In this article, we will learn the basics of the view concept in SQL Server and then explore methods to create a view in SQL using T-SQL and SQL Server Management Studio.
Definition
Most of the time, views can be defined as “virtual or logical” tables, but if we expand this basic definition we can understand the views more clearly. A view is a query that is stored in the database and returns the result set of the query in which it is defined. The query that defines the view can be composed of one or more tables. A view returns column or columns of the query in which it is referenced. However, we need to underline a significant point about the views, a simple view never stores data, merely it fetches the results of the query in which it is defined.
Query simplicity is the main advantage that comes first to our minds related to the views. We can encapsulate the complex query scripts into views so that we can use the views instead of the complex query codes. On the other hand, views can provide us to handle security issues. Each user can be granted authorization to see specific data through the views so we don’t have to struggle to give permissions to users for multiple-tables.
How to create a view in SQL with a single table
In this section, we will learn the syntax of the views. The following statement defines the syntax of a view:
|
1 2 3 4 |
CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition; |
At first, we need to specify the CREATE VIEW statement and then we have to give a name to the view. In the second step, we define the SELECT statement after the AS keyword. The following example will create a view that will be named as VProductSpecialList. VProductSpecialList view fetches data from the Product table and it only returns the ProductID, Name and ProductNumber columns of the Product table:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
CREATE VIEW VProductSpecialList AS select p.ProductID AS [ProductIdNumber] , p.Name AS [ProductName], p.ProductNumber [ProductMainNumber] from [Production].[Product] p WHERE ProductID >900 |
After the creation of the view, we can retrieve data using a simple SELECT statement. The following example shows how to fetch data from the VProductSpecialList view:
|
1 |
SELECT * FROM VProductSpecialList |
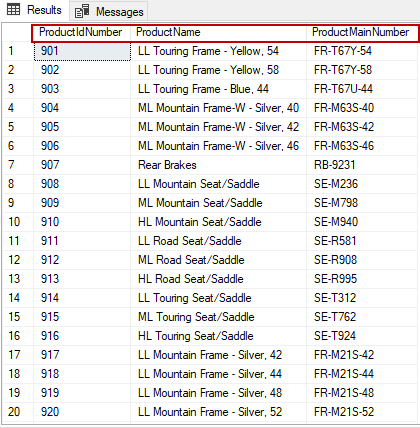
As you can see above, the column names have been replaced with aliases which are defined in the query definition of the view. In addition, the data which is fetched by the view is filtered according to the criteria of the WHERE statement.
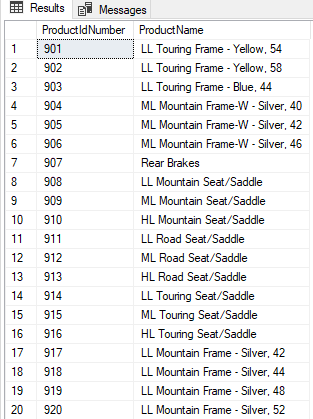
For the different circumstances, we may need some particular columns of the view for this we can only use these column names in the SELECT statement:
|
1 |
SELECT ProductIdNumber,ProductName FROM VProductSpecialList |
How to create a view in SQL with multiple-tables
In the previous example, we created a view for a single table but we can also create a view for joined multiple tables. In the following example, we will achieve this idea:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
CREATE VIEW VProductDetailList AS select p.ProductID AS [ProductIdNumber] , p.Name AS [ProductName], p.ProductNumber [ProductMainNumber], pm.Name as [ProductModelName] from [Production].[Product] p INNER JOIN [Production].[ProductModel] pm ON p.[ProductModelID] = pm.[ProductModelID] WHERE ProductID >900 GO SELECT * FROM VProductDetailList WHERE ProductModelName='LL Mountain Frame' |
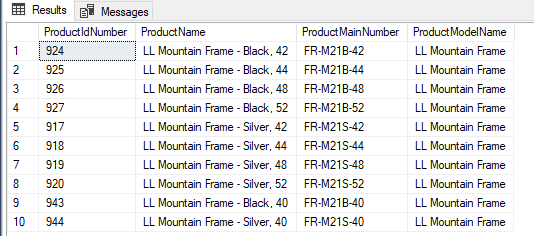
The above example demonstrated how to create a view from multiple tables and then we saw, how we fetch data from this view and we also filtered fetched data of the VProductDetailList view.
