Introduction
PowerShell is a shell used specially to automate administrative tasks.
It is an incredible tool used to programmatically automate tasks like SQL Server tasks, Exchange tasks, Windows tasks, etc. It is very useful to integrate different Microsoft and sometimes non-Microsoft programs.
In this new tutorial, we will show how to install PowerShell for Azure and then how to use it. We will create some databases, edit database properties and retrieve database information using PowerShell.
Figure 1. PowerShell and Azure
Requirements
- An Azure subscription.
- A local machine with Windows installed.
Getting started
In your local machine, we will first install Microsoft Azure PowerShell. You can download the installer here.

Figure 2. Downloading the installer.Once you have the installer, a configuration Windows will be displayed.

Figure 3. Time remaining to configure the Microsoft Web Installer.The Web Platform Installer will initiate the Microsoft Azure PowerShell wizard.
As any installer, it requires you to accept the terms and conditions.

Figure 5. Microsoft Agreement.Once it is installed, it will ask to restart the machine. You can restart immediately or later.

Figure 6. The restart message.On the Windows Start Menu, open the Microsoft Azure PowerShell. This is the command line used to automate some tasks.

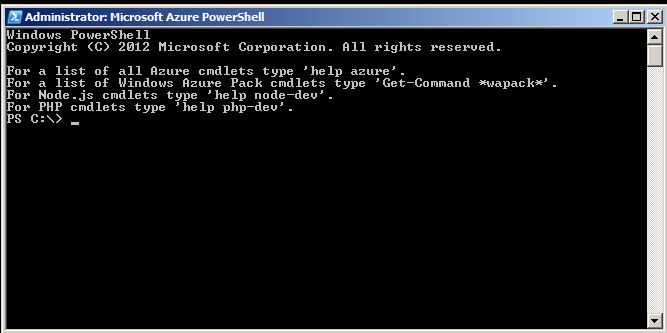
Figure 7. The Microsoft Azure PowerShellThe Microsoft Azure PowerShell will be similar to this screenshot.

Figure 8. The PowerShell Command lineThe PowerShell for Azure is different from the PowerShell installed by default in Windows 7, 8 or 2008 or 2012. It has exclusive commands (cmdlets) for Azure activities.
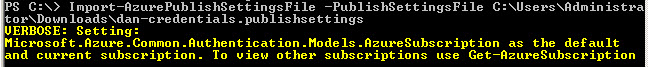
Once the Microsoft Azure PowerShell is installed, you can connect to your Azure Subscription using the Get-AzurePublishSettingsFile.
➜ Get-AzurePublishSettingsFileThis command is used to create a file to connect to your Azure Portal and automate tasks there.

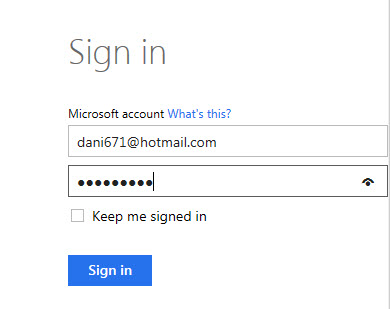
Figure 9. The Get-AzurePublishSettingsFile command.The command will prompt your browser in the Azure Portal. Choose the account than you want to use.

Figure 10. The Windows to the Azure Portal section to select an accountSpecify your login and password and Sign in.

Figure 11. The Login and Password to Sign inA subscription file will be downloaded. This file will be used to connect to Azure.
-
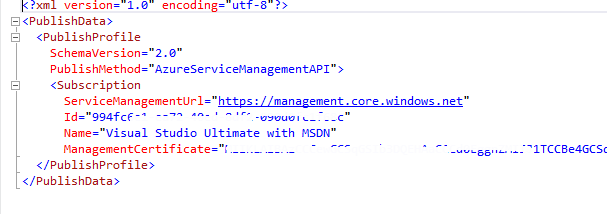
The subscription file generated is an xml file similar to this one.

Figure 13. The Published File. Once the file is generated, you can import the file using the Import-AzurePublishSettingsFile command like this:
>Import-AzurePublishSettingsFile –PublishSettingsFile
c:\yourpath\yourpublishfilename.publishsettings
Figure 14. The message after importing the file.With the import command you can now connect to your Azure Subscription.
You just need to specify the path of the subscription file.One good command to start it the get-azuresqldatabaseserver
>get-azuresqldatabaseserver
With this command you can obtain the SQL Server Name.

