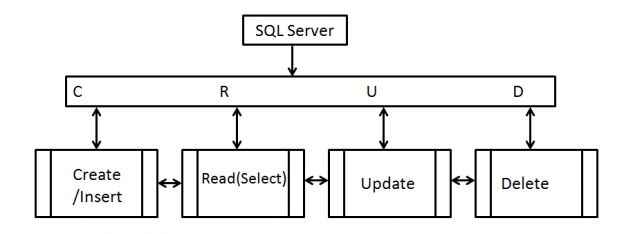
CRUD operations in SQL Server
December 10, 2018CRUD operations are foundation operations every database developer and administrator needs to understand. Let’s take a look at how they work with this guide.

CRUD operations are foundation operations every database developer and administrator needs to understand. Let’s take a look at how they work with this guide.
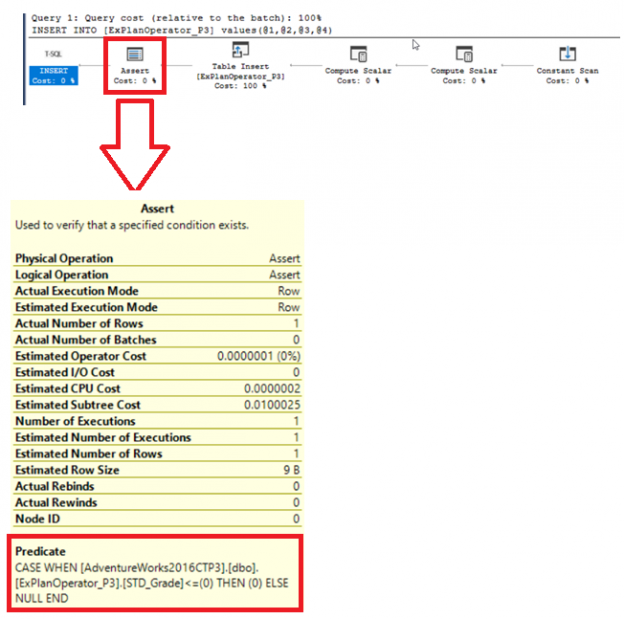
In the previous articles of this series, we discussed a group of SQL Server Execution Plan operators that you will face when studying the SQL Execution Plan of different queries. We showed the Table Scan, Clustered Index Scan, Clustered Index Seek, the Non-Clustered Index Seek, RID Lookup, Key Lookup and Sort Execution Plan operators. In […]
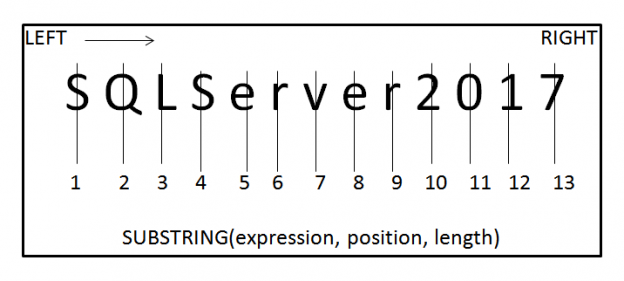
The requirement of data refactoring is very common and vital in data mining operations. In the previous article SQL string functions for Data Munging (Wrangling), you’ll learn the tips for getting started with SQL string functions, including the substring function for data munging with SQL Server. As we all agree that the data stored in […]
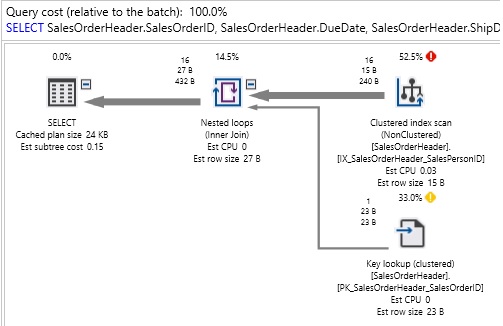
Description Of the many ways in which query performance can go awry, few are as misunderstood as parameter sniffing. Search the internet for solutions to a plan reuse problem, and many suggestions will be misleading, incomplete, or just plain wrong.