How to create a view in SQL via SSMS
SQL Server Management Studio AKA SSMS is the most popular and powerful tool to manage, configure, administer and do other uncountable operations in SQL Server. So, we can create a view through SSMS.
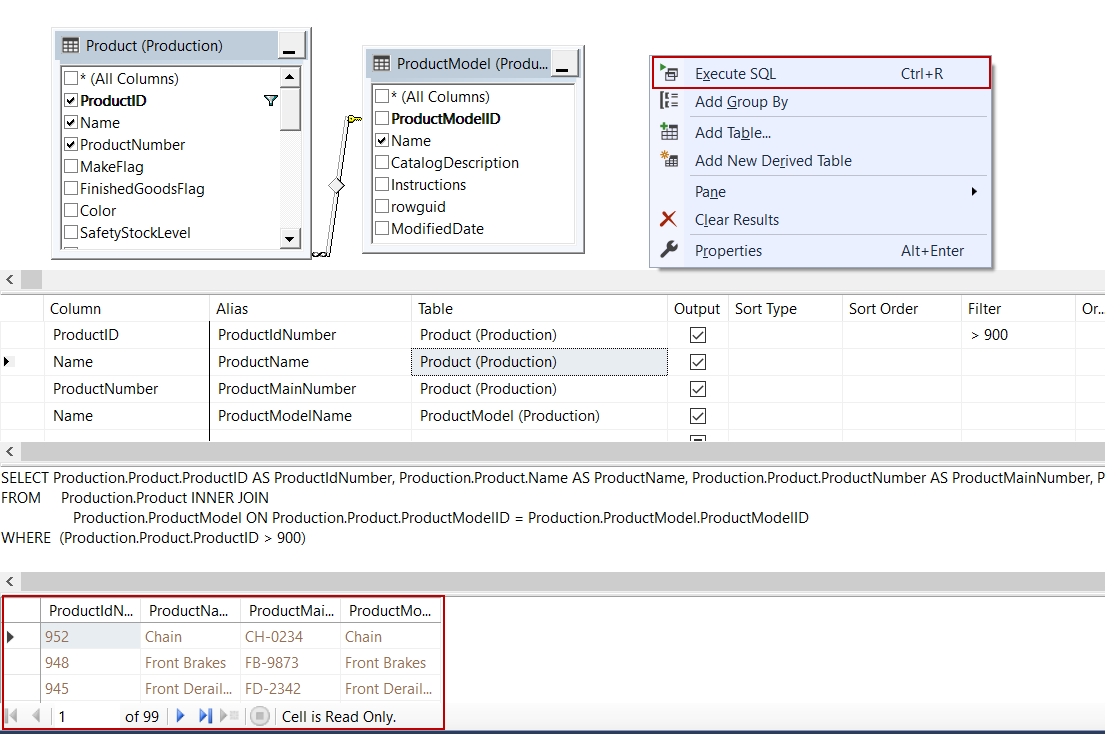
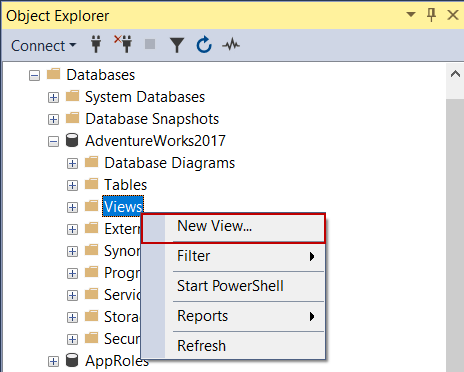
We will launch SSMS and login the database with any user who granted to create a view. Expand the database in which we want to create a view. Then right-click on the Views folder and choose the New View option:
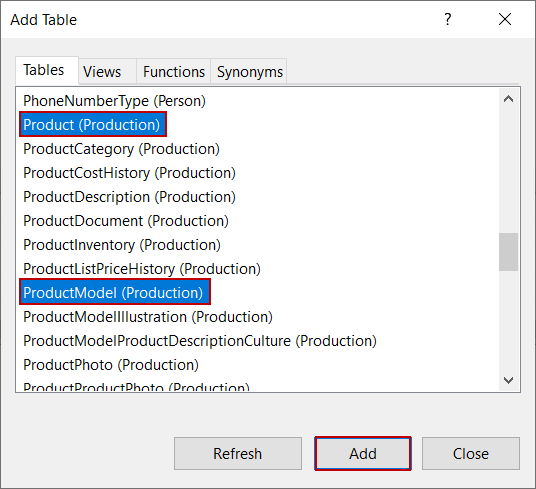