Figure 15. The Database Servers.In this example, you have 2 Server names, the location and the administrator login names.
-
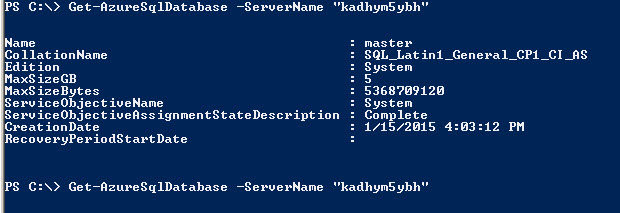
Another important command is the Get-AzureSqlDatabase. The command lists the databases of a specific server.
Get-AzureSqlDatabase -ServerName "kadhym5ybh"

Figure 16. The list of Azure DatabasesThe command will display all of the databases of the Server named kadhym5ybh. It will also display the CollationName, Edition, MaxSize in Gb, Bytes, the creating date, Service Objective Name and RecoveryPeriodStartDate.
-
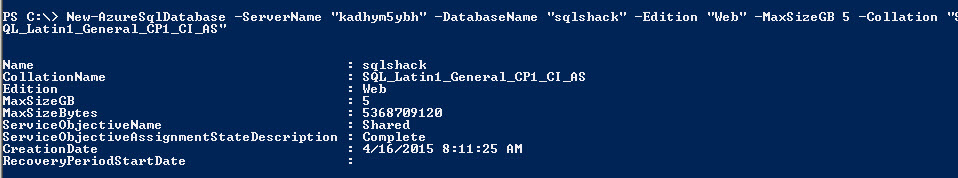
The other command is the New-AzureSqlDatabase. This command is used to create a New Database. You can also especify the Maximum Size, the Edition of the Database and the Collation. The following example creates a Database named Database1 in the kadhym5ybh Server. The database has a maximum size of 5 GB and it is a Web edition with the SQL_Latin1_General collation. The editions can be Web, Business, Basic, Standard, or Premium. The default edition is the Web edition.
New-AzureSqlDatabase -ServerName "kadhym5ybh" -DatabaseName "sqlshack" -Edition "Web" -MaxSizeGB 5 -Collation "SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS"
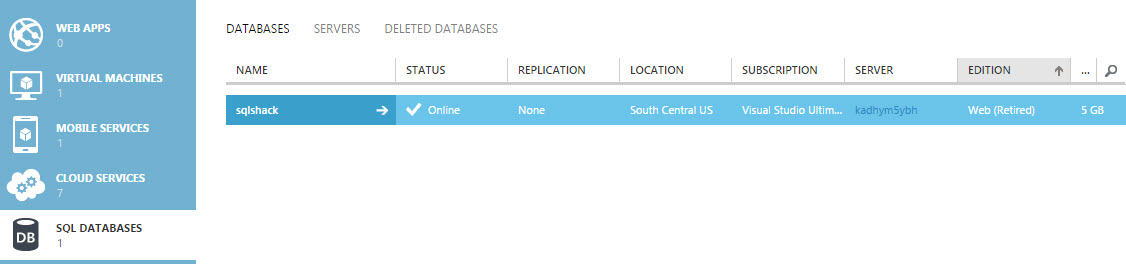
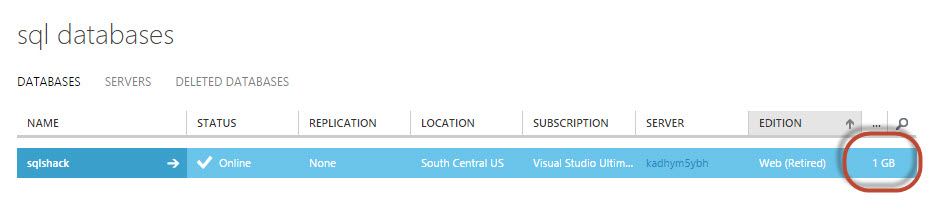
You can also verify if the database sqlshack was created with 5 GB in the Azure Portal in the Databases section.
Another PowerShell command is the set-AzureSqlDatabase. With this command you can modify the database properties.
To do this, first you need to store the database information in a variable. In this example the $db1 variable.
PS C:\> $db1 = Get-AzureSqlDatabase -ServerName "kadhym5ybh" -DatabaseName "sqlshack”
The next step is to use the Set-AzureSqlDatabase command to change a database property. In this example, we are modifying the Maximum size of the Database1 from 50 to 20.
PS C:\> Set-AzureSqlDatabase -ServerName "kadhym5ybh" -Database $db1 -MaxSizeGB 1
-
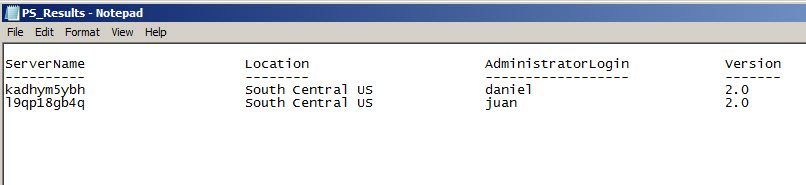
You can also store the information using the out-file cmdlet. The following example shows how to store the list of database servers in a text file named PS_Results.txt in the scripts folder:
get-azuresqldatabaseserver | out-file c:\scripts\PS_Results.txt
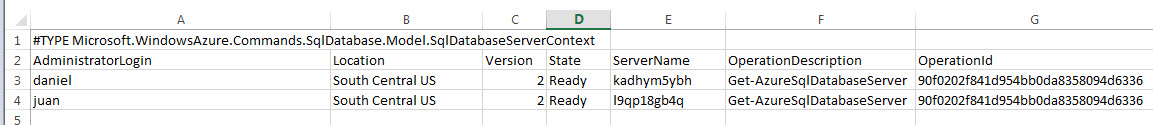
You can also export your values to a csv file using the export-csv cmdlet.
get-azuresqldatabaseserver | export-csv -path C:\scripts\csvresults.csv
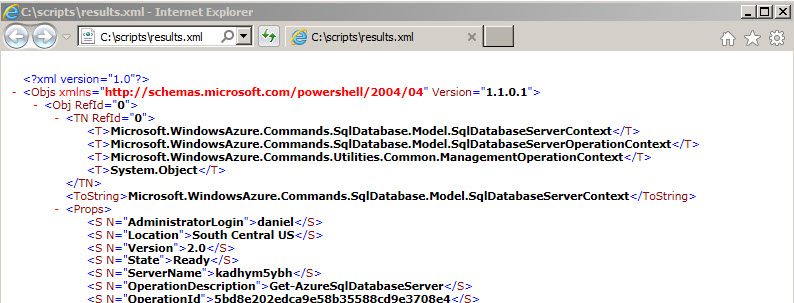
Or maybe in you will like the results in xml format using the Export-Clixml cmdlet:
get-azuresqldatabaseserver | Export-Clixml c:\scripts\results.xml
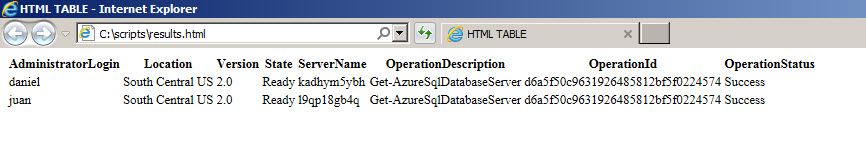
It is also possible to store the results in html format using the ConvertTo-HTML cmdlet combined with the Out-File.
get-azuresqldatabaseserver | ConvertTo-HTML | Out-File C:\Scripts\results.html
If you want to filter some columns, you can use the select command. The following example shows the use of the select and also set the format of the results as a list instead of a table.
get-azuresqldatabaseserver | select ServerName, Location | Format-List

