As I covered in a previous post How to connect to (and query) Power BI and Azure using PowerShell, Power BI can be difficult to manage and administer, unlike on-premises BI solutions. One such concern that will often require quick action is the failure of a dataset refresh.
If your reports and dashboards all rely on live connection or DirectQuery data sources like Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Data Warehouse or SQL Server Analysis Services (on-premises or in Azure) then you won’t have to worry about dataset refreshes and this post will just be some interesting reading.
Chances are, that you probably have at least one report that relies on an on-premises database or file source and you need to schedule it to refresh regularly to get up to date data. It’s in managing this functionality that the current offering within Power BI falls short, hopefully not for long with the rate updates are coming!
Built-in failure notifications
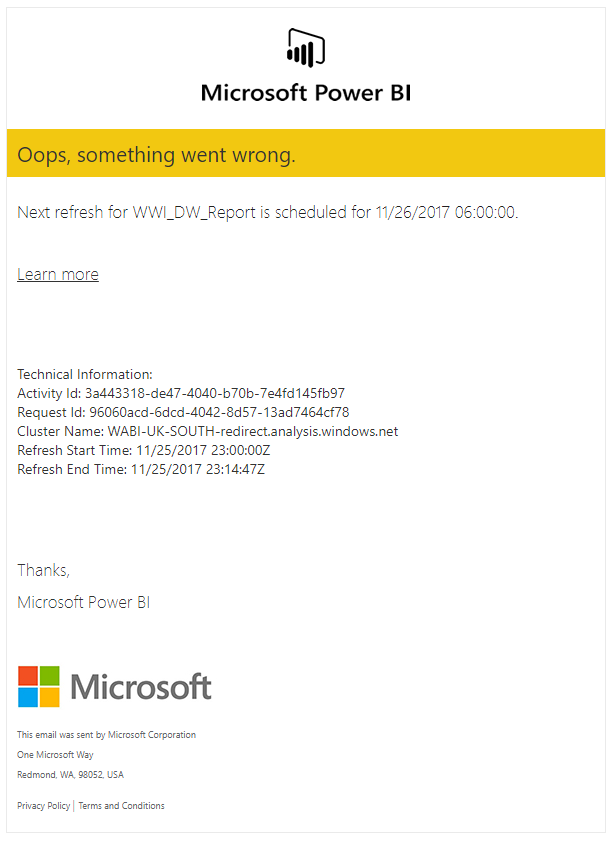
Power BI has a method to notify you of a failed dataset, which is great. You obviously want to know when data wasn’t updated & you probably want to notify users or customers too. You may have received such an alert already. They look something like this:
That’s a great first step but there is a great deal further we need to go to satisfy my inner Administrator.
Who owns this!?
You may have noticed the little checkbox near the bottom of each dataset settings page that lets you turn these failure notifications on.
The issue here is that there is no CC for a wider admin user or group. This notification will only email the current dataset owner in the event of a failure. Depending on your process for deploying content to Power BI or how users interact with it, this could be an analyst, a sales manager, a developer or indeed, the person who would be able to source & fix the issue.
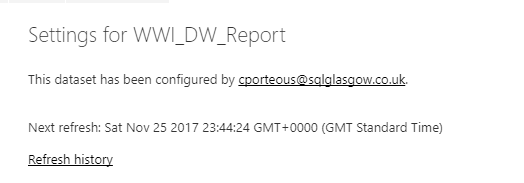
Even with processes in place to “hand over” dataset ownership to a single administrator account, there will always be fluidity in where these notifications get sent, thus delaying the resolution of any issues that arise
But WHAT went wrong!?
Oops, something went wrong! You’ve received your failure notification; now let’s check the email to see what happened.
Referring to the email excerpt above, we can see the dataset name & its next refresh time. Great, but what if you have the same dataset across several workspaces, maybe in a DEV, QA, PROD scenario?
There’s no link to the failing dataset or the parent workspace. At the time of writing this, the Learn More link also hits a 404.