The Add Table dialog appears on the screen. On this screen, we will find and then select the Product and ProductModel tables and click Add:
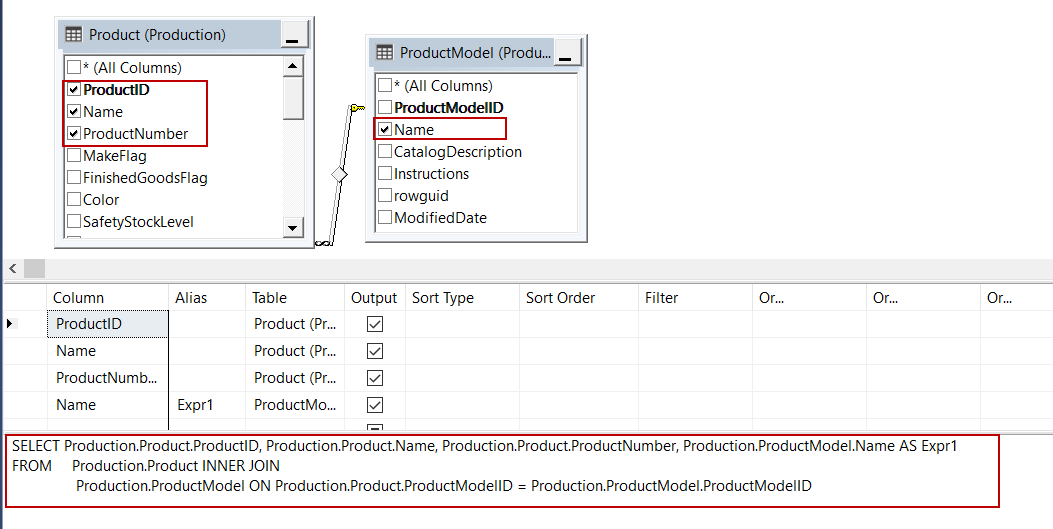
The relations between the tables are automatically detected and created by SSMS and at the same time, the view query will be generated in the query tab automatically:
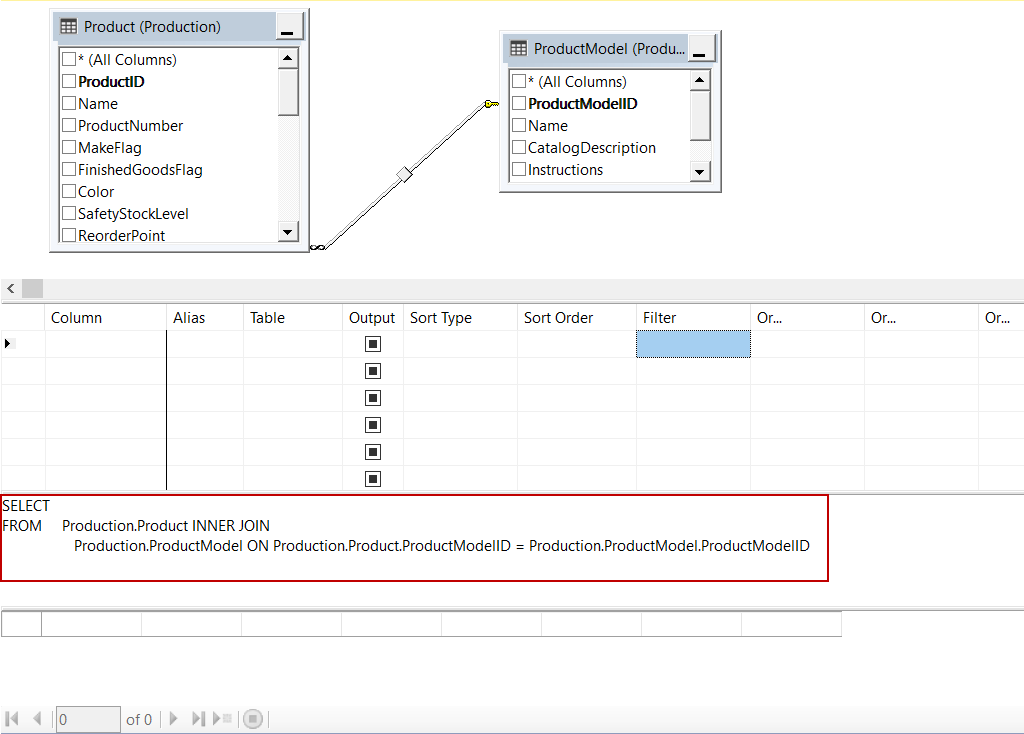
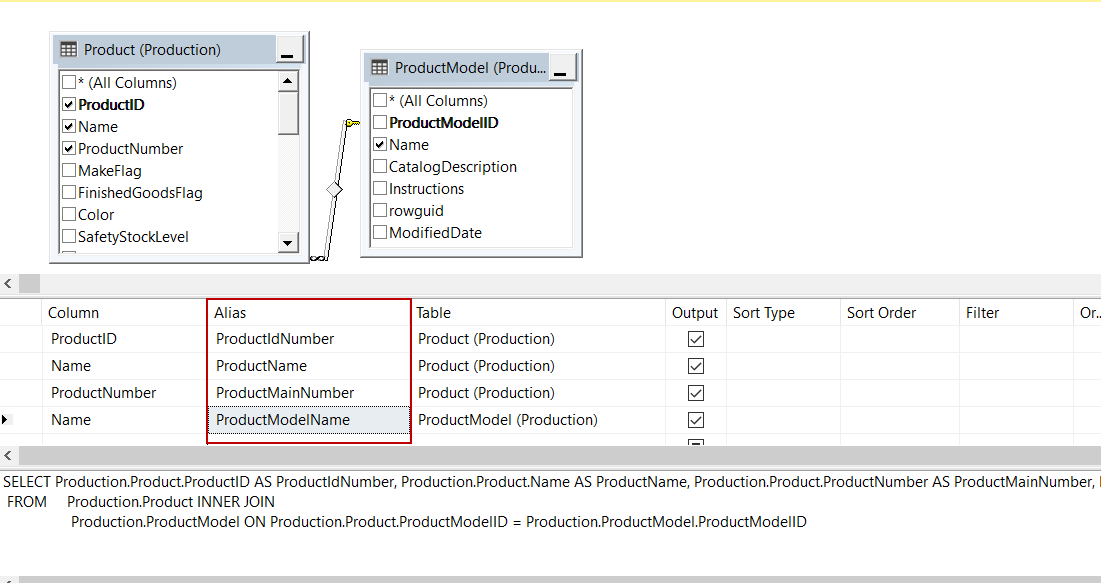
In this step, we will check in the necessary columns for the view. If we want to select all column names of the table we can check in the * (All Columns) option. We will check in ProductId, Name, ProductNumber