This article explains the SQL Server single-user mode and how to configure an automated email alert when the state of the user database changes to the single-user mode. To send an alert, we will create a DDL trigger that executes when the user runs the ALTER DATABASE query. It collects the pieces of information using EVENTDATA() function, saves it in a temporary table, and sends an HTML formatted email.
First, let me give you the summary of DDL triggers, EVENTDATA() function, and SQL Server single-user mode.
What are DDL triggers
SQL Server DDL trigger is a special procedure that is executed when any server-scoped or database-scoped event occurs. For example, a DDL trigger could be executed if we create a new database using the CREATE DATABASE command or alter the configuration of the database using the ALTER DATABASE command. It can be executed when any database scope event occurs, for example, if we create a table using the CREATE TABLE command, change the table structure using the ALTER TABLE command, or truncate the data from the table using TRUNCATE TABLE command. The changes are recorded in an XML format, which can be accessed using the EVENTDATA() function.
You can view the server scoped database in SQL Server Management Studio’s Object Explorer in the Triggers folder. To view it, navigate to SQL Server Database Engine | Server Objects | Triggers. See the following image:

You can also view database scoped triggers, just navigate to SQL Server Database Engine | database_name | Programmability | Database Triggers. See the following image:

Alternatively, you can view the database trigger by executing the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT name, object_id, type_desc, create_date FROM sys.triggers; |
Following is the output:

You can view the server scoped triggers by executing the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
SELECT name AS [Trigger Name], TriggerEvent.type_desc AS [Event], Triggers.type_desc AS [Trigger type], create_date FROM sys.server_trigger_events TriggerEvent INNER JOIN sys.server_triggers Triggers ON TriggerEvent.object_id = Triggers.object_id; |
Following is the output:

You can read Database Level DDL Triggers for Views, Procedures and Functions article to understand the concept of DDL triggers in detail.
What is EVENTDATA() function
As I mentioned, we are going to use the EVENTDATA() function in the DDL trigger to populate the data. It captures the XML-formatted data about the event that occurred in the DDL trigger. Following are the keynotes about the EVENTDATA() function:
- EventData returns data when directly referenced directly inside the DDL trigger
- The definition of the all events are in: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\100\Tools\Binn\schemas\sqlserver\2006\11\events\events.xsd
- The data becomes invalid after the transaction that called the EVENTDATA()
-
The EventData schema returns the following details:
- Type of event
- The timestamp of the event
- The SPID of the connection that executed the trigger
- Server Name
- Login Name
- T-SQL Query/command
SQL Server single-user mode
When the database is in the single-user mode, only one user can connect to the SQL Server instance. When you set the database to single-user mode, the following will happen. All the other connections will be closed automatically without a warning. When the database is in the single-user mode and if any user or application tries to connect the database, it gets the following error:
Msg 924, Level 14, State 1, Line 1
Database ‘DBA’ is already open and can only have one user at a time.
To put any user database in SQL Server single-user mode, you can use any of the following methods:
Using SQL Server Management Studio
To put a database to SQL Server single-user mode, open SQL Server Management Studio, expand Database Engine, right-click on the database which you want to put it in single-user mode, and select database properties. See the following image:

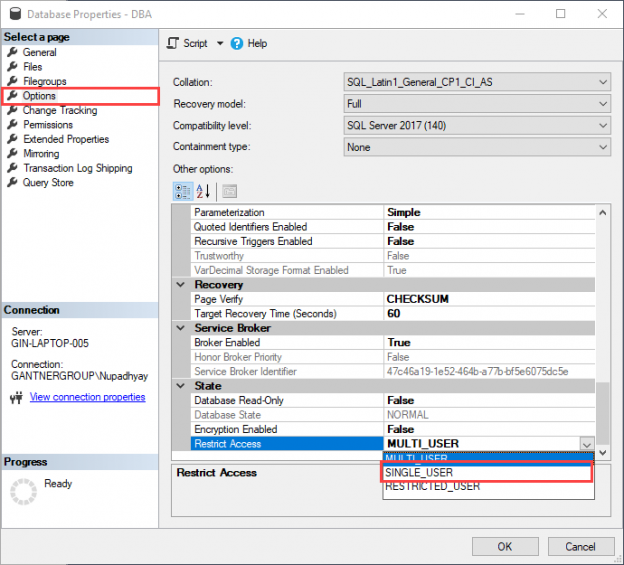
In the Database Properties dialog box, click on Options, and from the Restrict Access drop-down box, select SINGLE_USER and click OK. See the following image:

