In the 20th article of the SQL Server Always On Availability Group series, we will explore the process to refresh an availability group database using SQL scripts. In this article, we will use the DBATools commands for this purpose.
Introduction
As we explored earlier, the database refresh for an availability group database requires a few additional steps. At a high level, it requires the following steps:
- Remove the database from the primary replica of SQL Server Always On Availability Group
- Restore a database from the production database backup
- Add the database back to the availability group using manual or automatic seeding
- Validate the AG dashboard synchronization
- Failover to the current secondary replica and validate AG health
DBATools is a collection of useful PowerShell commands, and it helps database professionals to perform the task with minimum steps and less complexity. We have explored many useful DBATools commands on SQLShack. I would suggest you check out those articles as well.
Let’s explore useful DBATools commands for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups.
Install DBATools PowerShell module for SQL Server
To install the DBATools PowerShell module, run the following command. It downloads the module using an internet connection and installs it. You can refer to the article, DBATools PowerShell Module for SQL Server for detailed information.
|
1 |
>Install-Module DBATools |
Explore DBATools commands for SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Once we have installed the DBATools in the system, you can try exploring the commands for SQL Server. Here, I specify a few useful commands for availability groups.
Get-DbaAgReplica cmdlet to retrieve AG information
We can retrieve information about the availability group replicas. You can identify primary, secondary replica instances using this module.
It uses an argument -SqlInstanceName, and we can specify any of the primary replica, secondary replica or the SQL listener name in it.
In the below query, we input the SQL listener name (SQLShackLSN) and filtered output to return specific columns in the output such as Instance name, role, connection state, Synchronization status, Endpoint URL.
|
1 |
> Get-DbaAgReplica -SqlInstance SQLShackLSN | select |
Similarly, if we specify the primary replica SQL instance in the -SqlInstanceName parameter, it returns the same information.
In the below script, we do the following tasks:
- We used variable $SQLlistener and $availabiltyGroup to input the listener and availability group name
- We used the Get-DbaAgReplica command to gather information about AG and stored this information in a data set $availabilityGroupReplicas
-
In the next part, we filtered the information from the data set variable
- $primaryreplica: It stored the primary SQL instance in the AG
- $secondaryreplica: It stored the secondary SQL instance in the AG
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
$SQLlistener = "SQLShackLSN" $availabilityGroup = "SQLShackDemoAG" $availabilityGroupReplicas = Get-DbaAgReplica -SqlInstance $SQLlistener -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup $primary replica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Primary').Name $secondaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Secondary').Name $primaryReplica $secondaryReplica |
Remove-DbaAgDatabase cmdlet to remove the SQL Server Always On Availability Group database
It removes the database from the specified availability group. We specify the availability group name and the SQL instance to remove the specified database.
In this article, we need to restore the AG database [SQLShackDemo] from the production backup copy. Therefore, we need to remove this database from the availability group. Before dropping the database from the availability group, verify that AG is synchronized using a dashboard.

In the below script, we used the Remove-AGDatabase command and removed the database from the availability group. We stored the database name in a variable $databasename.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
$SQLlistener = "SQLShackLSN" $availabilityGroup = "SQLShackDemoAG" $databasename='SQLShackdemo' $availabilityGroupReplicas = Get-DbaAgReplica -SqlInstance $SQLlistener -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup $primary replica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Primary').Name $secondaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Secondary').Name Remove-DbaAgDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup -Database $databasename |
It asks for confirmation before proceeding with the operation. If you want to disable this prompt, add –Confirm:$false in the Remove-DbaAGDatabase command.
In the output, it confirms the status that the database [SQLShackDemo] is removed from the availability group.
You can verify in the AG dashboard that it does not show any database.