Figure 24. The results of the select in a Format of a list.In order to get a list of cmdlets available, you can use the Get-Command
Get-Command
If you want an example of a specific command, you can use the get help cmdlet.
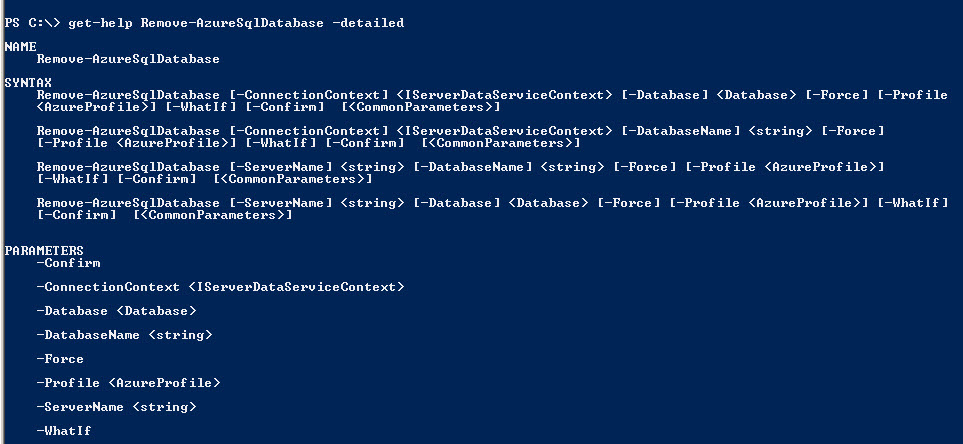
The following example shows how to use the the Remove-AzureSqlDatabase cmdlet.
get-help Remove-AzureSqlDatabase –detailed

Figure 26. The help of the Remove-AzureSqlDatabaseConclusion
In this article, we installed the Microsoft Azure PowerShell and then we used some PowerShell commands to create, modify Azure Databases from our local machine using PowerShell. We also stored the results in different formats like html, xml, csv and txt.
Latest posts by Daniel Calbimonte (see all)- PostgreSQL tutorial to create a user - November 12, 2023
- PostgreSQL Tutorial for beginners - April 6, 2023
- PSQL stored procedures overview and examples - February 14, 2023