Bringing impactful analysis into a data always comes with challenges. In many cases, we rely on automated tools and techniques to overcome many of these challenges.
In this article, we’ll describe a simple task to validate the table (row count only) between the databases on different SQL instances. For our use case, let us consider a scenario involving transactional replication, as a good practice; it is required to perform data validation test between Publisher and Subscriber databases to validate the integrity of our replication process. It is quite evident that a simple validation process helps to identify the state of the subscriber. If there is a difference in the data, it’s pretty much advised to re-initialize the subscription with the latest snapshot.
Introduction
There are several reasons why we might need to consider table comparison. In a robust replication system, one has to audit the integrity of the data. The audit process ensures that the data produced from various automation tools or batch jobs are correct. Also, when you pass the values on the subscription database, it should return the near-production values.
SQL Server Transactional replication has an option to validate the data at the Subscriber with data at the Publisher. Validation can be performed for specific subscriptions or for all subscriptions to a publication. We can specify the ‘Row count only’ option as the validation type and the Distribution Agent will validate data when it runs for the next time. But if we create our own replication scenario, independent of SQL Server replication, we will want to duplicate this feature to ensure our databases are in sync
In this article, we will simulate the “Row count only” process of Microsoft’s SQL Server database replication solution. In this validation process, the tables are compared for a number of rows between Publisher and Subscriber but it does not validate the content of the data. It is considered as a lightweight approach to validate the number of rows between publisher and subscriber.
Objective
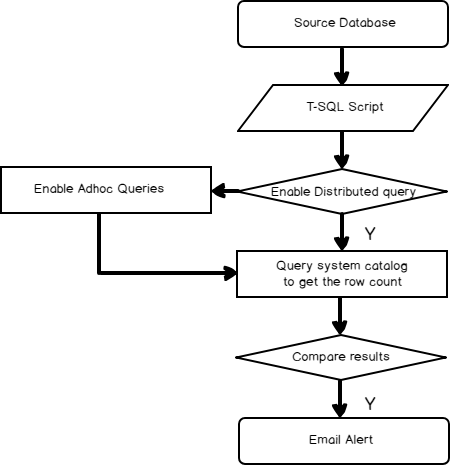
Implement “Row count only” process to compare a number of rows between Publisher and subscriber database and send out an alert email when the process finds a difference in the numbers of the rows between the tables.Overview of the implementation

Automation
The steps to setup automation are as follows:
-
Enable “Ad Hoc Distributed Queries” advanced configuration option
123456EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1RECONFIGUREGOEXEC sp_configure 'ad hoc distributed queries', 1RECONFIGUREGO -
Use OPENROWSET to query a remote SQL instance. To use the OPENROWSET ad hoc method, provide all the data source information in the connection string. For example, to run a remote query on XYZ server
- Use SQLNCLI provider
- Pass the <ServerName> as an input value to Server parameter
- Set the connection type. In this case, it’s trusted. So, its set to ‘yes’
- Pass T-SQL string
12SELECT q.*FROM OPENROWSET('SQLNCLI', 'Server=hqdbt01\SQL2017;Trusted_Connection=yes;', 'select * from [WideWorldImporters].[Sales].[Invoices]') as q;
-
Getting the row count of tables in the source database
There are several different ways get the row-count of the table in a database, but probably the fastest technique to get row count is by using system view sys.partitions.
Using the following SQL, the row count of the table is listed.
12345678910111213141516SELECTMax(@@SERVERNAME) ServerName,Max(DB_NAME(DB_ID())) DatabaseName,sch.name AS SchemaName,st.Name AS TableName,SUM(CASEWHEN (p.index_id < 2) AND (a.type = 1) THEN p.rowsELSE 0END) AS RowsFROM sys.partitions pINNER JOIN sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_idINNER JOIN sys.tables st ON st.object_id = p.object_idINNER JOIN sys.schemas sch ON sch.schema_id = st.schema_idGROUP BY st.name, sch.name -
Getting the row count of tables in the remote database
In order to do this, the OpenRowSet method is used. You can refer step2 for more information.
123456789101112131415161718SELECT a.*FROM OPENROWSET('SQLNCLI', 'Server=hqdbt01\SQL2017;Trusted_Connection=yes;','SELECTMax(@@SERVERNAME) ServerName,Max(DB_NAME(DB_ID(''WideWorldImporters''))) DatabaseName,sch.name AS SchemaName,st.Name AS TableName,SUM(CASEWHEN (p.index_id < 2) AND (a.type = 1) THEN p.rowsELSE 0END) AS RowsFROM WideWorldImporters.sys.partitions pINNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_idINNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.tables st ON st.object_id = p.Object_IDINNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.schemas sch ON sch.schema_id = st.schema_idGROUP BY st.name, sch.name') AS a; -
Compare the number of rows between source and Target
The step 3 sets up first part of the data set and step 4 defines the second data set. Both the result sets are captured in a table variable named @sourcedatabase and @targetDatabase.
