This article will explore the right way of moving integration services (SSIS) catalog SQL Database to a new instance.
Introduction
SSISDB is a repository for your SSIS package projects, package parameters, environments, execute and troubleshoot packages.
Once you create a catalog in the SSIS services, it creates an SSISDB catalog and SSISDB database. To configure the SSISDB catalog, it requires the following inputs.
- Enable CLR Integration
- We need to enable automatic execution of Integration Services stored procedure at SQL Server startup
- It requires a password for encrypting the catalog data
As shown below, we have a user database and Integration Services Catalogs SSISDB.

Suppose you have a user database [TrainingDB] and you want to move it from Instance A to Instance B. Let’s assume both instances are running on SQL Server 2019 RTM. How do you move the database from instance A to instance B?
- Take full database backup on Instance A
- Copy the backup file onto the instance B server
- Restore backup on Instance B SQL Server
Now, think of the above steps from the perspective of the SSISDB. Is it sufficient for you to follow backup and restore method for migrating SSISDB?
Let’s follow the steps for SSIDB migrations in this article.
Steps to take SSISDB SQL database backup
We follow the below steps for taking an SSISDB database backup.
Step 1: Verify SSISDB password
Verify you have the correct password for SSISDB encryption. You can use the following SQL script for verifying the password. If the password is correct, it returns Command Completed Successfully.
|
1 2 3 |
USE [SSISDB]; GO OPEN MASTER KEY DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = N'India@123' |
In case of the wrong password, you get the following error message – The key is not encrypted using the specified decryptor.

Step 2: Back up the master key
It is the most important step for SSISDB SQL database migration. We require the master key backup for the SSISDB database. In the below query, we specify a directory to save the master key backup and specify a password for encrypting it.
|
1 2 |
backup master key to file = 'c:\temp\SQLNode1MasterKey' encryption by password = 'P@ssw0rd' |

Step 3: Take full database backup of the SSISDB SQL database
In step 3, take a full database backup for the SSISDB database. You can take backup either from SSMS graphical interface or T-SQL script. In the below script, we take a full compressed backup in the specified directory.
|
1 |
BACKUP DATABASE [SSISDB] TO DISK = N'c:\sql\SSISDB.bak' WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NAME = N'SSISDB-Full Database Backup', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, COMPRESSION, STATS = 10 |
Step 4 : CREATE LOGIN script for ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##
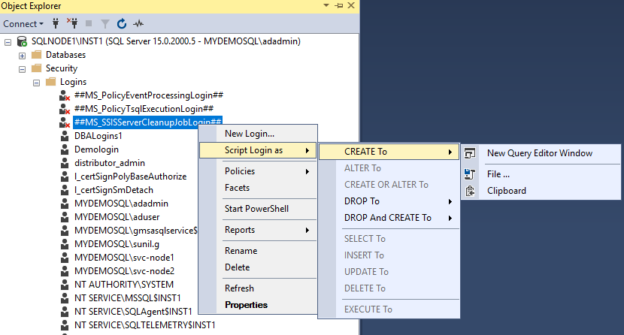
In the next step, you need to connect the Source SQL Server and generate the script ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin## for the SSIS SQL database.
You can generate script manually in SSMS by navigating to Security-> Logins -> Right-click on ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin## -> Script Login as -> Create To -> New Query Editor Window.
Alternatively, you can use the script specified in Move or copy SQL Logins by assigning roles and permissions.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
SELECT 'IF (SUSER_ID('+QUOTENAME(SP.name,'''')+') IS NULL) BEGIN CREATE LOGIN ' +QUOTENAME(SP.name)+ CASE WHEN SP.type_desc = 'SQL_LOGIN' THEN ' WITH PASSWORD = ' +CONVERT(NVARCHAR(MAX),SL.password_hash,1)+ ' HASHED, CHECK_EXPIRATION = ' + CASE WHEN SL.is_expiration_checked = 1 THEN 'ON' ELSE 'OFF' END +', CHECK_POLICY = ' +CASE WHEN SL.is_policy_checked = 1 THEN 'ON,' ELSE 'OFF,' END ELSE ' FROM WINDOWS WITH' END FROM sys.server_principals AS SP LEFT JOIN sys.sql_logins AS SL ON SP.principal_id = SL.principal_id WHERE SP.name ='##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##' |
It generates the CREATE LOGIN statement for the ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin## login.
Now, disable the login using the ALTER LOGIN statement.
|
1 |
ALTER LOGIN [##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##] DISABLE |
Step 5: Generate script for stored procedure sp_ssis_startup and Job SSIS Server Maintenance Job for SSIS
Suppose we want to restore the SSISDB database on a SQL Server instance where the SSISDB catalog is being created for the first time, we require to generate the script for sp_ssis_startup.
Expand master database in SSMS and navigate to Programmability -> Stored Procedure -> right-click on sp_ssis_startup stored procedure -> Choose Script Stored Procedure -> Create To -> New Query Editor Window.
It generates the stored procedure script, as shown below.