Here is a good alternative page for troubleshooting dataset refresh issues: Troubleshooting Refresh Scenarios
PowerShell alerting
Building on the API interactions within PowerShell from my previous blog posts I wanted to create my own dataset failure monitor. It’s not perfect but it will get me a lot more information than I get from the built-in functionality, and allow me to respond quicker too.
I started by splitting out two reusable components of this monitor script to functions. The authentication & the notification.
I reference these in the main script but I plan on expanding and building these into a module in the future. Keep an eye on my GitHub. For now, save them with their function names in the same folder as the monitor script and you’re ready to go.
Get-PBIAuthTokenUnattended
This first one is the authentication function. It enables unattended authentication into Azure with the use of an encrypted text file for your account’s password. The main blocker you will have with this function is the requirement for a Power BI “app”. If you already have your ClientID & Client Secret to hand, you can skip Steps 1 & 2.
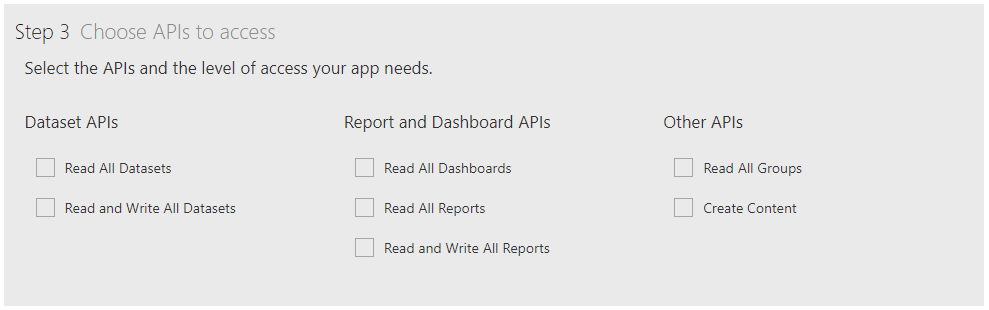
The Power BI app can be created from the Power BI app registration page. You do not need to be an Azure or Power BI admin to do so which is great. Make sure you choose the Server-side Web App type, which will generate both a ClientID and a Client_Secret. The ClientID can be retrieved from Azure if needed but if you don’t make note of the Client_Secret when you create the app, it’s gone. Start again. You will want to at least tick all the options under the Dataset API section for permissions.
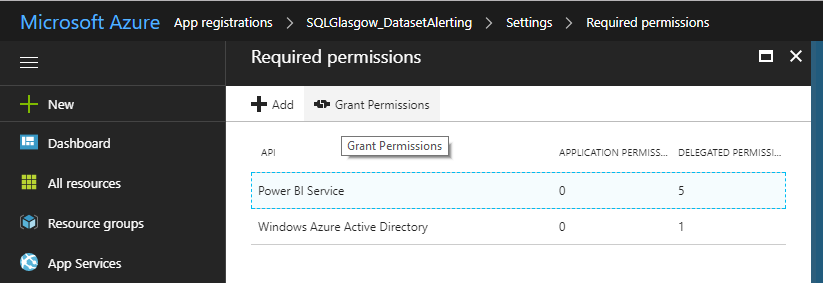
The next thing you will have to do is log in to Azure using the account you created the app with to Grant Permissions, allowing users to authenticate with the app. This can be found under the App Registrations section shown below.
- Your tenant ID can be found a few ways. The authentication script also tries to find it for you if you leave that parameter off when you call the script, based on the domain of the user you provide so don’t worry too much about that.
- Log in to Microsoft Azure as an administrator. In the Microsoft Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory. Under Manage, click Properties. The tenant ID is shown in the Directory ID box.
