This article walks through different versions of the T-SQL IF EXISTS statement for the SQL database using various examples.
- IF EXISTS in SQL 2014 or before
- DROP ..IF EXISTS in SQL Server 2016 to SQL Server 2019
Introduction
Suppose you want to deploy objects such as tables, procedures, functions in the SQL Server database. If you execute CREATE statements for these objects, and that object already exists in a database, you get message 2714, level 16, state 3 error message as shown below.

You may write a DROP statement before executing the create statement. It works fine if the object exists in the database.
In case the object does not exist, and you try to drop, you get the following error.

To avoid this situation, usually, developers add T-SQL If Exists statement and drop the object if it is already available in the database.
Let’s say we wish to deploy a stored procedure ‘stpGetAllMembers’ in the SQLShack test database. We can use multiple methods to check whether the procedure existence in the SQL database but let’s query sys.objects system table for it.
The following code does the below things for us:
- First, it executes the select statement inside the IF Exists
- If the select statement returns a value that condition is TRUE for IF Exists
- It starts the code inside a begin statement and prints the message
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
IF EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.stpGetAllMembers') ) BEGIN PRINT 'Stored procedure already exists'; END; |

If the procedure does not exist, it does not run the code in a begin statement.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
IF EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.stpGetAllMembers_1') ) BEGIN PRINT 'Stored procedure already exists'; END; |

Now, we want to drop this procedure if it already exists in the database. We can add a DROP PROCEDURE command inside a begin statement. It drops the stored procedure if it already exists in the database.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
IF EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.stpGetAllMembers') ) BEGIN DROP PROCEDURE stpGetAllMembers; END; |
We can use this method with other SQL Server objects as well. The following query checks for the SQL table existence and drops it if it is there.

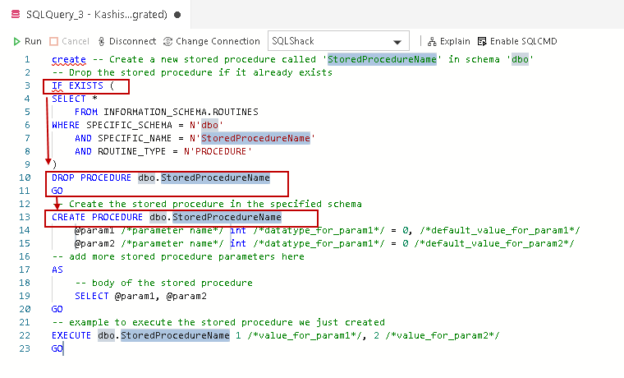
In the article, SQL Code Snippets in Azure Data Studio, we discussed code snippets for writing T-SQL. I thought of checking the syntax for the sqlCreateStoredProc snippet for a new stored procedure.
To view this snippet definition, type create proc, press the sqlCreateStoredProc and enter.
As shown in the following image, this snippet also uses the IF EXISTS method for writing a stored procedure.

DROP IF EXISTS statement
SQL Server 2016 provides an enhancement to check the object’s existence and drop if it already exists. It introduces DROP IF EXISTS command for this purpose.
The syntax for DROP IF EXISTS
DROP OBJECT_TYPE [ IF EXISTS ] OBJECT_NAME
- It drops the object if it already exists in the SQL database
- We can also use it to drop the column or constraints as well
- If the specified object does not exist, it does not give any error message. It continues the execution for the next command
We can use Database, Table, Function, Trigger, Stored Procedure, Column, User, View, Schema, Index, Role for this command.
Let’s understand this new T-SQL IF EXISTS clause using various examples.
DROP Stored Procedure IF EXISTS
In the previous example, we used DROP Stored Procedure stpGetAllMembers for demonstration purposes. This stored procedure does not exist now. Let’s use the new method and try to drop the stored procedure.
|
1 |
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS stpGetAllMembers; |

We can add further code such as print statements, create statements. The following code prints a message after the DROP PROCEDURE command.
|
1 2 |
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS stpGetAllMembers PRINT 'Stored proc does not exist' |
Let’s create the stored procedure using this new syntax T-SQL IF EXISTS command. The following query drops the stored procedure if it already exists, in case it does not exist, it will create one.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS stpGetAllMembers; GO CREATE PROCEDURE stpGetAllMembers AS SELECT table_catalog [database], table_schema [schema], table_name [name], table_type [type] FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES; |
DROP View IF EXISTS
We can use the following query for SQL 2016 or later to drop a view.
|
1 2 |
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS vwABC GO |
In SQL Server 2014 or earlier version, we use the following code. It checks the views using sys.objects for type V.
|
1 2 3 4 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'vwABC') AND type = N'V') DROP VIEW vwABC GO |
DROP Constraint IF EXISTS
We can use the following command to drop a UNIQUE constraint using DROP CONSTRAINT IF EXISTS statement.
|
1 2 |
ALTER TABLE DemoTable DROP CONSTRAINT IF EXISTS EmpID GO |
The following code works in SQL 2014 or before. Type UQ in the sys.objects refers to a UNIQUE constraint.
|
1 2 3 4 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'EmpID') AND type = N'UQ') ALTER TABLE DemoTable DROP CONSTRAINT EmpID GO |
For a check constraint, change the type from UQ to C in the SQL 2014 or before version query. We do not need to change the query specified using DROP CONSTRAINT IF EXISTS statement.
|
1 2 3 4 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'EmpID') AND type = N'C') ALTER TABLE DemoTable DROP CONSTRAINT EmpID GO |
DROP Table IF EXISTS
We can use DROP TABLE IF EXISTS statement to drop a SQL table as well in SQL Server 2016 or later.
|
1 2 |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS DemoTable GO |
For SQL 2014 or previous versions, we need to use IF EXISTS method as shown below. Type U refers to a user-defined SQL table.
|
1 2 3 4 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'DemoTable') AND type = N'U') DROP TABLE DemoTable GO |
DROP Database IF EXISTS
We can use the new T-SQL If Exists scripts for dropping a SQL database as well for SQL 2016 or later.
|
1 2 |
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS TargetDB GO |
Alternatively, use the following script with SQL 2014 or lower version. It is also valid in the higher SQL Server versions as well.
|
1 2 3 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.databases WHERE database_id = DB_ID(N'TargetDB')) DROP DATABASE TargetDB GO |
DROP Column IF EXISTS
Sometimes we require to drop a column from a SQL table. It is a good practice as well to drop unwanted columns as well. It saves efforts for the SQL engine and improves query performance while retrieving fewer records for the output.
We drop a column using the Alter Table statement. We can leverage DROP COLUMN IF EXISTS as well in this alter statement. Suppose we want to drop a Country column from the Employee table. We use the following alter table statement.
|
1 2 |
ALTER TABLE Employee DROP COLUMN IF EXISTS Country GO |
It is a single line and a straightforward query. Alternately, we use the following query using IF Exists. It seems to be more complicated than the earlier one. We should use the latest query syntax with the supported SQL Server versions.
|
1 2 3 4 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.columns Where object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'Employee') AND name = 'Country') ALTER TABLE Employee DROP COLUMN Country GO |
Conclusion
In this article, we explored two different versions of T-SQL IF Exists statements.
- IF EXISTS in SQL 2014 or before
- DROP [Object] IF EXISTS in SQL Server 2016 or later
You should choose the syntax suitable for you. I would recommend the latest one (Drop [object[ IF Exists), if you are on SQL 2016 or later versions.
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023