In this 36th article for SQL Server Always On series, we will explore various dynamic management views (DMV’s) for monitoring the AG replicas.
Introduction
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups gives you the ability to safeguard the SQL databases and implements a solution for high-availability and disaster recovery. Once we implement a HADR solution, the database administrator must monitor it. Previously, in the article Monitor SQL Server Always On Availability Groups, we explored the AG dashboard for monitoring AG replica, Availability databases, their synchronization states, Log sequence number (LSN) information, sync lag, estimated recovery time.
AG dashboard presents data in a friendly graphical interface, but if we manage many SQL instances, it is not practicable for us to monitor the AG with the dashboard for all instances manually. We can use various dynamic management views to retrieve the information for us.
In this article, we will explore a few useful dynamic management views for Availability Groups for WSFC in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Prerequisites
You should follow earlier articles in this series (TOC at the bottom) and configure two or more nodes of AG replicas in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
- Windows Failover Cluster name: SQLLABAG
- Primary Replica: SQLLAB2\INST1
- Secondary Replica: SQLLAB3\INST2
- Availability Group: DemoAG ( Owner: SQLLAb3)
- Availability Group: SQLAGDemo ( Owner: SQLLAb2)

Monitor SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Check Availability Groups Feature on a Server Instance
As we know, that we enable the SQL Server Always On feature from the SQL Server Configuration Manager on all participating replicas. To know about the HADR status of any replica, we can query SERVERPROPERTY() on the respective replica. It would return value 1 if we enabled AG feature on that instance.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
:Connect SQLLab2\INST1 Select serverproperty ('IsHadrEnabled') as HADROnSQLLAb2 Go :Connect SQLLab3\INST2 Select serverproperty ('IsHadrEnabled') as HADROnSQLLAb3 Go |

Monitoring Availability Groups on the WSFC Cluster
Traditionally, SQL Server Always On Availability Group was built on a Windows Failover Cluster. To monitor the Windows Failover Cluster for AG replicas, we can use the following views.
- sys.dm_hadr_cluster: We can use this view to get information about the Windows failover cluster
name and its quorum information. For example, in the below screenshot, we look at the following columns
- Windows Failover cluster name ( Cluster_name)
-
quorum_type: It returns the quorum type that we used for this cluster
- 0: Node Majority
- 1: Node and Disk Majority
- 2: Node and File Share Majority
- 3: No Majority:
- 4: Unknown Quorum
- 5:Cloud witness
- Note: You can refer to this article: Windows Failover Cluster Quorum Modes in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups to understand these quorum types in detail
- quorum_type_desc: Description for the Quorum as per the above table
- quorum_state and quorum_state_desc: It returns the status of the quorum
- Normal Quorum
- Forced Quorum
- Unknown Quorum state

- Note: We do not get any row in the output of sys.dm_hadr_cluster, if the Windows failover cluster does not have any Quorum
sys.dm_hadr_cluster_members: We can query this DMV to get a list of Windows failover cluster members in AG replica configuration, their status and the quorum votes
For example, in the screenshot, we can verify the following:
- Our WSFC has two nodes SQLLab2 and SQLLab3
- We have a File share witness configured for the Quorum
- The nodes and Quorum are up
- Each node has a vote in the WSFC configuration
It can show the following values for the cluster member type
- 0 = WSFC node
- 1 = Disk witness
- 2 = File share witness
- 3 = Cloud Witness

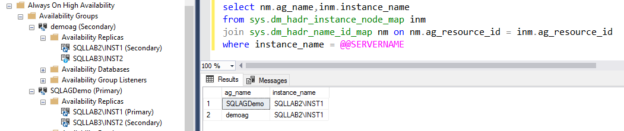
sys.dm_hadr_instance_node_map: This dynamic management view returns the availability replica node information that is joined to the Always On Availability Group
You can join this DMV with the sys.dm_hadr_name to get the SQL instance name for that node
1234select nm.ag_name,inm.instance_namefrom sys.dm_hadr_instance_node_map inmjoin sys.dm_hadr_name_id_map nm on nm.ag_resource_id = inm.ag_resource_idwhere instance_name = @@SERVERNAMEIn the DMV output, you can see the Availability group and the local SQL instance name of the replica.
sys.dm_hadr_name_id_map: It returns the Unique identifier (GUID) for the availability group (ag_id), resource and the WSFC group id. It is helpful to validate the availability groups in case WSFC resources are renamed