Description Fixing and preventing performance problems is critical to the success of any application. We will use a variety of tools and best practices to provide a set of techniques that can be used to analyze and speed up any performance problem!
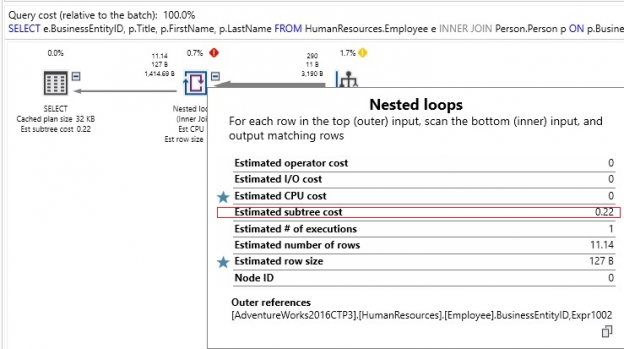
In the previous articles of this series (see the full article TOC at bottom), we discussed the internal structure of both SQL Server tables and indexes, the main guidelines that you can follow to design a proper index, the list of operations that can be performed on the SQL Server indexes, and finally how to […]

This collection of content will provide an overview of top SQL Server books, with Amazon links for each book. The list is a combination of top Amazon SQL Server books (by the highest number of customer reviews) and the books included on other available ‘Top SQL Server books’ lists (see reference links at the bottom) […]
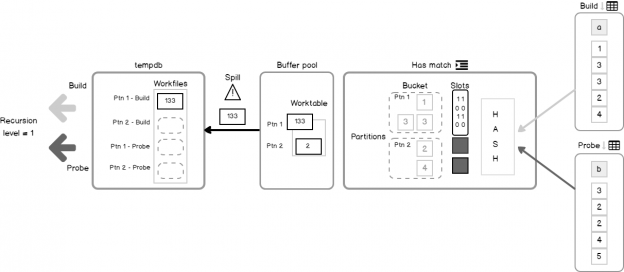
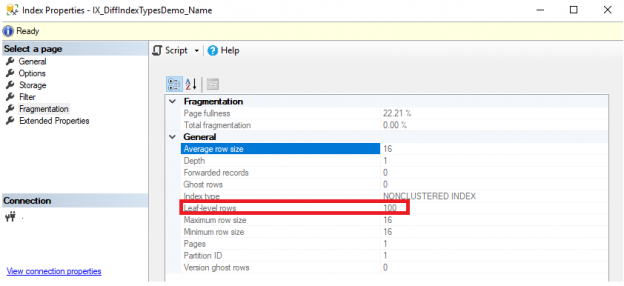
Some time ago, on the 24HOP Russia I was talking about the Query Processor internals and joins. Despite I had three hours, I felt the lack of time, and something left behind, because it is a huge topic, if you try to cover it in different aspects in details. With the few next articles, I’ll […]
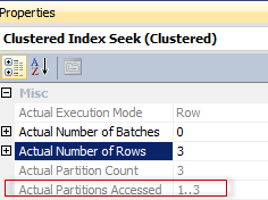
I would like to share one curios case that I recently came across. Long story short: This bug may lead to incorrect results if you use a partitioned table and the FORCESCAN hint. Bug Consider the following example, let’s keep it simple.
