In this article, I am going to explain how to set up your Visual Studio Code for Python Development. Visual Studio Code or, popularly known as VS Code, is one of the free and open-source code editors developed by Microsoft and is mostly preferred by developers of all the major programming languages due to its flexibility and other integrated development tools like debugging, IntelliSense, etc. Visual Studio Code is available to be downloaded for all the major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS. You can visit https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/ to download it based on the OS you are using.
Download and Install Visual Studio Code
As I have already mentioned, VS Code can be downloaded and installed on any of the operating systems. For the sake of this article, I am going to show how to install the same on Windows. Also, I will be using Windows as the development environment for setting up the python environment also. For Linux and macOS, the process will be almost similar; however, there might be some changes in the commands.
Navigate to https://code.visualstudio.com/download and select the appropriate platform to install the software. I am going to choose Windows, System Installer 64 bit, and proceed with the installation:
Figure 1 – Download Visual Studio Code for Windows
Once the download is completed, proceed with the normal installation. After the installation is successful, you can see Visual Studio Code being started, which looks like below:
Figure 2 – Visual Studio Code Started
Download and Install Python
Once Visual Studio Code is up and running, the next thing that we would need to set up is a python runtime environment. Again, we can install python on all three operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS. Let us first navigate to https://www.python.org/downloads/ and download Python 3.8.3:
Figure 3 – Download Python 3.8.3
Once python has been downloaded and installed, you can open up the command prompt and run the following command to verify if the installation has been successful.
python –version
If python has been installed successfully, this command will return the version of the python that has been installed. I have previously downloaded python, and my installed version is 3.8.1 and not 3.8.3:

Figure 4 – Verify Python Installation
Now that both the pre-requisites are installed, we can go ahead and start setting up the development environment for Visual Studio Code for python.
Install the Python extension for VS Code
First things first. By default, VS Code works just like a simple text editor and has no built-in support for python. What I mean by the previous statement is even though you can write python code in VS Code now, you won’t be able to leverage some of the developer tools or techniques that make writing code a lot easier. For example, let us start creating a python file with the name “main.py”, import the JSON module and print the statement “Hello World”. As you write the code, you can see that there is no auto-complete or no IntelliSense provided by the code editor and you need to write the entire statement on your own:

Figure 5 – Setting up Visual Studio Code for Python
To avoid that, we need to install the Python extension for Visual Studio Code by navigating to https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-python.python and download the extension:
Figure 6 – Download Python extension for Visual Studio Code
Alternatively, you can also hit the Extensions icon in the left-hand pane inside Visual Studio Code and search for the keyword “python”. Select the extension which is provided by Microsoft and click on Install. I have already installed the extension on my machine:
Figure 7 – Search and Install the Python extension for VS Code
As soon as the Python extension has been installed, you can see that a “Run” button on the extreme right-hand top appears using which you can run the python file directly within the integrated terminal in VS Code. Also, another thing that you can notice here is that you get several options as to how would you like to run the open python file:
Figure 8 – Features from the Python extension
Another point that you might notice after installing this extension is that it provides us with some sort of handy documentation when we hover the cursor over a specific object. For example, in the same file, if we hover over the keyword “json”, you can now see that a small tooltip is visible, which contains information about the json module. You can scroll below and find other information regarding how to use the module and so on:

Figure 9 – Documentation support in VS Code
IntelliSense in Visual Studio Code for Python
Secondly, talking about IntelliSense, you can see that it has now been enabled, and you can easily get the autocomplete keywords from a drop-down. For example, if you now start typing “import”, the editor will automatically start suggesting keywords that match the word as you are typing. This helps to achieve a faster speed in writing code as you need not manually type the entire words to make the script work:

Figure 10 – Intellisense in Visual Studio Code for Python
Snippets in Visual Studio Code
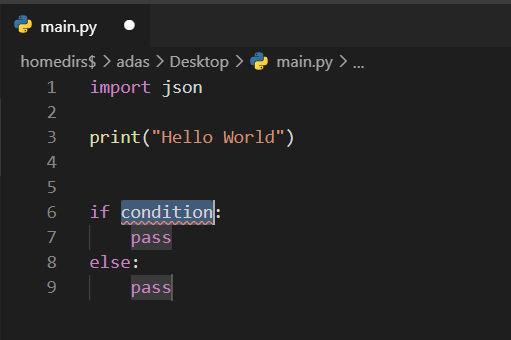
Snippets come in quite handy when you need to implement a block of statements in your code without having to write the entire syntax. You can consider this as a code template for a block such as an if-else block, and for statement block or a try-catch block. Let us now go ahead and try to write an if-else block by using the code snippet:

Figure 11 – Using the If Else code snippet
As soon as you select the if/else code snippet, you can see that a block of pre-defined code appears on the editor, and you can just edit the values without altering the block. You can use the “TAB” key and jump from the condition to the pass values:

Figure 12 – If Else Snippet
Debugging in Visual Studio Code for Python
One of the most important requirements while developing code is to set up a debugger, which can be used to execute the script line by line as the interpreter starts executing the program. It is useful to identify local variables and also potential bugs in the code by stepping over each line as the code executes. To start debugging the code, click on the Debug icon on the left-hand pane and select “Run and Debug”:

Figure 13 – Run and Debug Code
Select “Python File” from the Debug configuration drop-down, and that is it. You can now see that your code has been successfully executed by the debugger and the output is available on the terminal window below:
Figure 14 – Debugging Python code in Visual Studio Code
You can also attach breakpoints to your code by clicking on the left-hand side of the line number. This will add a red dot on that line, which means that the debugger will stop on that line and wait for your command before moving forward. You can use the navigation buttons to step forward and backward through your code and also see the variable values on the left hand “Variables” pane:
Figure 15 – Debug session in VS Code
Conclusion
In this article, I have explained how to download and install Visual Studio Code on your local machine and how to install an extension inside VS Code. I have also explained how to set up the Visual Studio Code for Python programming by installing the necessary extensions, which offers the developers with much more flexibility and IntelliSense and helps in writing code faster in a more productive way. Although in the article, I have mentioned only one extension as I am using it, there are a plethora of extensions that you can use to set up and customize your development environment accordingly. All the extensions for Visual Studio Code can be found in the marketplace for Visual Studio Code. I will write another article with a few more important articles that we can use to make or work more productive.
Table of contents
- Getting started with PostgreSQL on Docker - August 12, 2022
- Getting started with Spatial Data in PostgreSQL - January 13, 2022
- An overview of Power BI Incremental Refresh - December 6, 2021