In this article, we will explore various SQL Convert Date formats to use in writing SQL queries.
We need to work with date type data in SQL. It can be a complicated thing to deal with, at times, for SQL Server developers. Suppose you have a Product table with a column timestamp. It creates a timestamp for each customer order. You might face the following issues with it
- You fail to insert data in the Product table because the application tries to insert data in a different date format
- Suppose you have data in a table in the format YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm: ss. You have a daily Sales report, and in that, you want data group by date. You want to have data in the report in format YYYY-MM-DD
We do face many such scenarios when we do not have a date format as per our requirement. We cannot change table properties to satisfy each requirement. In this case, we need to use the built-in functions in SQL Server to give the required date format.
Data Types for Date and Time
We have the following SQL convert date and Time data types in SQL Server.
Date type | Format |
Time | hh:mm:ss[.nnnnnnn] |
Date | YYYY-MM-DD |
SmallDateTime | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss |
DateTime | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.nnn] |
DateTime2 | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.nnnnnnn] |
DateTimeOffset | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.nnnnnnn] [+|-]hh:mm |
In SQL Server, we have used built-in functions such as SQL GETDATE() and GetUTCDate() to provide server date and format in various formats.
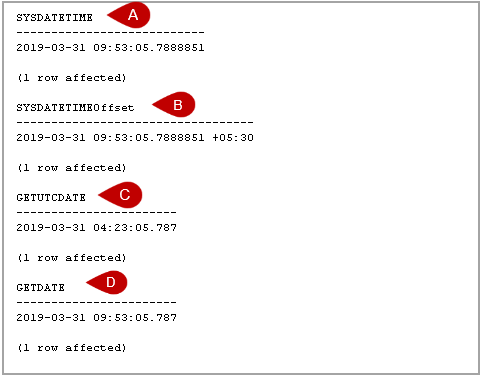
- SYSDATETIME(): To returns the server’s date and time
- SYSDATETIMEOffset(): It returns the server’s date and time, along with UTC offset
- GETUTCDATE(): It returns date and GMT (Greenwich Mean Time ) time
- GETDATE(): It returns server date and time
Execute the following queries to get output in respective formats.
-
1Select SYSDATETIME() as [SYSDATETIME]
-
1Select SYSDATETIMEOffset() as [SYSDATETIMEOffset]
-
1Select GETUTCDATE() as [GETUTCDATE]
-
1Select GETDATE() as [GETDATE]

SQL Convert Date Formats
As highlighted earlier, we might need to format a date in different formats as per our requirements. We can use the SQL CONVERT() function in SQL Server to format DateTime in various formats.
Syntax for the SQ: CONVERT() function is as follows.
|
1 |
SELECT CONVERT (data_type(length)),Date, DateFormatCode) |
- Data_Type: We need to define data type along with length. In the date function, we use Varchar(length) data types
- Date: We need to specify the date that we want to convert
- DateFormatCode: We need to specify DateFormatCode to convert a date in an appropriate form. We will explore more on this in the upcoming section
Let us explore various date formats using SQL convert date functions.
First, we declare a variable to hold current DateTime using the SQL GETDATE() function with the following query.
|
1 2 3 |
declare @Existingdate datetime Set @Existingdate=GETDATE() Print @Existingdate |

