In this 28th article for SQL Server Always On Availability Group series, we explore the high-availability for the SQL Server PolyBase(SSB) external tables using AG groups.
SQL Server PolyBase Introduction
It is a new feature from SQL Server 2016 to query the relational and non-relational database using data virtualization techniques. Previously, to access data from other data sources, we use the linked servers. Suppose you want to access the Oracle database data in your SQL instance. You need to install the OLE DB providers for Oracle and create a linked server to access the data.
The following table discusses the high-level differences in a linked server and SSB feature.
Linked Server | SQL Server PolyBase |
It uses OLE DB providers for connections | It uses ODBC connections. |
A linked server exists at the instance level | It is a database scoped configuration |
It supports both read and write transactions | We can use it for read-only transactions except for HADOOP and data pool insert operation |
Fetching data through linked servers are comparatively slow because these are single-threaded | It supports scale-out configurations and allows multiple threads and faster query execution |
Linked servers are suitable for small row sets | It can be used for queries to process extensive analytic data |
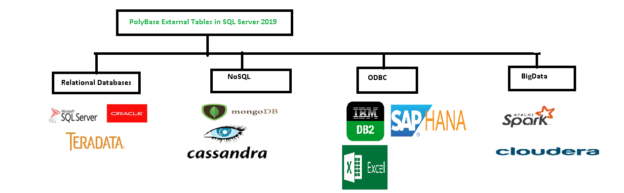
As shown below, we can use SSB with several relational and non-relational databases. You can refer to the PolyBase series for more details.

In this article, we explore the process of using SQL Server PolyBase with the SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Environment details
I have following the AG environment for this article:
- Two Nodes AG with synchronous data commit
- Primary replica: SQLAG1\INST1
- Secondary replica: SQLAG2\INST2
- External table destination: SQL Server ( SQLNode3\INST3)S
Steps to access external table in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Install SSB query service on the primary replica
We need to install the PolyBase feature on both replica nodes. Launch the SQL Server Installation center and add the feature in an existing instance.

Select the option – Add features to an existing instance of SQL Server 2019.

Select the PolyBase Query Service for External Data and move to the next page.

It shows a failure in my lab environment. Click on the Failed to get the error message.

Your SQL instance should be in running state while you add the feature to the instance.

Launch SQL Server Configuration Manager and start the SQL services.
As stated earlier, we can configure SSB in a scale-out group. For this article, we can go ahead with the standalone environment, as shown below.

On the next page, specify the service accounts for SQL Server PolyBase services.
I use the managed service account for these services. You can refer to the article Configure Managed Service Accounts for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups for the managed service accounts configuration.

Verify your instance configuration for Query service.

It is installed successfully on the primary replica.

Install query service on the secondary replica
You can follow the above steps to install the SSB service in the secondary replica.
Enable the SSB feature using the sp_configure command
Once we install the required service, we need to enable the feature using the sp_configure command. You can validate the configuration using the SERVERPROPERTY (‘IsPolyBaseInstalled’) statement. Perform this step on both primary and secondary replica SQL instance.
|
1 2 3 |
exec sp_configure @configname = 'polybase enabled', @configvalue = 1; RECONFIGURE; SELECT SERVERPROPERTY ('IsPolyBaseInstalled') AS IsPolyBaseInstalled; |
Restart Services for SQL Server Polybase(SSB) and SQL Server
Once we enable the SSB feature, restart the SQL Services on both primary and secondary SQL instances. You can use the following steps for restarting SQL Services.
- Change the failover type from Automatic to Manual for the SQL Server Always On Availability Group
- Restart SQL and SSB services on the secondary replica
- Perform a manual failover
- Restart SQL and SSB services on the new secondary replica
- Validate the AG dashboard
Your SQL Service and SSB services should be running on both replicas, as shown below.