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455DECLARE @SourceDatabase table(Instance sysname,DB varchar(100),SchemaName VARCHAR(100),TableName VARCHAR(100),Rows INT)INSERT INTO @SourceDatabaseSELECTMax(@@SERVERNAME) ServerName,Max(DB_NAME(DB_ID())) DatabaseName,sch.name AS SchemaName,st.Name AS TableName,SUM(CASEWHEN (p.index_id < 2) AND (a.type = 1) THEN p.rowsELSE 0END) AS RowsFROM sys.partitions pINNER JOIN sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_idINNER JOIN sys.tables st ON st.object_id = p.object_idINNER JOIN sys.schemas sch ON sch.schema_id = st.schema_idGROUP BY st.name, sch.nameDECLARE @TargetDatabase table(Instance sysname,DB varchar(100),SchemaName VARCHAR(100),TableName VARCHAR(100),Rows INT)INSERT INTO @TargetDatabaseSELECT a.*FROM OPENROWSET('SQLNCLI', 'Server=hqdbt01\SQL2017;Trusted_Connection=yes;','SELECTMax(@@SERVERNAME) ServerName,Max(DB_NAME(DB_ID(''WideWorldImporters''))) DatabaseName,sch.name AS SchemaName,st.Name AS TableName,SUM(CASEWHEN (p.index_id < 2) AND (a.type = 1) THEN p.rowsELSE 0END) AS RowsFROM WideWorldImporters.sys.partitions pINNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_idINNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.tables st ON st.object_id = p.Object_IDINNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.schemas sch ON sch.schema_id = st.schema_idGROUP BY st.name, sch.name') AS a; -
Join the two table variable using schema and tablename columns
1234567891011121314151617181920212223selects.Instance SourceInstance,t.Instance TargetInstance,s.DB SourceDatabase,t.DB TargetDatabase,s.SchemaName SourceSchemaName,t.SchemaName TargetSchemaName,s.TableName SourceTableName,t.TableName TargetTableName,s.rows as SourceRowCount,t.rows as DestRowCount,case when s.rows>t.rows then s.Rows-t.Rows else t.Rows-s.Rows end 'Missing Rows',case when s.rows>t.rows then '<='when s.Rows=t.Rows then '='else '=>' end 'Comparison'from@SourceDatabase s, @TargetDatabase twheres.SchemaName=t.SchemaName ands.TableName = t.TableName-- and--s.rows!=t.rowsYou can see the difference in number of rows in the following output
-
Prepare email alert
In this section, Let us make the necessary arrangement to wrap the values in the table data <TD> tag. This is the format needed to build HTML table tags. In this case, td is used as the column alias for all columns and specified by the ‘tr’ as the root element for each row. Then the concatenated output is sent as an HTML body using sp_send_dbmail option.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162IF((Select count(*) from@SourceDatabase s, @TargetDatabase twheres.SchemaName=t.SchemaName ands.TableName = t.TableNameands.rows!=t.rows)>0)beginDECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(MAX) ;SET @tableHTML =N'<H1>Row Comparison Report</H1>' +N'<table border="1">' +N'<tr><th>[Source Instance]</th><th>[Target Instance]</th><th>[Source DB] </th><th>[Target DB]</th><th>[Source Schema]</th><th>[Target Schema]</th><th>[Source Table]</th><th>[Target Table]</th><th>[Source RowCount]</th><th>[Target RowCount]</th><th> [Missing Rows]</th><th> [Compariosn]</th></tr>' +CAST ( (selecttd=s.Instance ,' ',td=t.Instance ,' ',td=s.DB,' ',td=t.DB, ' ',td=s.SchemaName,' ',td=t.SchemaName,' ',td=s.TableName,' ',td=t.TableName, ' ',td=cast(s.rows as varchar(10)),' ',td=cast(t.rows as varchar(10)), ' ',td=case when s.rows>t.rows then cast((s.Rows-t.Rows) as varchar(10))else cast((t.Rows-s.Rows) as varchar(10)) end ,' ',td=case when s.rows>t.rows then '<='when s.Rows=t.Rows then '='else '=>' end, ' 'from@SourceDatabase s, @TargetDatabase twheres.SchemaName=t.SchemaName ands.TableName = t.TableNameands.rows!=t.rowsFOR XML PATH('tr'), TYPE) AS NVARCHAR(MAX) ) +N'</table>' ;EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients='pjayaram@SQL.com',@subject = 'Row Comparison Report',@profile_name='PowerSQL',@body = @tableHTML,@body_format = 'HTML' ;END
Output
Wrap Up
So far, we’ve seen the steps to simulate “Row count only” option. In reality, there is no ideal method can be used to compare the results. If you’re working one of the very few tables, then tablediff is also an option. Also, you could rely on 3rd party tools such as ApexSQL Diff data compare option to validate a number of rows between the databases. I would leave this option open. What are your favorite methods? Please leave the feedback input in comments…