Dynamic management view for Monitoring Availability Groups
To monitor the availability group, SQL Server provides the following DMV’s:
- sys.availability_groups: This DMV is useful to check metadata information for the availability groups
A few useful columns in this DMV are as below:
|
1 2 3 4 |
Select name,failure_condition_level, health_check_timeout, automated_backup_preference, automated_backup_preference_desc, db_failover, dtc_support,is_distributed, cluster_type from sys.availability_groups |
Let’s understand the output of sys.availability_groups DMV.
Name: It is the availability group name
failover_condition_level: It shows the predefined failover conditions for an automatic AG failover. It can have the following values:
- 1: Automatic failover occurs if the SQL Services are down or lease expires for the availability group for WSFC because it does not receive any acknowledgement for a server instance
- 2: Either the availability replica is failed, or the health_check_timeout threshold exceeded
- 3: In this default value, automatic failover occurs for critical SQL Server internal errors
- 4: Automatic failover for moderate SQL Server internal errors
- 5: Automatic failover for Exhaustion of SQL Engine worker-threads and unsolvable deadlock
health_check_timeout: SQL Server uses sp_server_diagnostics stored procedure to access the health information of an instance. By default, it waits 30 seconds (30000 milliseconds) before it assumes that the instance is not responding
automated_backup_preference and automated_backup_preference_desc: We can set the preferred note for taking database backups. It can use secondary or primary replica depending upon the configuration
You can get the following values in this column:
- 0: Primary
- 1: Prefer secondary
- 2: Any replica
- Note: You can refer to these articles, Understanding backups on Always On Availability Groups – Part 1, Understanding backups on Always On Availability Groups – Part 2 and SQL Server Always ON Availability Group Log Backup on Secondary Replicas for more details
db_failover: It specifies whether we use Enhanced database failover for database-level health detection. It is an optional configuration. The value 0 shows we have not enabled database level health detection for the availability group
- Note: Refer to the article, Database-level health detection in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for more details
DTC_Support: It specifies if we have enabled per database DTC support for the availability group. We use the distributed transaction coordinator (DTC) for cross-database transactions. In this column, value 0 specifies that we do not use per database DTC support for availability group databases
- Note: You can refer to the article,Database-level health detection in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for more details
is_distributed: SQL Server supports distributed availability groups for configuring AG between multiple clusters, infrastructure sites. If we use a distributed availability group, it shows a value 1 in this column for the corresponding availability group
- Note: Check out the following articles to understand distributed AG’s: An overview of distributed SQL Server Always On Availability Groups and Deploy a Distributed Availability Group
- cluster_type: Once we configure the availability group, we have the option to set the cluster
type as Windows Failover cluster, External or None
- 0: Windows Server Failover Cluster
- 1: External ( for SQL Linux clusters)
- 0: Standalone servers
- sys.dm_hadr_availability_group_states: It gives you information about the primary and secondary
replica for the availability groups along with their health information. In the below table, we get the
following columns in the output:
- Primary replica: It specifies the primary replica for an availability group. As shown below, we have two availability groups. For the first availability group, the primary replica is SQLLAB2\INST1 while the SQLLab3\INST2 is the primary replica for another AG.
Primary_recovery_health: It shows the health of the primary replica for an availability group
- Value 0: In progress
- Value 1: Online
It shows the NULL values for the secondary replica
- Secondary_recovery_health: In this column, it shows the health of the secondary replicas similar to the primary_recovery_health column
- Synchronization_health: It shows the synchronization status between the primary and secondary replica. It can show the following values:
- 0: Not healthy
- 1: Partially healthy ( some replicas are not healthy)
- 2: Healthy( All replicas are in healthy status)
We can join these DMVs together to get detailed information. For example, the below query returns the availability group and their primary replica instance. It joins the sys.dm_hadr_availability_group_states with sys.availability_groups DMV.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT [Groups].[name],primary_replica, synchronization_health_desc FROM sys.dm_hadr_availability_group_states States INNER JOIN sys.availability_groups Groups ON States.group_id = Groups.group_id |
Here, in the output, you get a row for each availability group, their primary replica and the synchronization status.

Conclusion
In this article, we explored the dynamic management views for monitoring Availability Groups on the WSFC Cluster and individual availability group metadata, synchronization status. In the next article, we will explore a few more DMV’s for Monitoring Availability Replicas and Availability Databases. Stay Tuned.
Table of contents
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023