- Using this command, it will query Azure anonymously (thanks to user5347643 on StackOverflow):
1$tenantID = (Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing https://login.windows.net/sqlglasgow.onmicrosoft.com/.well-known/openid-configuration|ConvertFrom-Json).token_endpoint.Split('/')[3]
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 |
<# .SYNOPSIS Authenticate against the Power BI API .DESCRIPTION This is an unattended authentication function. # Prerequisites #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Client ID & Client Secret can be obtained by creating a Power BI app: # https://dev.powerbi.com/apps # App Type: Web App / API #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- .PARAMETER userName This is the user that will connect to Power BI. The datasets & groups that are returned are restricted by the user's permissions .PARAMETER tenantID #---------------------------------------- # To find your Office 365 tenant ID in the Azure AD portal # - Login to Microsoft Azure as an administrator. # - In the Microsoft Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory. # - Under Manage, click Properties. The tenant ID is shown in the Directory ID box. .PARAMETER clientId This is the ID generated by the Power BI App created above. It can also be found from within Azure .PARAMETER client_secret This is also generated when the Power BI App is created & must be noted as it is irretrievable once you leave the page .PARAMETER mailServer Your mail server .PARAMETER mailFrom Your selected FROM address to send error or notification emails .PARAMETER mailTo The recipient email address or addresses (separated by semicolons) that will receive error and notification emails .EXAMPLE $authtoken = Get-PBIAuthTokenUnattended -userName User@domain.com -tenantID "85b7f285-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-ec7116aa9ef5" -clientId "f40daa92-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-7e027fe03e2e" -client_secret "5bM2KeZl2nVXXXXXXXXXXXXi6IYVPOt8lAtPwXXXXXX="" #> function Get-PBIAuthTokenUnattended { [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $userName = "$(Read-Host 'Power BI Account')", [string] $tenantID, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $clientId, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $client_secret ) begin { #Include email function . ".\Invoke-AlertEmail.ps1" if($tenantID.Length -lt 36) { Write-Verbose 'Split the string on the username to get the Domain' $tenantDomain = $userName.Split("@")[1] Write-Verbose 'Querying Azure anonymously (this may not work for ALL tenant domains. Eg. Those that use .onmicrosoft.com)' $tenantID = (Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing https://login.windows.net/$($tenantDomain)/.well-known/openid-configuration|ConvertFrom-Json).token_endpoint.Split('/')[3] } $pbiAuthorityUrl = "https://login.windows.net/$tenantID/oauth2/token" $pbiResourceUrl = "https://analysis.windows.net/powerbi/api" Write-Verbose 'Test if ADAL module is installed & install if DLL not found' $moduleName = 'Microsoft.ADAL.PowerShell' Try { if (Get-Module -ListAvailable -Name $moduleName) { Import-Module -Name $moduleName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue } else { Install-Module -Name $moduleName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue } } Catch { throw '$moduleName module is not installed and could not be added' } Write-Verbose 'Get Username from encrypted text file' $path = (Resolve-Path .\).Path #Grab current user as encrypted file is tagged with who encrypted it $user = $env:UserName $file = ($userName + "_cred_by_$($user).txt") Write-Verbose 'Testing if credential file exists & create if not' if(Test-Path $file) { $Pass = Get-Content ($path + '\' + $file) | ConvertTo-SecureString } else{ Write-Host 'Encrypted Credential file not found. Creating new file.' Read-Host -Prompt "Please enter Password for $userName" -AsSecureString | ConvertFrom-SecureString | Out-File "$($path)\$($userName)_cred_by_$($user).txt" Write-Verbose 'Encrypted file created' $Pass = Get-Content ($path + '\' + $file) | ConvertTo-SecureString } } Process{ try { #Pull password from secure string $BSTR = [System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::SecureStringToBSTR($Pass) $textPass = [System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal]::PtrToStringAuto($BSTR) Write-Verbose 'Authenticating to Azure/PBI' $authBody = @{ 'resource'=$pbiResourceUrl 'client_id'=$clientId 'grant_type'="password" 'username'=$userName 'password'= $textPass 'scope'="openid" 'client_secret'=$client_secret } #Clear password variable immediately after use $textPass = $null $auth = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $pbiAuthorityUrl -Body $authBody -Method POST -Verbose #Clear auth array immediately after use $authBody = $null } catch { Write-Error 'Authentication or Connection failure.' $script = $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Name $subject = "$script Error: Authentication Failure" $htmlContent = $_.Exception.Message Invoke-AlertEmail -title $script -htmlContent $htmlContent -subject $subject -alertColour "#FF5733" throw $_ } Write-Verbose 'Authentication token retrieved' return $auth } } |
Invoke-AlertEmail
The notification function basically builds up a generic HTML email that I intend on using for more PowerShell scripts & error handling, so feel free to adjust as you wish. I replicated the style of the Power BI failure notifications as a quick, clean solution. There’s even a parameter to pass a hex colour to this function, so you can colour code your emails! If you need to authenticate to your mail server, we can use a similar method to the authentication function, by using an encrypted text file. I have included this and added a switch (-auth) when calling the script to enable that functionality.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 |
<# .SYNOPSIS This is an email function that builds an HTML email to be used for script outputs and error handling .DESCRIPTION Long description .PARAMETER subject This is the email subject and is a mandatory parameter. .PARAMETER title This is the title of the email that will be included in the top, color coded panel. It should contain the source script name or purpose .PARAMETER htmlContent This is the main body of the email and should be a string, constructed in the calling script to display the required information in the email .PARAMETER companyLogo This is a logo that will show above the title section of the email, for organization branding .PARAMETER companyLogoAlt Alternative text for the logo .PARAMETER team This is used in the email signature as the source "team or user" for the email .PARAMETER alertColour This is a hex color to color code the email title section .PARAMETER mailServer Mail server to be used for distribution. .PARAMETER mailFrom Email address to be displayed as the sender .PARAMETER mailTo Recipient(s) for the email .EXAMPLE Invoke-AlertEmail -subject "Test subject" -title "Email Title" -htmlContent "Test content</br>More content" .NOTES General notes #> function Invoke-AlertEmail { [CmdletBinding()] param( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $subject, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $title, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $htmlContent, [string] $companyLogo = 'https://i0.wp.com/sqlglasgow.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/sql-glasgow-logo-full-TEMP_SQL-Glasgow-copy-e1508254573114.png?fit=700%2C140', [string] $companyLogoAlt = 'CraigPorteous.com BI Team Logo', [string] $team = 'CraigPorteous.com BI Team', [string] $alertColour = 'D3D3D3', #Flag for Auth required for email server [switch] $auth, #Set Mail settings for error handling [string] $mailServer = "smtp.office365.com", [string] $mailFrom = "cporteous@sqlglasgow.co.uk", [string] $mailTo = "cporteous@sqlglasgow.co.uk" ) begin{ Write-Verbose 'Checking supplied Hex colour code' if($alertColour -Match '^#([A-Fa-f0-9]{6}|[A-Fa-f0-9]{3})$') { #Perfect match Write-Verbose 'Hex colour code Accepted' } elseif($alertColour -Match '^#?([A-Fa-f0-9]{6}|[A-Fa-f0-9]{3})$') { #Add # Prefix $alertColour = "#$($alertColour)" } else{ Write-Error 'Invalid HEX Colour code provided' $script = $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Name $subject = "$script Error: Invalid Hex Colour used" $htmlContent = "HEX used in script: $($alertColour)" Invoke-AlertEmail -title $script -htmlContent $htmlContent -subject $subject -alertColour "#FF5733" throw } if ($auth) { Write-Verbose 'Retrieving Credential component for mail servers that require Auth' #---------------------------------------------------------------------- Write-Verbose 'Get Username from encrypted text file' $path = (Resolve-Path .