Using T-SQL query
Alternatively, you can use the following command to put any user database in SQL Server single-user mode:
Alter database <UserDatabaseName> set single_user with <Termination_Option>
Alter database set single_user command can be combined with the following three termination options:
- With rollback immediate: When you use rollback immediate option, it rollback all the active incomplete transactions and put the database in SQL Server single-user mode
- With rollback AFTER [INT] SECONDS: When you use rollback after option, it will rollback all the active incomplete transactions after the seconds specified in the command
- With NO_WAIT: When you use NO_WAIT, it will try to run the ALTER database command. If the command cannot change the option, then the process which is running the alter database command terminates itself
Configure the SQL Server Database Mail
SQL Server Database Mail is used to send the email using the Database Engine. This is handy when we want to send the query result, configure any alert or notification. SQL Server Database Mail uses the SMTP protocol to send emails.
Now, to send the email notification, I am going to use my personal email account. I am using Microsoft Outlook; hence, I will use the SMTP configurations of Microsoft Outlook. I am adding SMTP server details of Gmail Outlook and Microsoft Live/Hotmail.
Mail service providers | SMTP server name | Port |
Microsoft Hotmail | smtp.live.com | 587 |
Gmail | smtp.gmail.com | 587 |
Microsoft Outlook | smtp.office365.com | 587 |
To configure the database mail, you should enable the database mail feature in SQL Server. To do that, you must run the following query in sequence:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
/*Enable advanced option*/ sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO /*Enable database mail*/ sp_configure 'Database Mail XPs', 1; GO RECONFIGURE GO |
Following is the output:

Once database mail is enabled, execute the following scripts to configure Database Mail. We must run these queries in the proper sequence:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
/*Configure SQL Database mail using the SMTP server of Microsoft Outlook*/ EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_account_sp @account_name = 'Database_Mail_Account', @email_address = 'nisargupadhyay87@outlook.com', @mailserver_name = 'smtp.office365.com', @port=587, @enable_ssl=1, @username='nisargupadhyay87@outlook.com', @password='<YourPassword>' /*Create database mail profles*/ EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profile_sp @profile_name = 'Database_Mail_Profile', @description = 'DB Mail Service for SQL Server' /*Add database mail account to the profile*/ EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profileaccount_sp @profile_name = 'Database_Mail_Profile', @account_name = 'Database_Mail_Account', @sequence_number =1 ; /*Grant access to the database mail profile*/ EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_principalprofile_sp @profile_name = 'Database_Mail_Profile', @principal_id = 0, @is_default = 1 |
To configure Database Mail profile and database mail account, execute the following queries in SQL Server Management Studio:

You can review Database Mail settings by executing the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
SELECT p.NAME AS ProfileName, email_address AS [EmailAddress], display_name AS [Display Name], servername AS [SMTP Server Name], port AS [Prot Number], enable_ssl AS [Is SSL enabled?] FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_profile p JOIN msdb.dbo.sysmail_profileaccount pa ON p.profile_id = pa.profile_id JOIN msdb.dbo.sysmail_account a ON pa.account_id = a.account_id JOIN msdb.dbo.sysmail_server s ON a.account_id = s.account_id |
Following is the output:

If you, for some reason, get into trouble while setting up Database Mail – check out the following detailed article on this subject: How to configure database mail in SQL Server
T-SQL script of DDL trigger
The DDL trigger executes when the ALTER DATABASE command issues on the SQL Server database. The trigger collects details of command, processID, time and from EVENTDATA() function and stores it in the temporary table named #TempAudit. See the following code fragment:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
create table #TempAudit (Command varchar(50),SQLCommand varchar(5000),LoginName varchar(100),DBName varchar(500)) Insert into #TempAudit SELECT EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/EventType)[1]','nvarchar(max)') , EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/TSQLCommand/CommandText)[1]','nvarchar(max)') , EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/LoginName)[1]','nvarchar(max)') , EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/DatabaseName)[1]','nvarchar(max)') |
To display the T-SQL Command, SQL Query, LoginName, and database name in tabular format, we have created a dynamic SQL query with HTML tags and save the query in @tableHTML variable. See the following code fragment:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
DECLARE @subject NVARCHAR(max) DECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(max) SET @subject = 'Critical Alert: Database State has been changed on : ' + @@servername SET @tableHTML = ' <html><Body><style type="text/css">table {font-size:9.0pt;font-family:verdana;text-align:left;}tr {text-align:left;} h3 {display: block;font-size: 15.0pt;font-weight: bold; font-family: verdana; text-align:left; } </style><H3>Critical Alert: Database State has been changed on '+ @@servername + '</H3>' + N'<table border="1">' +N'<tr><th>Command</th><th>SQL Query</th><th>Command Executed By</th><th>Database Name</th></tr>' + Cast((SELECT Command AS 'TD', '', SQLCommand AS 'TD', '', LoginName AS 'TD', '', DBName AS 'TD', '' FROM #TempAudit FOR xml path ( 'tr' ), root) AS NVARCHAR(max)) + N'</table> </html> </Body>' |
Using SQL Server Database Mail, it sends the data to the desired recipients. See the following code fragment:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
EXEC msdb..Sp_send_dbmail @profile_name = 'TestDBMail', @recipients = 'nisargupadhyay87@outlook.com', @subject = @subject, @importance = 'High', @body = @tableHTML, @body_format = 'HTML'; Drop table #TempAudit |
Following is the entire script of the database trigger:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.server_triggers WHERE name = 'ddl_trig_changedbstat') DROP TRIGGER ddl_trig_changedbstat ON ALL SERVER; GO CREATE TRIGGER ddl_trig_changedbstat ON ALL SERVER FOR ALTER_DATABASE AS create table #TempAudit (Command varchar(50),SQLCommand varchar(5000),LoginName varchar(100),DBName varchar(500)) Insert into #TempAudit SELECT EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/EventType)[1]','nvarchar(max)') , EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/TSQLCommand/CommandText)[1]','nvarchar(max)') , EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/LoginName)[1]','nvarchar(max)') , EVENTDATA().value('(/EVENT_INSTANCE/DatabaseName)[1]','nvarchar(max)') DECLARE @subject NVARCHAR(max) DECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(max) SET @subject = 'Critical Alert: Database State has been changed on : ' + @@servername SET @tableHTML = ' <html><Body><style type="text/css">table {font-size:9.0pt;font-family:verdana;text-align:left;}tr {text-align:left;} h3 {display: block;font-size: 15.0pt;font-weight: bold; font-family: verdana; text-align:left; } </style><H3>Critical Alert: Database State has been changed on '+ @@servername + '</H3>' + N'<table border="1">' +N'<tr><th>Command</th><th>SQL Query</th><th>Command Executed By</th><th>Database Name</th></tr>' + Cast((SELECT Command AS 'TD', '', SQLCommand AS 'TD', '', LoginName AS 'TD', '', DBName AS 'TD', '' FROM #TempAudit FOR xml path ( 'tr' ), root) AS NVARCHAR(max)) + N'</table> </html> </Body>' EXEC msdb..Sp_send_dbmail @profile_name = 'TestDBMail', @recipients = 'nisargupadhyay87@outlook.com', @subject = @subject, @importance = 'High', @body = @tableHTML, @body_format = 'HTML'; Drop table #TempAudit GO |
Test DDL trigger
To test the trigger, we will change the DBA database to SQL Server single-user mode. Following T-SQL query changes the state of DBA database to SQL Server single-user mode:
|
1 |
Alter database [DBA] set single_user with rollback immediate |
Once the command executed successfully, the database mode changes to a single-user, and I received an email notification in my mailbox. See the following screenshots:

Following is the screenshot of the email:

Conclusion
In this article, I have explained about the DDL Triggers, SQL Server single-user mode, and EVENTDATA() function. I have also explained the DDL trigger, which can be used to send an email alert when any user changes the mode of the database.
- Different ways to identify and change compatibility levels in SQL Server - July 22, 2024
- Copy SQL Databases between Windows 10 and CentOS using SQL Server data tools - October 19, 2022
- Changing the location of FILESTREAM data files in SQL Database - October 14, 2022