This is the 2nd article of Move SQL databases to a different mount point series. In the previous article, Create a new mount point in Linux, I have explained how we can create a mount point in Ubuntu Linux. In this article, I am going to cover the following topics:
- Grant appropriate permission on the directories
- Move the AdventureWorks2019 SQL database to the new mount point
- Move system databases to the new mount point
- Change the default data file, log file, and backup file locations
First, let’s grant appropriate permissions. I have added another virtual disk to copy the database files and mount the disk on /SQLDatabases directory. To keep the database files, I have created three directories. Details are the following:
|
Database file type |
New Location |
|
Primary data file |
/SQLDatabases/Data |
|
Transaction log file |
/SQLDatabases/Log |
|
TempDB data file |
/SQLDatabases/TempDB |
|
Backup data file |
/SQLDatabases/Backup |
We are giving read, write, and execute permission on all specified directories. To grant access, we are using the chmod command. Commands are the following:
Grant access to the /SQLDatabases
root@LinuxSQL02:/# chmod -R a+rwx /SQLDatabases
Grant access to the /SQLDatabases/Data
root@LinuxSQL02:/# chmod -R a+rwx /SQLDatabases/Data
Grant access to the /SQLDatabases/Log
root@LinuxSQL02:/# chmod -R a+rwx /SQLDatabases/Log
Grant access to the /SQLDatabases/TempDB
root@LinuxSQL02:/# chmod -R a+rwx /SQLDatabases/TempDB
Grant access to the /SQLDatabases/Backup.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# chmod -R a+rwx /SQLDatabases/Backup
To view the permission that has been granted, run the following command:
root@LinuxSQL02:/# chmod -R a+rwx /SQLDatabases/Backup
Output:

As you can see, the access has been granted.
- Note: In the demo setup, I have granted read, write, and execute permission to all users. If you are working in a production environment, then make sure you grant the required permission only
Move AdventureWorks2019 database
Before moving the database, let us view the current location of the files.
Query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
USE adventureworks2019 go SELECT NAME [Logical Name], type_desc [Type of file], physical_name [file location] FROM sys.database_files |
Output:

Before detaching the database, disconnect all the users by dropping the connection and then executing the sp_detach_db command to detach the database.
Query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
use master go Alter database [AdventureWorks2019] set single_user with rollback immediate go exec sp_detach_db [AdventureWorks2019] Go |
Now, move the *.mdf file to /SQLDatabases/Data directory and *.ldf file to /SQLDatabases/Log directory by executing the following commands:
Command to move MDF files
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /MSSQL/SQLData/AdventureWorks2019.mdf /SQLDatabases/Data/
Command to move LDF files
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /MSSQL/SQLLog/AdventureWorks2019_log.ldf /SQLDatabases/Log/
Now, attach the database by executing query.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
USE [master] GO CREATE DATABASE [AdventureWorks2019] ON ( FILENAME = N'/SQLDatabases/Data/AdventureWorks2019.mdf' ), ( FILENAME = N'/SQLDatabases/Log/AdventureWorks2019_log.ldf' ) FOR ATTACH GO |
Let us verify the location of AdventureWorks2019 database files.
Query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
USE adventureworks2019 go SELECT NAME [Logical Name], type_desc [Type of file], physical_name [file location] FROM sys.database_files |
Output:

As you can see in the above screenshot, the database files have been moved.
Move MSDB and MODEL system databases
To change the location of the model and msdb system database, we must follow steps as shown below:
- Change the location of the files in SQL Server metadata by using the ALTER DATABASE MODIFY FILE query
- Stop SQL Server services
- Move the files to the new location
- Start the services
To change the location of the database files, execute the following ALTER DATABASE MODIFY FILES command.
Query to change the location of the MSDB database
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
ALTER DATABASE msdb MODIFY FILE ( NAME = MSDBData, FILENAME = '/SQLDatabases/data/MSDBData.mdf'); GO ALTER DATABASE msdb MODIFY FILE ( NAME = MSDBLog, FILENAME = '/SQLDatabases/log/MSDBLog.ldf'); GO |
Query to change the location of the MODEL database
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
ALTER DATABASE model MODIFY FILE ( NAME = modeldev, FILENAME = '/SQLDatabases/data/model.mdf'); GO ALTER DATABASE model MODIFY FILE ( NAME = modellog, FILENAME = '/SQLDatabases/log/modellog.ldf'); GO |
Now, stop the SQL Server services using the systemctl command.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# systemctl stop mssql-server
Move the data files to /SQLDatabases/data and log files to /SQLDatabases/Log directory using the mv (move) command.
Command to copy MSDB data and log files
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/msdbdata.mdf /SQLDatabases/Data/
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/msdblog.ldf /SQLDatabases/Log/
Command to copy Model data and log files
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/model.mdf /SQLDatabases/Data/
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/modellog.ldf /SQLDatabases/Log/
Start the SQL Server services.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# systemctl start mssql-server
Verify the changes by running following query in SQL Server management studio.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT Db_name(database_id)AS[Database Name], NAME AS[Logical Name], physical_name AS[File Location] FROM sys.master_files WHERE Db_name(database_id) IN ( 'model', 'msdb' ) |
Output:
As you can see, the MODEL and MSDB databases have been moved /SQLDatabase mount point.
Move TempDB databases
To change the location of the TempDB database, follow the below steps.
- Change the location of the files in SQL Server metadata by using the ALTER DATABASE MODIFY FILE query
- Restart the services
To change the location of the database files, execute the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
ALTER DATABASE tempDB MODIFY FILE ( NAME = tempdev, FILENAME = '/SQLDatabases/data/tempdb.mdf'); GO ALTER DATABASE tempDB MODIFY FILE ( NAME = templog, FILENAME = '/SQLDatabases/log/templog.ldf'); GO |
Now, restart the SQL Server services using the systemctl command.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# systemctl restart mssql-server
Verify the changes by running the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT Db_name(database_id)AS[Database Name], NAME AS[Logical Name], physical_name AS[File Location] FROM sys.master_files WHERE Db_name(database_id) IN ( 'tempdb' ) |
As you can see, the databases have been moved /SQLDatabase mount point.