That’s all for now…
Appendix
Another solution we can use is tablediff utility. For example, if you want to compare two tables (ExportALLCities) from two databases on two different servers, you run the following command
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\140\COM>tablediff -sourceserver hqdbt01 -sourcedatabase WideWorldImporters -sourcetable ExportALLCities -destinationserver HQDBT01\SQL2017 -destinationdatabase WideWorldImporters -destinationtable ExportALLCities
T-SQL Script
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 |
EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1 RECONFIGURE GO EXEC sp_configure 'ad hoc distributed queries', 1 RECONFIGURE GO DECLARE @SourceDatabase table ( Instance sysname, DB varchar(100), SchemaName VARCHAR(100), TableName VARCHAR(100), Rows INT ) INSERT INTO @SourceDatabase SELECT Max(@@SERVERNAME) ServerName, Max(DB_NAME(DB_ID())) DatabaseName, sch.name AS SchemaName, st.Name AS TableName, SUM( CASE WHEN (p.index_id < 2) AND (a.type = 1) THEN p.rows ELSE 0 END ) AS Rows FROM sys.partitions p INNER JOIN sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_id INNER JOIN sys.tables st ON st.object_id = p.object_id INNER JOIN sys.schemas sch ON sch.schema_id = st.schema_id GROUP BY st.name, sch.name DECLARE @TargetDatabase table ( Instance sysname, DB varchar(100), SchemaName VARCHAR(100), TableName VARCHAR(100), Rows INT ) INSERT INTO @TargetDatabase SELECT a.* FROM OPENROWSET('SQLNCLI', 'Server=hqdbt01\SQL2017;Trusted_Connection=yes;', 'SELECT Max(@@SERVERNAME) ServerName, Max(DB_NAME(DB_ID(''WideWorldImporters''))) DatabaseName, sch.name AS SchemaName, st.Name AS TableName, SUM( CASE WHEN (p.index_id < 2) AND (a.type = 1) THEN p.rows ELSE 0 END ) AS Rows FROM WideWorldImporters.sys.partitions p INNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_id INNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.tables st ON st.object_id = p.Object_ID INNER JOIN WideWorldImporters.sys.schemas sch ON sch.schema_id = st.schema_id GROUP BY st.name, sch.name') AS a; select s.Instance SourceInstance, t.Instance TargetInstance, s.DB SourceDatabase, t.DB TargetDatabase, s.SchemaName SourceSchemaName, t.SchemaName TargetSchemaName, s.TableName SourceTableName, t.TableName TargetTableName, s.rows as SourceRowCount, t.rows as DestRowCount, case when s.rows>t.rows then s.Rows-t.Rows else t.Rows-s.Rows end 'Missing Rows', case when s.rows>t.rows then '<=' when s.Rows=t.Rows then '=' else '=>' end 'Comparison' from @SourceDatabase s, @TargetDatabase t where s.SchemaName=t.SchemaName and s.TableName = t.TableName and s.rows!=t.rows IF((Select count(*) from @SourceDatabase s, @TargetDatabase t where s.SchemaName=t.SchemaName and s.TableName = t.TableName and s.rows!=t.rows)>0) begin DECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(MAX) ; SET @tableHTML = N'<H1>Row Comparison Report</H1>' + N'<table border="1">' + N'<tr><th>[Source Instance]</th> <th>[Target Instance]</th> <th>[Source DB] </th> <th>[Target DB]</th> <th>[Source Schema]</th> <th>[Target Schema]</th> <th>[Source Table]</th> <th>[Target Table]</th> <th>[Source RowCount]</th> <th>[Target RowCount]</th> <th> [Missing Rows]</th> <th> [Compariosn]</th> </tr>' + CAST ( ( select td=s.Instance ,' ', td=t.Instance ,' ', td=s.DB,' ', td=t.DB, ' ', td=s.SchemaName,' ', td=t.SchemaName,' ', td=s.TableName,' ', td=t.TableName, ' ', td=cast(s.rows as varchar(10)),' ', td=cast(t.rows as varchar(10)), ' ', td=case when s.rows>t.rows then cast((s.Rows-t.Rows) as varchar(10))else cast((t.Rows-s.Rows) as varchar(10)) end ,' ', td=case when s.rows>t.rows then '<=' when s.Rows=t.Rows then '=' else '=>' end, ' ' from @SourceDatabase s, @TargetDatabase t where s.SchemaName=t.SchemaName and s.TableName = t.TableName and s.rows!=t.rows FOR XML PATH('tr'), TYPE ) AS NVARCHAR(MAX) ) + N'</table>' ; EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients='pjayaram@SQL.com', @subject = 'Row Comparison Report', @profile_name='PowerSQL', @body = @tableHTML, @body_format = 'HTML' ; END |
Table of contents
See more
- Stairway to SQL essentials - April 7, 2021
- A quick overview of database audit in SQL - January 28, 2021
- How to set up Azure Data Sync between Azure SQL databases and on-premises SQL Server - January 20, 2021