We can see various date formats in the following table. You can keep this table handy for reference purpose in the format of Date Time columns.
|
|
| ||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
| |||
Standard: German |
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
| |||
|
|
|||
|
| |||
Standard: Default + milliseconds |
|
|||
|
| |||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
|
In the table, we can see various formats to SQL convert date as per your requirements. In the following table, you can see all SQL date formats together.
Date format option | SQL convert date output |
0 | Dec 30 2006 12:38AM |
1 | 12/30/06 |
2 | 06.12.30 |
3 | 30/12/2006 |
4 | 30.12.06 |
5 | 30/12/2006 |
6 | 30-Dec-06 |
7 | Dec 30, 06 |
8 | 00:38:54 |
9 | Dec 30 2006 12:38:54:840AM |
10 | 12-30-06 |
11 | 06/12/1930 |
12 | 61230 |
13 | 30 Dec 2006 00:38:54:840 |
14 | 00:38:54:840 |
20 | 30/12/2006 00:38 |
21 | 38:54.8 |
22 | 12/30/06 12:38:54 AM |
23 | 30/12/2006 |
24 | 00:38:54 |
25 | 38:54.8 |
26 | 2006-30-12 00:38:54.840 |
27 | 12-30-2006 00:38:54.840 |
28 | 12-2006-30 00:38:54.840 |
29 | 38:54.8 |
30 | 30-2006-12 00:38:54.840 |
31 | 2006-30-12 |
32 | 12-30-2006 |
33 | 12-2006-30 |
34 | 30/12/2006 |
35 | 30-2006-12 |
100 | Dec 30 2006 12:38AM |
101 | 12/30/2006 |
102 | 2006.12.30 |
103 | 30/12/2006 |
104 | 30.12.2006 |
105 | 30/12/2006 |
106 | 30-Dec-06 |
107 | Dec 30, 2006 |
108 | 00:38:54 |
109 | Dec 30 2006 12:38:54:840AM |
110 | 12-30-2006 |
111 | 30/12/2006 |
112 | 20061230 |
113 | 30 Dec 2006 00:38:54:840 |
114 | 00:38:54:840 |
120 | 30/12/2006 00:38 |
121 | 38:54.8 |
126 | 2006-12-30T00:38:54.840 |
127 | 2006-12-30T00:38:54.840 |
130 | 10 ?? ????? 1427 12:38:54:840A |
131 | 10/12/1427 12:38:54:840AM |
Let us next explore a function that is useful for SQL convert date.
DATEADD
We can use the SQL DATEADD function to add a particular period to our date. Suppose we have a requirement to add 1 month to current date. We can use the SQL DATEADD function to do this task.
The syntax for SQL DATEADD function is as following
|
1 |
DATEADD(interval, number, date) |
Interval: We can specify an interval that needs to be added in the specified date. We can have values such as year, quarter, month, day, week, hour, minute etc.
Number: It specifies the number of the interval to add. For example, if we have specified interval as Month and Number as 2, it means 2 months needs to be added in date.
In the following query, we want to add 2 months in the current date.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT GETDATE() as Currentdate SELECT DATEADD(month, 2, GETDATE()) AS NewDate; |
You can see the output in the following screenshot.

Similarly, lets us add 1 year to current date using the following query.
|
1 2 3 4 |
select GETDATE() as Currentdate SELECT DATEADD(Year, 1, GETDATE()) AS NewDate; |

We can combine the SQL DATEADD and CONVERT functions to get output in desired DateTime formats. Suppose, in the previous example; we want a date format in of MMM DD, YYYY. We can use the format code 107 to get output in this format.
Execute the following code to get New date and ConvertedDate.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT DATEADD(YEAR,1,GETDATE()) AS [NewDate] ,CONVERT(varchar(110),DATEADD(YEAR,1,GETDATE()),107) AS [ConvertedDate] |

Conclusion
In this article, we explored various SQL convert date formats. It allows getting a date in required format with Covert function easily. You can use this article to take a reference for all date formats and use in your queries.
See more
ApexSQL Complete is a SQL code complete tool that includes features like code snippets, SQL auto-replacements, tab navigation, saved queries and more for SSMS and Visual Studio

- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023










![Datetime format as
[MMM DD YYYY hh:mm:ss:mmm(AM/PM)]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-as-mmm-dd-yyyy-hhmmssmmmam-p.png)








![Datetime format in [yyyy-mm-dd]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-in-yyyy-mm-dd.png)
![Datetime format in [hh:mm:ss]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-in-hhmmss.png)
![Datetime format in [mm-dd-yyyy hh:mm:ss.mmm]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-in-mm-dd-yyyy-hhmmss-mmm.png)
![Datetime format in [MMM DD YYYY HH: SS (AM/PM)]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-in-mmm-dd-yyyy-hh-ss-am-pm.png)
![Datetime format in [MM/DD/YYYY]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-in-mm-dd-yyyy.png)
![Datetime format in [YYYY.MM.DD]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-in-yyyy-mm-dd-1.png)






![Datetime format as
[MMM DD YYYY hh:mm:ss:mmm(AM/PM)]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/datetime-format-as-mmm-dd-yyyy-hhmmssmmmam-p-1.png)








![SQL Convert Date - Datetime format in [DD MMM YYYY hh:mi:ss:mmm(AM/PM)]](/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/sql-convert-date-datetime-format-in-dd-mmm-yyyy.png)