Similarly, generate the script for SQL Server agent job SSIS Server Maintenance Job. To generate the job script, expand SQL Server Agent > Job -> Right-click on the job and generate script in a new query window as shown below.

It generates the job script in the MSDB SQL database, as shown below.
Steps to restore integration services (SSIS) SQL database backup on a new Instance
Suppose we want to restore SSISDB on a new SQL Server instance. Therefore, you can follow the below steps.
Step 6: Verify that Integration services is installed on the new instance
SQL Server Integration Service should be running on the new instance as well. If it is not already present, you can install it using the add features to an existing installation option.
As shown below, the Integration Service is installed on the new instance.
SQL Server Integration Service is running.
Step 7: Verify that the Integration services is installed on the new instance
In a new SQL Server instance, run the following query to enable the common language runtime (CLR).
|
1 2 3 4 |
use Master GO sp_configure 'clr enabled', 1 reconfigure |
Step 8: Create the asymmetric key and assign UNSAFE permissions to ##MS_SQLEnableSystemAssemblyLoadingUser## login
In this step, we create the asymmetric key and assign permissions in the following T-SQL.
- Create the asymmetric key. In the executable file, specify the path of Microsoft.SqlServer.IntegrationServices.Server.dll. It exists in the Binn directory of your SQL Server installation directory
- Create the login ##MS_SQLEnableSystemAssemblyLoadingUser## from the asymmetric key
- We need to grant the UNSAFE permission to the ##MS_SQLEnableSystemAssemblyLoadingUser## because this login requires access to Microsoft Wind32 API resources
Step 9: Restore the full SQL database backup
In this step, copy the backup taken in Step 3 and restore SSISDB backup into the new SQL Server instance. It restores the data files on instance default directories.
|
1 2 |
USE [master] RESTORE DATABASE [SSISDB] FROM DISK = N'C:\Backup\SSISDB.bak' WITH FILE = 1, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 5 |
Step 10: Execute the scripts on the new SQL Server instance
In this step, execute the scripts generated in step 4 and step 5 on a new SQL Server instance.
- Create login [##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##]
- Create the stored procedure sp_ssis_startup
- Create the SSIS Server Maintenance Job
We need to set the stored procedure sp_ssis_startup for the automatic execution. It sets the argument in the sp_procoption SP and enables automatic execution on instance restart.

Step 11: Map the SSISDB user ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser## and ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##
In this step, we check the ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser## user in the SSISDB database and if it does not exist, map it with the login ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
USE SSISDB GO If Not Exists(Select * From sys.sysusers Where [name] = '##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##') BEGIN CREATE USER [##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##] FOR LOGIN [##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##] WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA=[dbo] PRINT 'User ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser## created' END ELSE PRINT 'User ''##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##'' already exists' |
Alternatively, you can map the SSISDB user with the corresponding login using the SSMS login properties.
Step 12: Restore the master key
Case1: You have database master key backup and password for encryption from step 2
In this case, consider that you’ve got a backup of the database master key. You have a password used to encrypt the master key as well.
After we restored the SSISDB database and map the SSISDB user, we need to restore the master key using the backup taken in step 2. In the below step, we specify the following passwords.
- Decryption by password: We used the password in step 2 to encrypt the master key
- Encryption by password: Enter a new password
|
1 2 3 4 |
Restore master key from file = 'C:\Backup\SQLNode1MasterKey' Decryption by password = 'P@ssw0rd' Encryption by password = 'P@ssw0rd@New' Force |
It gives the warning message – “The current master key cannot be decrypted. The error was ignored because the FORCE option was specified”. We can ignore this warning message because we use the force argument for restoring the master key.”
Case2: If you have an SSISDB encryption password (Verified from step 1)
If you know the SSISDB encryption password, you can decrypt the encryption key using the altered master key statement for encryption by the service master key.

Verification
You can now connect to the new SQL Server instance, verify the SSISDB catalog and projects, and packages inside it.

You can execute the package from the new instance as well for verification purposes. As shown below, the Integration Service package executed successfully validates the successful migration.
- Note: if you do not have the master key backup from the source server, you might get the following error:
Error 15581: Please create a master key in the database or open the database master key before operating
You should add the master key backup in the backup steps for SSISDB. This way, you can ensure the master key backup is available for restore in case of any issues of SSISDB on the source server.
Conclusion
This article explored the steps for migrating an SSIS catalog SQL database and database to another instance. As discussed in this article, we require a few additional backup and restoration steps for the SSIS package database than a regular user database. You should note these things and plan the backups accordingly to avoid any last-minute failures.
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023