Create the database master key on the primary replica
In this step, create a database master key and specify a password for encryption purposes.
|
1 |
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'India@123'; |
Create a database scoped credential
We want to use the [SQLPolybase] database in the primary replica for the external tables. It uses a CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL statement.
|
1 2 3 |
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL credential_name WITH IDENTITY = 'identity_name' [ , SECRET = 'secret' ] |
In the following statement, specify the database name and the user credentials in the IDENTITY section.
|
1 2 |
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL SQLPolyBase WITH IDENTITY = 'SQLPolyBase', Secret ='India@123'; |
Create an external data source
In this article, we use the SQL Server (SQLNode3\INST3) as an external data source. To create an external table, we require an external data source.
In the query, we use the following arguments.
- Location: It specifies the connectivity protocol and the external data source. For SQL Server, it uses [sqlserver] in the location followed by the SQL server
- Connection_Options: For a named instance, we specify the instance name in this argument
- Credentials: Specify the credential we created in the earlier step
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE DS_SQLPolyBase WITH ( LOCATION = 'sqlserver://SQLNode3' , CONNECTION_OPTIONS = 'Server=%s\INST3' , CREDENTIAL = SQLPolyBase ); |
You can refer to Microsoft docs for all supported values in the location argument for various data sources.
Create an external table on the primary replica of SQL Server Always On Availability Group
Before we create an external table, connect to the destination instance, and create a new table with the following script. It creates a table [ABC] and inserts one row in it.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
create table ABC ( id int, [Name] varchar(50) ) GO Insert into abc values(1,'Rajendra') |
Now, connect to the primary replica and create an external table in the [SQLPolybase] database. You need to specify the data source and table location in the external table statement.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [EX_SQLPolybase] ( id [int], [Name] varchar(50) ) WITH (DATA_SOURCE = [DS_SQLPolyBase],LOCATION = N'[MyData].dbo.ABC') |
You get a login failure message for the [SQLPolyBase] user.

In the earlier step, we created a credential and used the [SQLPolyBase] user. We did not create this user in the destination SQL instance SQLNode3\INST3. It uses the credential account to connect with the external data source and create an external table. Connect to the SQLNode3\INST3 and create a login with db_datareader permissions on the [Mydata] database. Now, the external table script executes successfully.

Access the external table similar to a traditional SQL table, and it fetches the records successfully.

Configure the SQL Server PolyBase database in SQL Server Always On Availability Group
In the previous article, we already explored the process of creating a new availability group and adding a database.
You can also add the SSB database following similar steps with a slight difference. In the select database page, it asks for you a password, as shown below.

Earlier, we used the Database Master Key to encrypt the database. We specified a password in the CREATE MASTER Key statement. We need to Specify that password in this wizard to add the database into the availability group.
Click on the password column in front of the database, specify a password, click Refresh to enable the Next page option.

Verify your AG group configurations and proceed.

AG dashboard is healthy for the newly added database, as shown below.

Perform the SQL Server Always On Availability Group failover and access the external table
As shown earlier, we can access the external table from the primary replica SQLAG2\INST2. The external table should be accessible from the new primary replica SQLAG1\INST1 after failover. Perform an availability group failover, as shown below.

Validate that the AG group points to the new primary replica, and the dashboard is healthy as well.

Expand the [SQLPolybase] database and verify you have the external table we created earlier.

Try to access the external table from the new primary replica. It complains about the database master key.

To create a database master key on the new primary replica and save the secret in the credential, we use the sp_control_dbmasterkey_password stored procedure.
In this command, specify the same database name, master key password ( same password we used in the primary replica).
|
1 2 |
Exec sp_control_dbmasterkey_password @db_name=N'SQLPolybase', @password=N'India@123', @action=N'add' |
Now, if I try to access the external table, I get a different error from the new primary. It gave an internal query processor error/

The error comes if the SQL Server PolyBase data movement service is stopped. I noticed that if I start this service, it stops again after some time. It was causing an error in accessing the external table.

To investigate the error, go to your instance Log-> PolyBase folder and open the *_DMS_movement log file.

In this error log, it stats about the shared memory segment.
In the SQL Server Configuration Manager, go to protocols. Here, it shows the shared memory protocol in a disabled state.

Enable the Shared Memory protocol, as shown below.

The data movement service starts, and it does not stop automatically now.

You can access the external table from the new primary replica as well.

Conclusion
In this article, we explored the integration of SQL Server PolyBase and SQL Server Always On Availability Groups. It is an excellent feature to access various data sources. We used SQL Server as an external data source in this article. You can explore it with data sources such as Oracle, Teradata.
Table of contents
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023