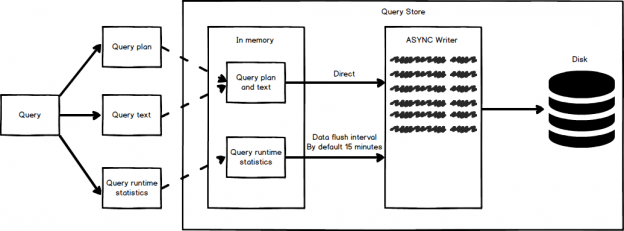
The SQL Server Query Store is a relatively new feature introduced in SQL Server 2016. It is basically a SQL Server “flight recorder” or “black box”, capturing a history of executed queries, query runtime execution statistics, execution plans etc. against a specific database. This information helps in identifying performance problems caused by query plan changes […]
Applies to Operating System Description The current percentage of page file in use. If the Operating System is paging this can be problematic as SQL pages can be pushed into the page file, causing delays for SQL to read what it thinks is in memory from disk. This counter should be as close to zero […]
Applies to SSAS Description An obvious benefit to having aggregations in Analysis Services is that you are likely to have fast running queries at the expense of incurring additional size increase of your Analysis Services database. Having some of the aggregations in memory cache can save you valuable resources. This performance counter measures, in kilobytes […]
Applies to Operating System Description Reports the amount of memory in MB that is available for the operating system to use. The operating system must reserve the sufficient amount of memory in order to keep the SQL Server memory paging to minimum to prevent the dramatic performance degradation. Resolved by DBAs Suggested solutions Increase the […]
Applies to SSIS Description This counter monitors the total number of chunks of memory currently being used by the data flow engine. The value of this performance counter is measured in bytes and fluctuates during package execution. The value is reset whenever the service is restarted. Resolved by DBAs, Server administrators, ETL developers Suggested solutions […]
Applies to SSIS Description When Integration Services runs out physical or virtual memory during process/package execution, it will begin spooling buffers to hard disk. This performance counter measures the total number whereby spooling of buffers to hard disk was done by Integration Services service. An increase in value of this counter may indicate that you […]
Applies to SSIS Description This performance counter measures the actual amount of physical memory currently allocated to the integration services. This memory block cannot be shared with any other processes. The value of this performance counter is measured in bytes and is usually high. The value is reset back to zero whenever the integration server […]
Applies to SSAS Description This performance counter monitors the total number of entries that are currently stored in memory cache of the Analysis Services engine. The value of this counter is reset whenever the service is restarted. Resolved by DBAs, Server administrators, BI developers Suggested solutions Add more physical memory to the computer Partition large […]
Applies to SSAS Description This performance counter measures the total number of sub-cube queries that have been answered from data in memory cache since the Analysis Services service was started. The value of this counter is generally high. It should be compared to Total Misses performance counter to evaluate the percentage of sub-cube queries that […]
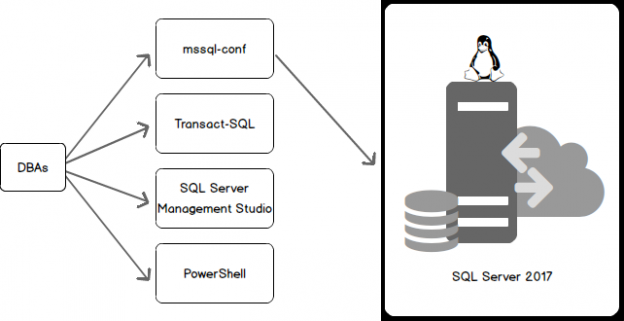
Configuration of any system plays a vital role in its working efficiently. However, configuring a system needs not necessarily be a daunting task. There are several tools that help with the process. SQL Server on Linux provides a wide range of options for configuration, management and administration. mssql-conf Transact-SQL SQL Server Management Studio PowerShell
Description In SQL Server, internal latch architecture protects memory during SQL operations. It ensures the consistency of memory structures with read and write operation on pages. Rudimentarily, it has two classes, buffer latches, and non-buffer latches which perform lightweight synchronization in the SQL Engine.