columns in the Production table and Name column in ProductModel table. We can observe the query changing when we check in the names of the columns in tables:
We will set aliases of the columns:
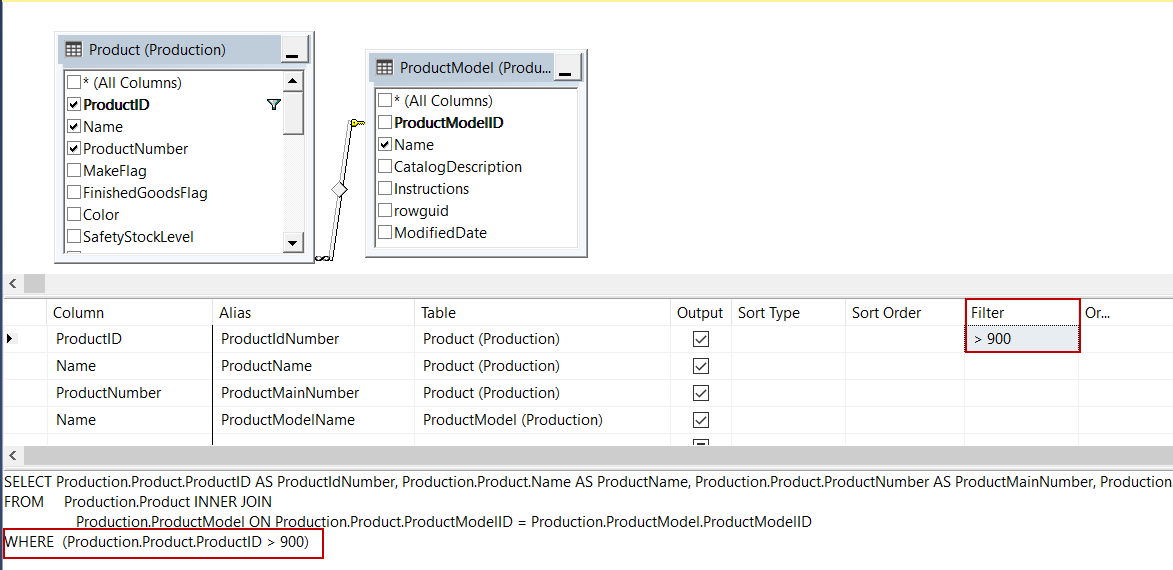
We will set the filter criteria and it will be automatically added into the WHERE condition of the query:
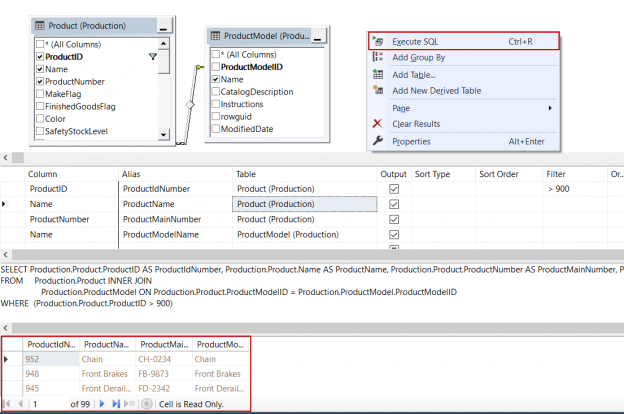
We can right-click in the table panel so that we can execute the view. The result data shows at the bottom of the screen:
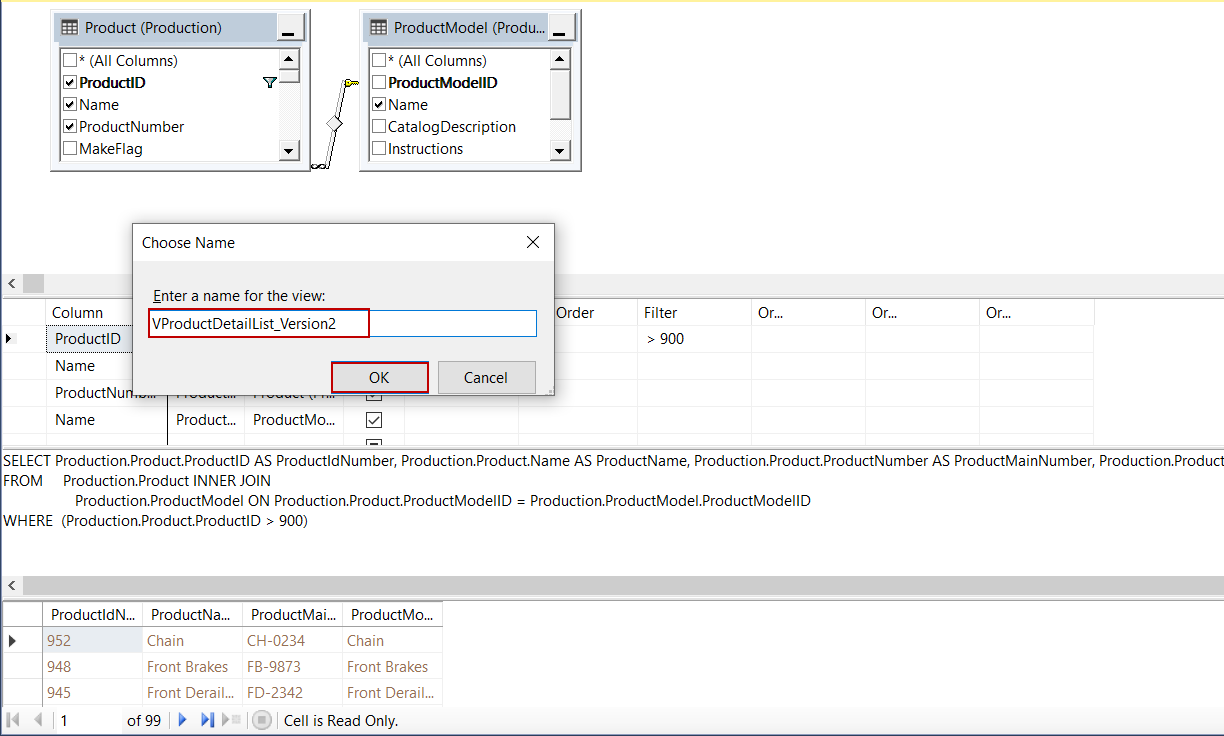
Finally, we will press CTRL+S keys in order to save the view and give a name to the view and click OK:
The created view can be found under the Views folder:
How to drop a view in SQL
In order to delete a view in a database, we can use the DROP VIEW statement. However, the DROP VIEW statement may return an error if the view we want to delete do not exists in the database. To overcome this issue, we can use the IF EXISTS keyword with the DROP VIEW statement. The following script deletes the vProductSpecialList from the database:
|
1 |
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS [VProductSpecialList] |
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the view notion in SQL and then we learned how to create a view in SQL with two different methods. In the first one, we used the T-SQL method and the second one we used SQL Server Management Studio.
See more
ApexSQL Complete is a SQL code complete tool that includes features like code snippets, SQL auto-replacements, tab navigation, saved queries and more for SSMS and Visual Studio

- SQL Performance Tuning tips for newbies - April 15, 2024
- SQL Unit Testing reference guide for beginners - August 11, 2023
- SQL Cheat Sheet for Newbies - February 21, 2023