\).Path #Grab current user so encrypted file is tagged with who encrypted it $user = $env:UserName $file = ($mailFrom + "_cred_by_$($user).txt") Write-Verbose 'Testing if credential file exists & create if not' if(Test-Path $file) { $Pass = Get-Content ($path + '\' + $file) | ConvertTo-SecureString } else{ Write-Host "Encrypted Credential file not found. Creating new file." Read-Host -Prompt "Please enter Password for $mailFrom" -AsSecureString | ConvertFrom-SecureString | Out-File "$($path)\$($mailFrom)_cred_by_$($user).txt" Write-Verbose 'Encrypted file created' $Pass = Get-Content ($path + '\' + $file) | ConvertTo-SecureString } $Cred = new-object -typename System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -argumentlist $mailFrom, $Pass #---------------------------------------------------------------------- } } process{ Write-Verbose 'Build email HTML header' $htmlHeader = "<style type=""text/css""> .auto-style1 { text-align: center; } .auto-style2 { text-align: left; } .auto-style3 { font-family: 'Segoe UI Semilight', 'wf_segoe-ui_light', 'Segoe UI Light', 'Segoe WP Light', 'Segoe UI', 'Segoe WP', Tahoma, Arial, sans-serif; } .auto-style4 { font-family: 'Segoe UI', 'Segoe UI Light', 'Segoe WP Light', 'Segoe WP', Tahoma, Arial, sans-serif; } </style>" Write-Verbose 'Build email HTML Body' $htmlBody = "<table width=""100%"" cellpadding=""0"" cellspacing=""0"" border=""0""> <tbody> <tr> <td valign=""top"" width=""50%""></td> <td valign=""top"" style=""padding-top: 20px""> <table width=""600"" cellpadding=""10px 10px"" cellspacing=""0"" style=""border-collapse: collapse""> <tbody> <!-- Company/Dept Logo --> <tr><td text-align=""center"" valign=""top""><img src=""$($companyLogo)"" alt=""$($companyLogoAlt)""></br></td></tr> <!-- Email Title / Source script --> <tr><td class=""auto-style4"" style=""margin: 5px 5px; padding: 10px 10px; font-size: 23px; background-color: $($alertColour); color: #333333""></br><div>$($title)</div></br></td></tr> <!-- Content generated by calling script --> <tr class=""auto-style2 auto-style4"" style=""font-size: 22px;""> <td> </br>$($htmlContent) </td> </tr> <!-- Email footer --> <tr class=""auto-style2 auto-style4"" style=""font-size: 16px; color: #333333""> <td> </br><div>Thanks,</div> <div>$($team)</div> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </td> <td valign=""top"" width=""50%""></td> </tr> </tbody> </table>" $htmlEmail = ConvertTo-Html -Head $htmlHeader -Body $htmlBody | Out-String try { if($auth) { Write-Verbose 'Send Mail using authentication & SSL' send-mailmessage -SmtpServer $mailServer -From $mailFrom -To $mailTo -Subject $subject -BodyAsHtml -Body $htmlEmail -Credential $Cred -UseSsl -Port "587" } else { Write-Verbose 'Send Mail' send-mailmessage -SmtpServer $mailServer -From $mailFrom -To $mailTo -Subject $subject -BodyAsHtml -Body $htmlEmail } } catch { #Catch an issue throw $_ } } } |
PowerBI_Dataset_Alerting
Finally, here is the actual monitoring script. You’ll notice that I use the email function above in my catch blocks; this is because the script is intended to be run as a scheduled task so email makes the most sense to notify of exceptions.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 |
<# .SYNOPSIS This script will alert by email, on any datasets that have failed a refresh & a subsequent manual refresh attempt. .DESCRIPTION This script will iterate through all datasets in all Workspaces within Power BI that the chosen user has access to. It will then attempt to force a refresh of any datasets with a failed status. The script should be scheduled to run at a regular interval. Upon the next run, it will send a notification email on any failed refreshes made by the API (on the last run). There is a time limiter parameter that will stop the repetitive alerting of a failed dataset. .PARAMETER userName This is the Power BI user that the API will use to query workspaces and datasets. The datasets & groups that are returned