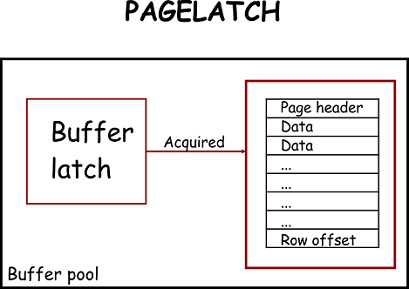
SQL Server locks, discussed in the article All about locking in SQL Server, which is applied on data for the duration of the logical operation to preserve logical transaction consistency. SQL Server latches, however, are a special type of low-level system locks which are held as long as the physical operation lasts on the memory […]
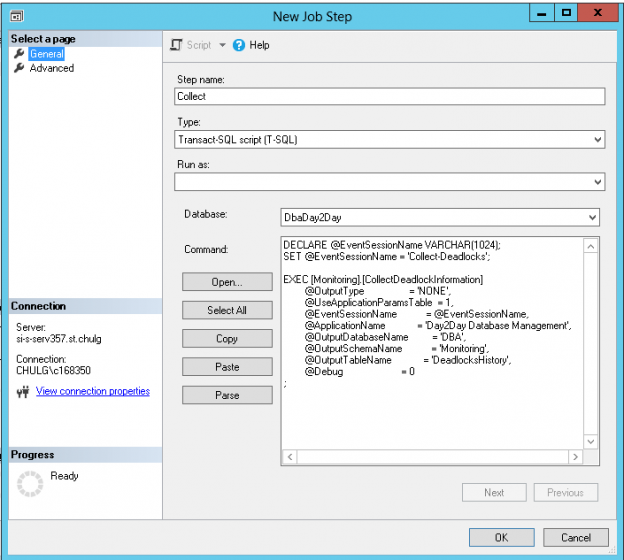
Introduction This article is the last one of a series in which we discussed how to collect data about deadlocks so that we can not only monitor them but also build reports based on our collection results.
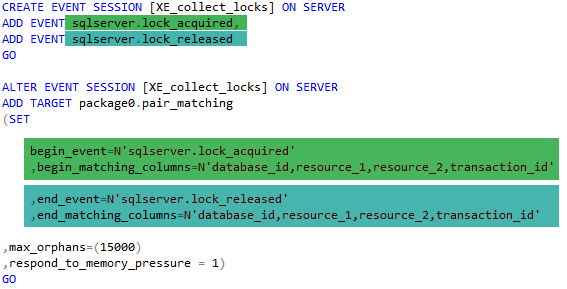
Extended event sessions can use multiple targets to store captured information. We should use different targets depending on the type of data we are capturing and the structure of the data outcome we desire. The available targets include the following: event counter, ring buffer, event file, histogram, event tracing for Windows (ETW), and Event Pairing.
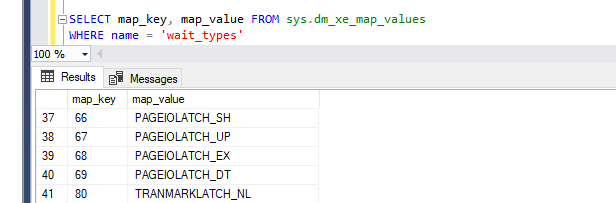
An Extended events target is the destination for all of the information that is captured by Extended Events sessions. You can rely on couple of different targets such as event counter, event file, event tracing for Windows (ETW), ring buffer, event pairing, and histogram.
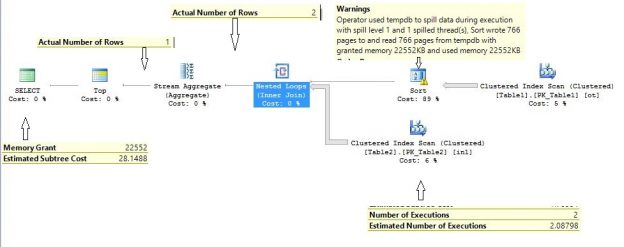
Basics of TOP Operator The TOP keyword in SQL Server is a non-ANSI standard expression to limit query results to some set of pre-specified rows. As an argument, it takes 0 to positive Bigint (9223372036854775807) and anything beyond or less gives an error message. TOP without an order by clause, in production, seems buggy because […]
© Quest Software Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. | GDPR | Terms of Use | Privacy