This article explores the DATEADD SQL function and its usage scenarios with various examples.
Usually, we work with date data type in SQL Server. We need to do manipulations with dates as well. In my previous article DATEPART SQL FUNCTION, we explored to retrieve specific part from the date such as day, year, month, quarter, day of the year.
We can use the SQL SERVER DATEADD function to add or subtract specific period from a gives a date.
Syntax
DATEADD (datepart, number, date)
- Datepart: It specifies the part of the date in which we want to add or subtract specific time interval. It can have values such as year, month, day, and week. We will explore more in this in the example section
- Number: It is the number by which we want to increase or decrease date. It should be an integer
- Date: We can specify the date here. In this date, we want to add a specified number on datepart
Suppose we want to add ten days to the current date. In this example, the variables would be
- Datepart value: Day
- Number: 5
- Date: Getdate() – Current date
Explore the SQL SERVER DATEADD function with examples
Example |
Datepart |
Query with output |
||
Add 10 days to specified date |
dd d |
Output – 2019-05-09 00:00:00.000 |
||
Subtract one day from a specified date | dd D |
Output -2019-04-28 00:00:00.000 | ||
Add two years in a specified date | YYYY YY |
Output – 2021-04-29 00:00:00.000 | ||
Subtract three years from a specified date | YYYY YY |
Output – 2016-04-29 00:00:00.000 | ||
Add 4 Months in specified date | MM |
Output – 2019-09-29 00:00:00.000 | ||
Add 2 hours to a date | HH |
Output – 2019-04-29 02:00:00.000 In this example, we did not specify any time with the input date. By default, SQL Server considers time 00:00.000 | ||
Subtract 120 minutes from date | MM |
Output – 2019-04-28 22:00:00.000 | ||
Add 1 quarter in specified date |
Output – 2019-07-29 00:00:00.000 | |||
Add 100 days of the year in a specified date | DY |
Output – 2019-08-07 00:00:00.000 | ||
Invalid value – Add 12578995 years in specified date | Year |
We cannot specify invalid values or out of range values in the SQL SERVER DATEADD function. We get following error message Output – Msg 517, Level 16, State 1, Line 1: Adding a value to a ‘datetime’ column caused an overflow. | ||
Out of range number value – In the DATEADD number parameter, we can specify only integer values. | Integer value range: -231 (-2,147,483,648) to 231-1 (2,147,483,647) |
In this example, we specified value 2147483648 in number parameter. This value does not fall inside an integer range. Once we execute this query, we get the following error message. |
Data types in the SQL SERVER DATEADD function
We can use the following data type in date expression.
- date
- DateTime
- datetimeoffset
- datetime2
- smalldatetime
- time
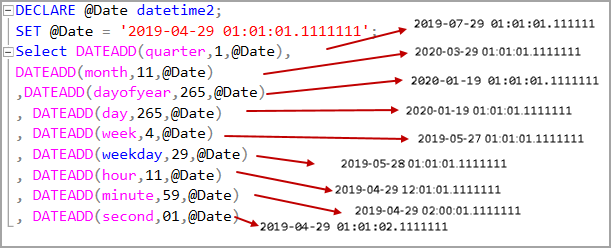
In the following query, we declared a variable @date having a datetime2 datatype. We can use the DATEADD SQL function as per the following query.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
DECLARE @Date datetime2; SET @Date = '2019-04-29 01:01:01.1111111'; Select DATEADD(quarter,1,@Date), DATEADD(month,11,@Date) ,DATEADD(dayofyear,265,@Date) , DATEADD(day,265,@Date) , DATEADD(week,4,@Date) , DATEADD(weekday,29,@Date) , DATEADD(hour,11,@Date) , DATEADD(minute,59,@Date) , DATEADD(second,01,@Date) , DATEADD(millisecond,1,@Date); |

Using the SQL SERVER DATEADD function to get records from a table in specified date range
We can use the DATEADD SQL function to retrieve records from a table for a period. In the following query, we specified a date with parameter @Startdate. We want to retrieve records from Orders table. We need to get records between @StartDate and @Enddate ( add 1 hour in start date) .
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
DECLARE @StartDate DATETIME= '2013-05-01 11:00.000'; DECLARE @Hours INT= 1; SELECT OrderID, LastEditedWhen FROM [WideWorldImporters].[Sales].[Orders] WHERE LastEditedWhen BETWEEN @StartDate AND DATEADD(HOUR, @Hours, @StartDate); |
We get the following output.