are restricted by the user's permissions .PARAMETER tenantID # To find your Office 365 tenant ID in the Azure AD portal # - Login to Microsoft Azure as an administrator. # - In the Microsoft Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory. # - Under Manage, click Properties. The tenant ID is shown in the Directory ID box. .PARAMETER clientId This is the ID generated by the Power BI App created above. It can also be found from within Azure .PARAMETER client_secret This is also generated when the Power BI App is created & must be noted as it is irretrievable once you leave the page .PARAMETER maxTime The time window of how long you want to alert on failed refreshes via the API. Eg. 30 = If Last refresh end time is beyond 30 mins, do not alert. This will reduce spam of alert emails when issues may take time to resolve. .PARAMETER mailServer Your mail server .PARAMETER mailFrom Your selected FROM address to send error or notification emails .PARAMETER mailTo The recipient email address or addresses (separated by semicolons) that will receive error and notification emails .EXAMPLE .\PowerBI_Dataset_Alerting.ps1 -userName 'Username@Domain.com' -tenantID "85b7f285-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-ec7116aa9ef5" -clientId "f40daa92-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-7e027fe03e2e" -client_secret "5bM2KeZl2nVXXXXXXXXXXXXi6IYVPOt8lAtPwXXXXXX=" .NOTES #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Client ID & Client Secret can be obtained by creating a PowerBI app: # https://dev.powerbi.com/apps # App Type: Server-side Web app #------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #> [CmdletBinding()] param ( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $userName = "$(Read-Host 'Power BI Account')", [string] $tenantID, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $clientId, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [string] $client_secret, [int] $maxTime = 30 ) begin { Write-Verbose 'Add Authentication & Notification Functions' . ".\Get-PBIAuthTokenUnattended.ps1" . ".\Invoke-AlertEmail.ps1" if($tenantID = $null) { Write-Verbose 'Split the string on the username to get the Domain' $tenantDomain = $userName.Split("@")[1] Write-Verbose 'Querying Azure anonymously (this may not work for ALL tenant domains. Eg. Those that use .onmicrosoft.com)' $tenantID = (Invoke-WebRequest https://login.windows.net/$($tenantDomain)/.well-known/openid-configuration|ConvertFrom-Json).token_endpoint.Split('/')[3] } } process { try { Write-Verbose 'Authenticate to Power BI using Get-PBIAuthTokenUnattended' $auth = Get-PBIAuthTokenUnattended -userName $userName -tenantID $tenantID -clientId $clientId -client_secret $client_secret Write-Verbose 'Building Rest API header with authorization token' $authHeader = @{ 'Content-Type'='application/json' 'Authorization'='Bearer ' + $auth.access_token } } catch { Write-Error 'Authentication failure' $script = $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Name $Subject = "$script Error: Authentication Failure" $htmlContent = $_.Exception.Message Invoke-AlertEmail -title $script -htmlContent $htmlContent -subject $subject -alertColour "#FF5733" throw $_ } try{ Write-Verbose 'Retrieve all Power BI Workspaces' $uri = "https://api.powerbi.com/v1.0/myorg/groups" $allGroups = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri -Headers $authHeader -Method GET Write-Verbose 'Storing time interval provided as window to alert on failed datasets (reduces SPAM from datasets failing regularly)' $timeWindow = (Get-Date).AddMinutes(-$maxTime) Write-Verbose "Monitor will not alert on API based failures older than $($timeWindow)" Write-Verbose 'Loop through Workspaces to query datasets' foreach($group in $allGroups.value) { Write-Verbose 'Build Group path for API call' $groupsPath = "myorg/groups/$($group.id)" Write-Verbose 'Build Dataset API String' $uri = "https://api.powerbi.com/v1.0/$groupsPath/datasets" Write-Verbose 'Return all datasets in Workspace' $datasets = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri -Headers $authHeader -Method GET Write-Verbose 'Loop through datasets to query refresh info' foreach($dataset in $datasets.value) { if($dataset.isRefreshable -eq $true) #We can