In this article, I am going to show different methods to identify the SQL Server version number and its edition. Also, I have included the list of known SQL Server version numbers, Service Packs (SP), and Cumulative Updates (CU of MS SQL Server 2019, 2017). I have not included the hotfixes and CUs of SQL Server 2008 R2 and earlier versions.
Before going through the list, let us understand the terms RTM, Service Packs, and Cumulative Update.
RTM: RTM is the acronym of release to manufacturing. It is also known as “going gold”. This term is used when the product is ready to be delivered. This build may be digitally signed that allows users to verify the authenticity of software which they had purchased. RTM is the precedence of the General Availability (GA).
Service Pack: A Service Pack (SP) is a collection of updates, hotfixes or it can be the enhancement to the existing software program. Prior to SQL Server 2017, Microsoft often released service packs based on the issues and feedbacks reported by the users. The service pack is considered a stable version and usually released after one or two years after the product’s release. Service packs are delivered in the single installable package.
Cumulative Update: Cumulative Update is a rollup of multiple hotfixes. Cumulative updates are tested as a group. When you’re building a new SQL Server from scratch, then it is advisable to apply all the recent service packs and cumulative updates.
The following is the list of SQL Server version number, release type, and release date:
SQL Server release | Version Number | Type | Release Date |
SQL Server 2019 | 15.0.2000.5 | RTM | 2019-11-04 |
SQL Server 2017 | 14.0.1000.169 | RTM | 2017-10-02 |
CU 17 |
Cumulative Update (Note: After SQL Server 2017, | 2019-10-08 | |
SQL Server 2016 | 13.0.1601.5 | RTM | 2016-06-01 |
13.0.4001.0 | Service pack 1 | 2016-11-16 | |
13.0.5026.0 | Service pack 2 | 2018-04-24 | |
SQL Server 2014 | 12.0.2000.8 | RTM | 2014-04-01 |
12.0.4100.1 | Service pack 1 | 2015-05-14 | |
12.0.5000.0 | Service pack 2 | 2016-07-11 | |
12.0.6024.0 | Service pack 3 | 2018-10-30 | |
SQL Server 2012 | 11.0.2100.60 | RTM | 2012-03-06 |
11.0.3000.0 | Service pack 1 | 2012-11-06 | |
11.0.5058.0 | Service pack 2 | 2014-06-10 | |
11.0.6020.0 | Service pack 3 | 2015-11-23 | |
11.0.7001.0 | Service pack 4 | 2017-10-05 |
How to identify the SQL Server version number
We can identify the SQL Server version numbers using the following methods:
- SQL Server Management Studio
- SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Windows Registry
- T-SQL query
- SQL Server error log file
- PowerShell command
Method 1 – Identify SQL Server version number using SSMS
First, open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the Database Engine. See the following image:
Right-click on an instance name and select Properties. See the following image:
In the Server Properties dialog box, you can see in opposite to Version. Alternatively, you can see the version in Object Explorer. See the following image:
Method 2 – SQL Server Configuration Manager
To obtain the SQL Server version numbers, open SQL Server Configuration Manager. Click on SQL Server Services. Right-click on SQL Server instance, SQLServer (SQL2017) in my case, and choose Properties. See the following screenshot:
In Properties dialog box, click on the Advanced tab. You can see the SQL Server edition in Stock Keeping Unit Name text box and its version number in the Version text box. See the following image:

Method 3 – Using Windows Registry
To obtain the SQL Server version numbers, open Registry Editor and find the registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\Setup
In the key, the value of PatchLevel indicates the current version number of SQL Server. See the following image:
Method 4 – T-SQL query
To obtain the SQL Server version numbers using T-SQL, execute the following query in the SQL Server Management Studio:
|
1 2 |
SELECT @@version AS [SQL Server version number]; GO |
Following is the output:
Microsoft SQL Server 2017 (RTM) – 14.0.1000.169 (X64)
Aug 22 2017 17:04:49
Copyright (C) 2017 Microsoft Corporation
Developer Edition (64-bit) on Windows 10 Pro 10.0
If you run the same query on Azure instance, the following should be the output:
Microsoft SQL Azure (RTM) – 12.0.2000.8
Oct 12 2019 22:46:48
Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation
Method 5 – SQL Server error log file
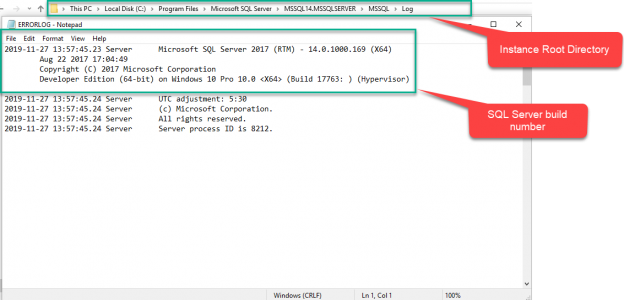
To obtain the SQL Server version numbers from the error log file, open the ERRORLOG.txt file of SQL Server. The default location of the ERRORLOG file is C:\<InstanceRootDirectory>\<MajorBuildVersion>.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Log. I have installed the SQL Server using default settings; therefore, the ERRORLOG file is in C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL14.SQL2017\MSSQL\Log directory.
Open the ERRORLOG file using Notepad or any other text editor, and you can see the SQL Server edition, its version number, and build number on the first line of the ERRORLOG. See the following image:

Method 6 – PowerShell Command
To obtain the SQL Server version numbers using PowerShell, execute the following command:
|
1 |
Invoke-Sqlcmd -ServerInstance "Nisarg-PC" -Query "Select @@version" |
Following is the screenshot of the output:

Conclusion
In this short article, I have explained what RTM, Service Packs, and Cumulative Updates are. I have also included the list of major SQL server versions and their service packs with respective build numbers. Furthermore, I have explained the different methods to identify the SQL Server build number and its edition.
- Different ways to identify and change compatibility levels in SQL Server - July 22, 2024
- Copy SQL Databases between Windows 10 and CentOS using SQL Server data tools - October 19, 2022
- Changing the location of FILESTREAM data files in SQL Database - October 14, 2022