In this 21st article on SQL Server Always On Availability Group series, we will explore the AG dashboard and its various options for monitoring purposes.
Introduction
Monitoring is an essential and critical aspect of database professionals. You can identify potential issues, rectify them proactively. As you configure SQL Server Always On Availability Group for the high availability and disaster recovery solution in SQL Server, you must monitor them along with SQL Server instance. Suppose you configured Synchronous replicas and it is not healthy, it might cause various issues for you such as transaction log growth, inconsistent data at secondary replica (in case of readable secondary), risk of losing data in case of any issue at the primary replica.
SQL Server management studio provides an in-built AG dashboard to monitor AG replicas, its synchronizations, and various other factors to monitor. In this article, we will explore the AG dashboard.
Requirements
- You should set up SQL Server Always On Availability Group before going further in this article. You can refer to series articles (TOC at the bottom) for this purpose
- You should also use the latest version of SQL Server Management Studio to explore all AG dashboard options. Download the latest version 18.6 (at the time of writing this article) using Microsoft docs

Explore the AG dashboard for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Connect to the primary replica, right-click on the availability group folder and click on the Show Dashboard.

Here, it shows all configured availability groups in your SQL instance. A green tick for each availability group shows it is in a healthy state.
To launch the dashboard for a particular availability group, click on its name and you get the corresponding dashboard.
The AG dashboard has the following sections:

Availability group details
This section gives high-level information for the availability group.
- Availability group name, current owner and replica role: It shows the AG name, the instance from which we launched dashboard and its role (primary or secondary). In this example, it shows the availability group [SQLLogShipAG] launched from [SQLAG1\INST1] instance and it is a primary replica for this AG
Availability group state: It shows the state of the AG. Currently, it is showing healthy. In case of any issues, it shows the status like below
- Failover Mode: We can have manual or automatic failovers in an SQL Server Always On
Availability Group. The failover mode also depends on the availability mode
- Asynchronous mode: Manual failover
- Synchronous mode: Manual and automatic failover
Cluster State: It shows the Windows cluster name and the quorum configuration. In my case, the failover cluster name is [SQLCluster2]
- Cluster type: Usually, cluster type is Windows Server Failover Cluster
Availability replicas
In the availability replicas, you get the following details:
- AG replicas: It shows the configured AG replicas for the availability group. In my example, it shows two AG replicas SQLAG1\INST1 & SQLAG2\INST2
- Role: It shows the replica role in the AG group. You can have only one primary replica and multiple secondary replicas (depending upon SQL Server versions). Here, SQLAG1\INST1 is the primary replica
-
Availability mode: We can have synchronous or asynchronous availability mode for AG replica. Here, it shows the Synchronous availability mode
- Seeding Mode: We can have manual or automatic seeding modes for an availability group
- Manual: It is the default behavior. In this mode, we need to manually restore the database copy on the secondary replica before configuring AG
- Automatic: It is available from SQL Server 2016. We can use automatic seeding for initial data synchronization. Refer to Automatic Seeding in Always On Availability Groups for more details
- Synchronization State: The synchronization state depends upon the availability mode
- Synchronous availability mode: Synchronized state
- Asynchronous availability mode: Synchronizing state
In the above image, we see AG is in the Synchronized state due to the synchronous commit availability mode. In case you change the availability mode to Asynchronous mode (using AG properties), it immediately changes state to the Synchronization state.
We can add more details to the AG dashboard availability replica section. Click on the Add/Remove columns, and you get a list of options. Currently, it shows a few options in the default view, and you can see a tick for those options.
For example, in the below screenshot, I added the Primary connection mode, secondary connection mode, Quorum votes and member state.
- Primary Connection Mode: It shows the connections for the primary AG replica
- Secondary Connection Mode: It shows the connections for the secondary AG replica. We can configure the secondary replica to disallow all connections
- Quorum votes: It shows the votes held by the replica
Group by: Availability group replica details
By default, AG dashboard groups the information as per the availability replicas as shown below.
In this section, you get details for the individual AG replicas.
You can change the group by selection for availability databases and synchronization state.
Group by: availability databases: It groups the details as per the availability database.
Group by: synchronization state: It groups the details as per their synchronization state.
By default, it also gives details for the failover readiness and existing issues. You should monitor the failover readiness before initiating an AG failover to ensure you do not lose any data.
Similar to the availability replica section, we can more details here as well.
It gives LSN (log sequence number) information for all AG replica using the *LSN options such as End of Log LSN, Recovery LSN, Truncation LSN. You can refer to Data synchronization in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups and Measuring Availability Group synchronization lag for more details.
You can also estimate the recovery time and data loss using this dashboard. In my case, it does not have any data loss.
AG dashboard also gives information a few counters to monitor AG performance. These counters are Log send queue size (KB), Log send rate (KB\sec), Redo queue size (KB), Redo Rate (KB\sec). You can refer to Microsoft docs for this counter information.
Auto-refresh
By default, SSMS refreshes the AG dashboard every 30 seconds. At the top, the dashboard shows the last refresh time.
We can pause the auto-refresh from the dashboard. As shown below, the AG dashboard refresh is stopped.
To change the refresh interval, go to Tools-> Options-> SQL Server Always On-> Dashboard and modify the refresh interval (in seconds) as per your requirements.

SQL Server Always on extended events
SQL Server automatically configures an extended event AlwaysOn_Health to monitor various events in SQL Server Always On Availability Group. The AG dashboard gives a shortcut View always-on health events to open the event file and view the records.

View Cluster quorum information
We can view failover cluster quorum information such as cluster name, quorum model, member state and vote counts using the AG dashboard Cluster Quorum information for SQL Server Always On Availability Group.

Collect latency data
We can use this option to collect the latency bottleneck information between the AG replicas. Once you click on the collect latency data, it creates a SQL agent job AlwaysOn_Latency_Data_Collection and collects the relevant data for you.
SQL Agent service should be running so that it can create and execute the job as shown below.

Now, you can navigate to the availability group and view the reports.
- Primary replica latency ( from primary replica instance)
-
Secondary replica latency( from secondary replica instance)
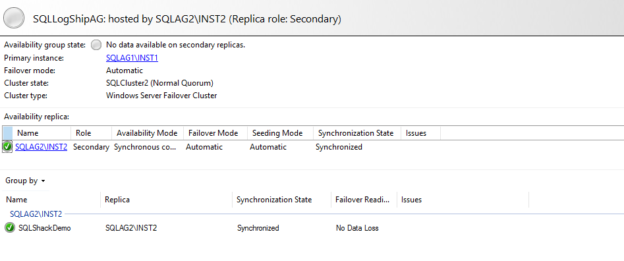
You should launch the AG dashboard from the primary replica. In case you launch it from the secondary replica, you don’t get many details.
As we can see in the below screenshot, it does not give the health status of the availability group. Similarly, you only get details for the secondary replica.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned the SQL Server Always On Availability Group dashboard and its various option. You can monitor AG using T-SQL, PowerShell scripts along with the third-party tools. You can use any monitoring medium as per your comfort level.
Table of contents
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023