Restore-DbaDatabase cmdlet to restore a SQL database
The Restore-DBADatabase command is for restoring the database backup. As we have removed the database from the availability group, it is similar to a standalone database. You can go through SQL Restore Database using DBATools for the detailed implementation of this command.
In the below script, we did the following tasks:
- Defined a variable to store the backup directory
- We already removed the database in the previous command, so commented the line for Remove-DbaAgDatabase
- We use the Restore-DbaDatabase command and specify the database name, backup directory and use the option -WithReplca to replace the existing database on the primary replica
- In my case, the backup file is C:\SQL\SQLShackDemo; therefore, I specify the path using the variables (“$backupDirectory\$databasename.bak) followed by backup file extension
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
$SQLlistener = "SQLShackLSN" $availabilityGroup = "SQLShackDemoAG" $databasename='SQLShackdemo' $backupDirectory='C:\SQL' $availabilityGroupReplicas = Get-DbaAgReplica -SqlInstance $SQLlistener -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup $primaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Primary').Name $secondaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Secondary').Name #Remove-DbaAgDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup -Database $databasename Restore-DbaDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -DatabaseName $databasename -Path "$backupDirectory\$databasename.bak" -WithReplace |
DBATools restores the database with the specified configuration and gives the following output.
Remove-DbaDatabase DBATools command
Earlier, we removed the database from the availability group using the Restore-DBADatabase cmdlet. It does not remove the secondary database. To remove the secondary database, we can use the Remove-DbaDatabase command of the DBATools.
In the Remove-DbaDatabase, we specify the secondary replica name (using variable $secondaryReplica), database name (using variable $databasename) and use the argument confirm:$false to disable confirmation prompt.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
$SQLlistener = "SQLShackLSN" $availabilityGroup = "SQLShackDemoAG" $databasename='SQLShackdemo' $backupDirectory='C:\SQL' $availabilityGroupReplicas = Get-DbaAgReplica -SqlInstance $SQLlistener -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup $primaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Primary').Name $secondaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Secondary').Name #Remove-DbaAgDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup -Database $databasename #Restore-DbaDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -DatabaseName $databasename -Path "$backupDirectory\$databasename.bak" -WithReplace Remove-DbaDatabase -SqlInstance $secondaryReplica -Database $databasename -Confirm:$false |
It dropped the database [SQLShackDemo] from the secondary replica [SQLAG2\INST1] as shown below:
Add the database into the SQL Server Always On Availability Group
Once we have restored the database into the primary replica and dropped the existing database from the secondary replica, we can add it back to the availability group using the Add-DbaAgDatabase.
We can use the automatic seeding from SQL Server 2016 to initialize a database in the secondary replica. It eliminates the need to take a backup from the primary replica, restore on the secondary replica instance.
You can refer to this article, Automatic Seeding in Always On Availability Groups to understand automatic seeding process in detail.
In the Add-DbaAgDatabase command, we specify the primary replica, availability group under which this database should exist, database name and seeding mode. In case you use the backup restore method for secondary database initialization, use the manual seeding mode.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
$SQLlistener = "SQLShackLSN" $availabilityGroup = "SQLShackDemoAG" $databasename='SQLShackdemo' $backupDirectory='C:\SQL' $availabilityGroupReplicas = Get-DbaAgReplica -SqlInstance $SQLlistener -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup $primaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Primary').Name $secondaryReplica = ($availabilityGroupReplicas | Where-Object role -eq 'Secondary').Name #Remove-DbaAgDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup -Database $databasename #Restore-DbaDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -DatabaseName $databasename -Path "$backupDirectory\$databasename.bak" -WithReplace #Remove-DbaDatabase -SqlInstance $secondaryReplica -Database $databasename -Confirm:$false Add-DbaAgDatabase -SqlInstance $primaryReplica -AvailabilityGroup $availabilityGroup -Database $databasename -SeedingMode Automatic |
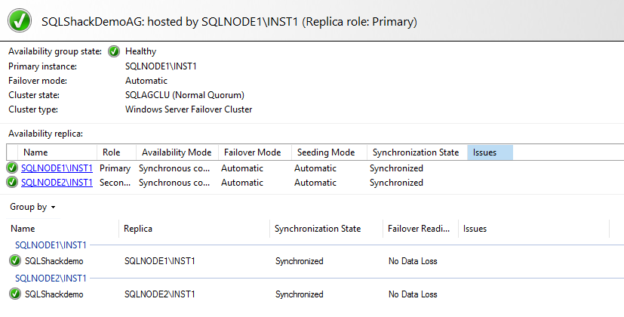
It adds the database successfully in the availability group replicas. As shown in the below screenshot, both the primary and secondary replica databases are in Synchronized mode.
To validate manually, connect to the primary replica and launch the availability group dashboard. As shown below, the dashboard is healthy.

If you get regular database refresh requirements for the SQL Server Always On Availability Group, you can schedule the scripts, and it automates the tasks database refresh for you. You can also add commands to take production database backup and put it in a shared location. In this way, you do not require copy files into the development environment manually.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored useful commands for DBATools PowerShell to refresh a SQL Server Always On Availability Group database. DBATools scripts are easy to write and implement. It makes database professional life more manageable. I recommend you to explore these as per your requirements.
Table of contents
See more
For High-speed SQL Server backup, compression and restore see Quest LiteSpeed, an enterprise tool to schedule, automate and backup SQL databases

- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023