only return refresh info on datasets that can be refreshed { Write-Verbose 'Build Refresh API String' $uri2 = "https://api.powerbi.com/v1.0/$groupsPath/datasets/$($dataset.id)/refreshes" Write-Verbose 'Return refresh info for each dataset' $refreshes = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri2 -Headers $authHeader -Method GET if($($refreshes.value[0].status) -eq 'Failed' -And $($refreshes.value[0].refreshType) -eq 'Scheduled' ) { Write-Verbose 'Force refresh of failed Scheduled refreshes' $forcerefresh = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri2 -Headers $authHeader -Method POST #$forcerefresh } elseif ($($refreshes.value[0].status) -eq 'Failed' -And $($refreshes.value[0].refreshType) -eq 'ViaApi' -And [DateTime]$($refreshes.value[0].endTime) -gt $timeWindow) { Write-Verbose 'Notifying of refreshes that failed via the API' #Build email HTML and pass to function $title = "Power BI Dataset Alerting" $subject = "$($title): $($dataset.name)" $htmlContent = "</br><div>Scheduled & Forced Refreshes have both failed! Please investigate</div>" $htmlContent += "</br><div>Workspace: <a href=""https://app.powerbi.com/groups/$($group.id)/contentlist?onlySharedWithMe=false"">$($group.name)</a></div>" $htmlContent += "</br><div>DataSet: <a href=""https://app.powerbi.com/groups/$($group.id)/settings/datasets/$($dataset.id)"">$($dataset.name)</a></div>" Invoke-AlertEmail -title $title -htmlContent $htmlContent -subject $subject -alertColour "#F2C811" } } } $datasets = $null } } catch{ Writ-Error 'Data collection failure' $script = $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Name $subject = "$script Error: Data Collection Failure" $htmlContent = $_.Exception.Message Invoke-AlertEmail -title $script -htmlContent $htmlContent -subject $subject -alertColour "#FF5733" throw $_ } } |
Here’s an overview of what the script does:
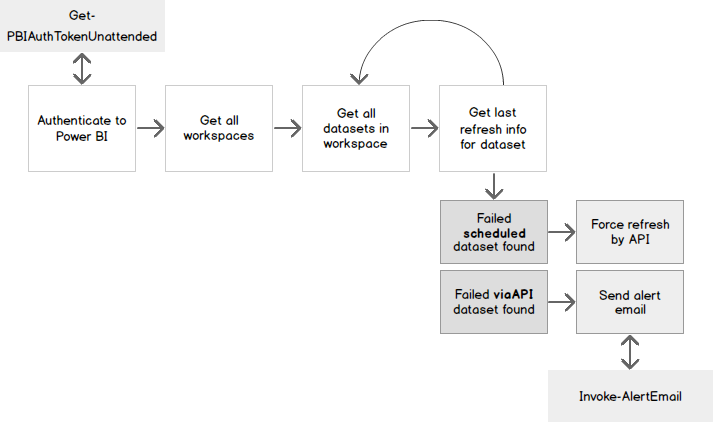
You will want to schedule the monitor script to run at the interval to suit your SLA/OLAs. I set it to run every 15 minutes. This means, at the longest interval, it would take up to 14 minutes to detect a failed dataset, force a manual refresh, then another 15 minutes before it would email out to warn of the failure. This is a good window to accommodate a timeout failure where the manual refresh might run for a while before completing or failing again.
Oops, this is what went wrong…
So, my dataset has failed and then failed again when we tried to force a refresh which means it’s likely not a short-term issue that will resolve itself. The refresh failure email will then be sent to your chosen recipient(s).
It’s going to contain:
- A relevant title, (in this case, the name/purpose of the script)
- The name of the parent workspace & a hyperlink to that workspace
- The name & a link to the failing dataset’s settings page so you can diagnose the failure easily
- A courteous Thank you from the script owner ? (which can be set in the parameters)

Some things to consider with this script:
- The user account you use to connect to Power BI with is very important, it doesn’t have to own any of the datasets but it cannot monitor datasets if it doesn’t have the permission to the workspace the dataset is contained in. Bear this in mind. In my case, I have implemented an admin account that gets added to all workspaces as a matter of process but even this can miss user created workspaces. You may have better luck with an Azure admin. Please let me know if you do.
Further analysis with PowerShell
You can use an extension of this script to query all dataset refresh history & store it in a local database. This could be used to pick up more nuanced issues
- Repeated failure trends
- Refresh durations over time
- Datasets being refreshed too often, or not often enough
References
- Connect & Query Power BI with PowerShell
- My GitHub Profile
- Dead ‘Learn More’ Link
- Troubleshooting Refresh Scenarios
- Power BI App Registration
- StackOverflow TenantID command
- How to secure Reporting Services with Group Managed Service Accounts (GMSA) - November 7, 2018
- Contribute, contribute, contribute! - June 20, 2018
- Top 10 things you must document in SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) - February 26, 2018