In this 20th article for the SQL Server Always On Availability Group series, we will cover the steps to restore an existing availability group database.
Requirement
Suppose we have multiple database environments for a critical application. These environments can be development, stage, UAT (user acceptance testing). You might have configured the development database also in an availability group configuration. Usually, developers ask to refresh the development databases from production data. It helps them to test the code for production data before actual production implementation. Refreshing the lower environment databases might be a regular(monthly) activity as well, so you can automate the steps easily using the SQL scripts.
You might think a question here– We can take production database backup and restore it on the development database. What difference does it make in a standalone database restore or availability group database restore?
Database restore works with the standalone database, but if the database is configured in the availability group, we cannot directly restore the database. It requires additional steps because of the AG configurations. Our database should be in the same state (AG synchronized) after the database restores as well.
In this article, let’s cover the steps to restore an existing availability group database in the SQL Server Always On Availability Group.
Prerequisites
You should have two or more nodes in SQL Server Always On Availability Group configuration.
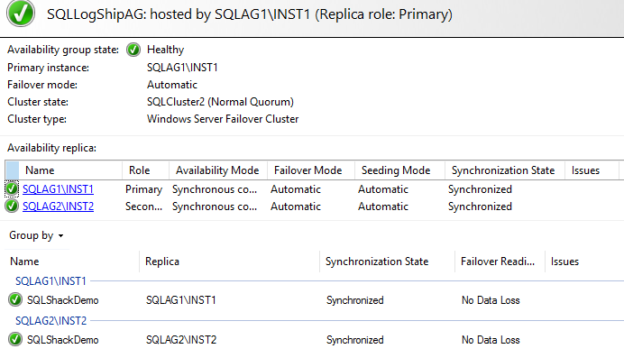
In this article, we have the following environment for demonstration purposes,
- Nodes: SQLAG1 & SQLAG2
- Availability Group: [SQLLogShipAG]
- Database: [SQLShackDemo]
- Synchronization state: Synchronized
- Failover Mode: Automatic
- AG dashboard: Healthy
You can follow the SQL Server Always On Availability Group series (ToC at the bottom) to prepare the complete AG environment for this article. You should also understand the availability group concepts to be familiar with its terminology.
Steps to restore an availability group database in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Suppose you require to restore the [SQLShackDemo] database from the production to the development environment. In my development environment, the database is part of the availability group.
I took the production database full backup and copied the backup file on the development server. To restore this backup on a development instance, right-click on the development [SQLShackDemo] database and navigate to Tasks -> Restore-> Database. In the restore database wizard, specify the backup file location and click ok. You will get the following error message.

As per the error message, we cannot restore the database because it is part of an availability group. To restore the availability group database, we need to evict the database from the availability group, restore the database, and add in the availability group. Let’s explore the details step and restore the database.
Step 1: Remove the database from an availability group in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Connect to the primary replica instance in SSMS and expand availability databases. You might have multiple availability groups in a SQL instance. You need to remove the specific database from the availability group.
Right-click on the database and click on Remove Database from Availability Group…

It opens the following remove database from the availability group wizard.

You can also generate the script from this wizard. It uses the Alter availability group statement with the Remove database clause.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
USE [master] GO ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [SQLLogShipAG] REMOVE DATABASE [SQLShackDemo]; GO |
It removes the database from the availability group, so if you refresh the AG dashboard, it shows you the following error and warnings. It shows synchronization status also as Not Synchronizing in the dashboard.

Click on the critical error in the availability group state. It does not point to you that there is no database in the availability group. It says that some availability replicas are not synchronizing data.

Step 2: Restore the database from the production backup in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups
Now, you can restore the database similar to a standalone database. The database is in the online status on the primary replica; therefore, in the restore wizard, it asks you for the tail-log backup.

Click on Options and do the following tasks.
- Remove the tick from the Take tail-log backup before the restore. We do not want any tail-log backup and want to restore the production database backup. You can refer to Tail-Log Backup and Restore in SQL Server for more details on tail-log backups
- Put a check on the Close existing connections to the destination database. It removes all existing database connections and makes the database available for the restore. If you do not put this check on the restore wizard and the database has existing connections, you get an error message about existing connections. In that case, you have to close all existing connections using the KILL SPID statement manually

Click Ok to start database restore. You get another error because the database is online, and we have a disabled tail-log backup. We need to replace the database using WITH REPLACE clause in the restore database statement.

To replace the database, put a check on the Overwrite the existing database (WITH REPLACE).

It restores the [SQLShackDemo] successfully. The database restoration time depends upon the database size and the storage disk IOPS.

Step 3: Add database back in the SQL Server Always On Availability Group
In the previous step, we restored the database on the primary replica. This database needs to be added again to the availability group.
In the primary replica availability group, right-click on the availability databases and add the database.

In the Add Database to Availability Group wizard, select the database SQLShackDemo. This database meets prerequisites for the AG.

Connect to existing secondary replicas.

In the next part, we need to select how data synchronization happens from the primary to the secondary replica. You can prepare your database before adding it to the availability group.

To prepare the secondary database, You can do the following tasks.
- Take a full and transaction log backup on the primary replica
- Restore these backup in the secondary replica in NORECOVERY mode
In this article, we use the automatic seeding that creates the secondary database automatically. It also synchronizes both primary and secondary replicas. You must have good network bandwidth for the automatic data seeding, especially for a vast database.
In my case, the database size is small, so that we can go ahead with the automatic seeding. In the next step, it performs validation.
We get an error message in the below screenshot. In the step1, we removed the database from the primary replica availability group. It evicts the database from the AG but does not remove the secondary replica database. The secondary replica database goes into the restoring mode.
We need to connect to the secondary replica instance and delete the database manually if you use automatic seeding. In the case of backup restore, we can use the WITH REPLACE clause to replace the existing database.

To resolve this error, execute the following script on the secondary replica instance.
- It deletes the backup history for the [SQLShackDemo] database from the MSDB
- It drops the database
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_delete_database_backuphistory @database_name = N'SQLShackDemo' GO USE [master] GO DROP DATABASE [SQLShackDemo] GO |
After dropping the database, click on re-run validation, and it shows successful validations.

Verify your choices in the add database wizard. We can note that it adds [SQLShackDemo] database in the [SQLLogShipAG] availability group using automatic seeding.

In the next step, verify the results. It adds the database in the availability group.

Verify the availability group database in the object explorer and dashboard.

Conclusion
In this article, we explored the overall process to restore an availability group database in the SQL Server Always On Availability Group.
Table of contents
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023