Moving master databases
To move the master database, we must use the mssql-config tool. It is a SQL Server configuration tool that is used to configure the various parameters of the SQL Server. You can read the article How to configure SQL Server 2017 on Linux with mssql-conf and other available tools to know more about the mssql-config tool. To move the master database, follow the below steps.
- Change the default locations of the data file and log file of a master database
- Stop the SQL Server services
- Move the files to a new location
- Start the services
To change the location of the data files and log files, we are using mssql-config with set option. The command is following
root@LinuxSQL02:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.masterdatafile
/SQLDatabases/data/master.mdf
root@LinuxSQL02:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.masterlogfile
/SQLDatabases/Log/mastlog.ldf
Now, stop the SQL Server services.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# systemctl stop mssql-server
Move the master.mdf to /SQLDatabase/Data and mastlog.ldf to /SQLDatabase/Log directory.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/master.mdf /SQLDatabases/Data/
root@LinuxSQL02:/# mv /var/opt/mssql/data/mastlog.ldf /SQLDatabases/Log/
Start the SQL Server services.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# systemctl start mssql-server
Verify the changes by running following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT Db_name(database_id)AS[Database Name], NAME AS[Logical Name], physical_name AS[File Location] FROM sys.master_files WHERE Db_name(database_id) IN ( 'master' ) |
Output:

As you can see, the databases have been moved /SQLDatabase mount point.
Change the default location of data files, log files, and backup files
To change the default locations, we must use mssql-config with a set option. To change the default locations, run the following commands.
Change the default location of SQL Database File
root@LinuxSQL02:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.defaultdatadir /SQLDatabases/Data/
Change the default location of SQL Log File
root@LinuxSQL02:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.defaultlogdir /SQLDatabases/Log/
Change the default location of SQL Backup File
root@LinuxSQL02:/# sudo /opt/mssql/bin/mssql-conf set filelocation.defaultbackupdir /SQLDatabases/Backup/
Now, restart the services.
root@LinuxSQL02:/# systemctl restart mssql-server
Now, to verify the changes, create a new SQL Database. The database files should be created in /SQLDatabases mount point.
Create database TestDatabase
Verify the location data file and log file of SQL Database.
Query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
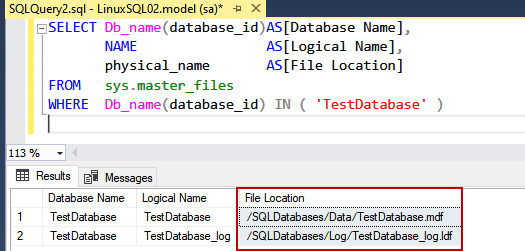
SELECT Db_name(database_id)AS[Database Name], NAME AS[Logical Name], physical_name AS[File Location] FROM sys.master_files WHERE Db_name(database_id) IN ( 'TestDatabase' ) |
Output:

As you can see, the data file and log file of TestDatabase are created in /SQLDatabases/Data and /SQLDatabases/Log directory.
Summary
This article explained how we can grant the directory level permission, move the user database and system database files to the new mount point. Additionally, I have also explained how we can change the default location of the data file, log file, TempDB files, and backup files by using the configuration file named mssql-config file.
Table of contents
| Move SQL database files in SQL Server 2019 on Linux |
| Move SQL databases to a different mount point: Create a new mount point in Linux |
| Move SQL databases to a different mount point: Granting permissions and moving System and User databases |
- Different ways to identify and change compatibility levels in SQL Server - July 22, 2024
- Copy SQL Databases between Windows 10 and CentOS using SQL Server data tools - October 19, 2022
- Changing the location of FILESTREAM data files in SQL Database - October 14, 2022