Using the SQL SERVER DATEADD function to get date or time difference
We can use the DATEADD SQL function to get time difference between the start date and end date. Many times, we want to use the SQL SERVER DATEADD function to get date difference. For example, we want to know how long it took to complete an order or how long it took to reach from home to office.
Execute the following query to get the difference between starttime and endtime. We use the DATEADD SQL function along with the DATEDIFF SQL function.
|
1 2 |
DECLARE @StartTime DATETIME= '2019-04-29 20:30:00', @EndTime DATETIME= '2019-04-30 01:00:00'; SELECT DATEADD(Minute,DATEDIFF(Minute, @StartTime, @EndTime),0) AS ElapsedTime; |
It gives the elapsed time in minutes. We specified value 0 in the DateADD SQL function. It takes date value 1900-01-01 00:00:00.000

We can use SQL Convert date format to represent this in HH:MM:SS format.
|
1 2 |
DECLARE @StartTime DATETIME= '2019-04-29 20:30:00', @EndTime DATETIME= '2019-04-30 01:00:00'; SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), DATEADD(Minute, DATEDIFF(Minute, @StartTime, @EndTime), 0), 108) AS ElapsedTime; |
It gives the time difference in HH:MM:SS format as shown in the following image.

Specify the SQL SERVER DATEADD function result as a new column
We can use the SQL SERVER DATEADD function to get a new column after adding the required date value. In the following query, we want to add two days in the start date and represent this as a new column.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
DECLARE @StartDate DATETIME= '2013-05-01 11:00.000'; DECLARE @Day INT= 2; SELECT OrderID, LastEditedWhen, DATEADD(day, @Day, LastEditedWhen) AS NewDateColumn FROM [WideWorldImporters].[Sales].[Orders]; |

Scalar sub queries and scalar functions in the DATEADD SQL function
We can use the SQL SERVER DATEADD function with scalar sub queries and scalar functions as well. In the following query, we want to add number of days in max date value of LastEditedWhen in the Sales.orders table.
The first subquery gives the number 16496 and second sub query provides a date. We used the SQL SERVER DATEADD function to add number of days, and we get the following output.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
SELECT DATEADD(dd, ( SELECT TOP 1 BusinessEntityID FROM Person.Person ), ( SELECT MAX(LastEditedWhen) FROM [WideWorldImporters].[Sales].[Orders] )); |

Numeric expressions in the SQL SERVER DATEADD function
We can use numeric expressions as well in SQL SERVER DATEADD function. In the following query, we use a numeric expression to calculate the number and give us an output.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT GETDATE() AS CurrentDate, DATEADD(month, -(12 / 6), GETDATE()) AS ModifiedDate; |

Using DATEADD with the Rank function
We can use the DATEADD SQL function in a rank function as well. We can use it for the number argument. In the following query, you can see Row_Number() function to use number parameter and the values as date parameter.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT OrderID, CustomerID, DATEADD(day, ROW_NUMBER() OVER( ORDER BY CustomerPurchaseOrderNumber), SYSDATETIME()) AS 'Row Number' FROM [WideWorldImporters].[Sales].[Orders]; |

Conclusion
In this article, we explored various uses and examples of the DATEADD SQL function. It allows us to add or subtract datepart values from the specified date. I hope you like this article. Feel free to provide feedback in the comments below.
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023