved. You can refer to the article, SQL Server Reporting Services Architecture and Component Topology to understand these components in detail.

As per best practice, we should use the reporting services separated from the database instance. For this article, firstly, we configure the reporting services for the following SQL environment.
- Reporting Services: SQLNode3\INST1
- Reporting services database: SQLNode1\INST1
It creates the [ReportServer] and [ReportServerTempDB] database on the SQLNode1\INST1. As of now, these databases are not part of any SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
You can download the Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Reporting Services from the Microsoft.

Launch the SSRS installation with the following welcome screen.

Choose an edition. We use the developer edition of SQL Server Reporting Services 2019.

On the next page, it shows that it installs the reporting services only. It does not install the SQL database engine for you that is required to store SSRS databases. You should install SQL Services on it or a separate instance. As highlighted earlier, we use the SQLNode1\INST1 for the SSRS databases.

Select the reporting services installation directory. We can go ahead with the default directory.

After installation, it asks you to configure the report server using the Reporting Services Configuration Manager. Click on Configure Report Server.
It opens the Reporting Services Configuration Manager. Click on Start to run the reporting services.

We do a minimum required configuration in this article. You can refer to this article, SQL Server Reporting Service Configuration Manager to understand complete SSRS configurations.
Service account configuration: In the service account page, specify a domain account to run the reporting service. It automatically restarts the reporting services once you apply the service accounts
Web Service URL: It prefills the default configuration for the SSRS web service URL
Click on Apply, and it configures the web service URL. You can click on the hyperlink to open the web URL.
Report Server Database configuration
First, we need to create the reporting services databases on the SQL instance that works as a primary replica. Currently, it does not show any SSRS database details
Click on Change Database. We do not have any existing database so choose “Create a new report server database”

Specify the SQL instance name (Current primary replica) and authentication type. I use Windows authentication for the DB connection purpose

You get the flexibility to specify the database name in the report server wizard. By default, it creates a new database [ReportServer]. You should not change the database names unless you have any specific requirements

Specify the service credentials to connect with the report server database. SSRS wizard automatically assigns the required permissions for the SQL account we specify here

Verify your configurations in the report server database configuration. You can note here that it creates two SSRS databases – ReportServer and ReportServerTempDB

On the next page, it completes the SSRS configurations, as shown below.

You can see the database name, SQL instance and the credentials in the database page.
Similar to the Web Server URL, configure the Web Portal URL. You get the hyperlink for URL after configuration
Connect to the SQL Server instance, and you can see both databases in the object explorer
Change the recovery model for SSRS databases
As shown above, reporting services databases have the following recovery models:
- ReportServer – Full
- ReportServerTempDB- Simple
As you know, for a database in SQL Server Always On Availability groups, we require databases in the full recovery model. Open the ReportServerTempDB database properties, click on the options and change the recovery model to FULL.
Our both SSRS databases are in the Full recovery model now.
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for Reporting services database
In this article, we create a new availability group for both reporting services databases. You can add databases in an existing availability group as well. You can refer to earlier articles for detailed steps on creating a new availability group.
In the new availability group wizard, specify the AG group name.
I took full backups of both databases; therefore, it meets prerequisites to be part of an AG.
We have two nodes in the cluster. AG should be in the Synchronized mode.
Specify listener name and IP address for this SQL Server Always On Availability Group. SQL listener is a must for the reporting services database in AG configuration.
Once it creates the new SQL Server Always On Availability Group, launch the dashboard, and we see reporting services databases added successfully.

Deploy a sample report and create a subscription
Deploy a report in your new SSRS configuration. You can refer to SSRS articles on SQLShack for reference purposes.
For this article, I deployed a sample SSRS report. This report connects to the [AdventureWorks] database and pulls the required data.
I have also configured a report server subscription. This subscription export the report in PDF format and stores at a shared location on a scheduled time.
SSRS schedule creates a SQL Server agent job on the SSRS database instance. Connect to your SQL instance and verify that the job exists. You can filter the agent jobs using the Report Server category. Do not modify this job manually in SSMS. You must use SSRS reports for any changes like report schedule, frequency, shared location or email id specifications.

Reconfigure Report Server database configurations to SQL listener
At this step, we have done the following configurations so far in the article.
- Our reporting services databases are configured in the SQL Server Always On Availability Group
- We deployed a sample SSRS report
Think of a question now- If the AG failover happens and SSRS databases become active on the current secondary ( after failover – primary) what happens to my report subscriptions?
As you have seen earlier, the report subscription is a SQL agent job. Do you need to create these jobs on the new primary replica manually? I have hundreds of report subscriptions; Do I need to create all jobs?
We instructed earlier to not perform any changes to these jobs manually. If we script out jobs and configures on the new primary replica, Does it work?
Hold your horses! We have configured the databases in the high availability, but our report server is not aware of any changes? If you perform a failover, the report server won’t recognize the new primary replica instance.
Switch to the Report Server Configuration Manager -> Database -> Change Database ->Choose an existing report server database.
In the server name, specify the SQL listener that we created earlier for SSRS SQL Server Always On Availability Group. A SQL listener always points to the primary replica. Once we configure the listener in the report server configuration, in case of failover, it automatically connects to the databases on a new primary replica.

Select the report server database from the drop-down.

Specify the service credentials.

Verify your configuration. You can verify the SQL Server instance is the SQL listener name along with the port number.

It reconfigures your report server configuration.

Verify the listener’s name in the database tab.
Failover testing for SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) in a high availability mode
For testing purposes, perform a manual failover. It makes the SQLNode2\INST1 as the new primary replica.

Our first test passed. AG dashboard is healthy for both SSRS databases after failover as well.

Launch the SSRS portal and view the sample report we deployed. It is also working as expected. It passes the second validation.
The third validation is for the report server subscription. Select the report subscription and run it manually.
It runs fine. You can verify the last run and the result. In case of any error, you get an error message in the result column.
For the final validation, instead of running the report subscription manually, schedule it to run after 2-3 minutes from the current time. It also runs successfully.
Now it is time to recall your earlier questions. We can see the report schedule SQL agent job on the new primary replica. We have not created it manually.
SSRS automatically creates the report subscription jobs on the new primary replica. Microsoft recommends restarting the SQL Server reporting services after the AG failover as well. You should do the following tasks in case any failover happens using a SQL agent job.
- Restart SQL Server reporting services after failover
- Remove the SSRS jobs from the old primary replica. It ensures that during failback, all SSRS jobs are created with the latest configurations
Conclusion
In this article, we configured the SQL Server Reporting Services in a high availability solution using SQL Server Always On Availability Configuration. It ensures your reports are always running if one of your database instances has some issues. You can go through these Microsoft documentations: High availability in SQL Server Reporting Services and Reporting Services with Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server).
Table of contents
See more
For an SSRS and database documentation tool, consider ApexSQL Doc, which can document SSRS reports from file system, Native web service and SharePoint web service in different output formats e.g. HTML, PDF, Word etc.

- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023