Introduction to SQL Server Statistics
SQL Server Statistics are an essential part of query performance in SQL Server. They help the query optimizer to prepare a query plan using the distribution of values in participating rows. If we do not have updated statistics, it might lead to resource intensive query execution plan. For example, for a large table having a billion records, SQL may choose to have an index scan instead of an index seek.
In most cases, query optimizer takes care of creating and updating the distribution statistics. In SQL Server, we have three options to set the behavior of statistics. Let’s take a brief overview of these options.
Right click on a database and open database properties.

- Auto Create Statistics: By default, SQL Server enables Auto Create Statistics (In the image – Auto Create Statistics = True). It creates statistics objects on the required column in the query predicate. All statistics created using this option have a prefix _WA. SQL Server also generates SQL Server statistics for an object once you create an index or key such as the primary key
1234567891011121314Selecttop 10object_name(s.object_id) as table_name,s.name as stat_name,s.is_temporary,ds.last_updated,ds.modification_counter,ds.rows,ds.rows_sampled,ds.stepsfrom sys.stats as s (nolock)cross apply sys.dm_db_stats_properties(s.object_id, s.stats_id) as dsWHERE s.name like '_WA%' and object_name(s.object_id) not like '%sys%'ORDER BY s.name; - Auto Update Statistics: Query optimizer does internal calculations based upon several inserts, update, delete and update the stats automatically when Auto Update Statistics = true
- Auto Update Statistics Asynchronously: If this option is true (Default setting – false), SQL Server checks for the synchronous or asynchronous statistics updates
SQL Server Statistics behavior in SQL Server Always On Availability Group
SQL Server Always On Availability Groups configures primary and secondary replica to provide high availability and disaster recovery solution. Starting from SQL Server 2016, we can Read-Only Routing in SQL Server to route the read workload to the secondary replica. We can do read-write transactions in primary replica only. Read more about it in the How to Configure Read-Only Routing for an Availability Group in SQL Server 2016 article.
In SQL Availability groups, SQL Server creates and maintains statistics on primary replica databases. These SQL Server statistics from primary replica are sent to secondary replica similar to other transaction log records. If we are using the secondary replica for the reporting purpose and all the reports query fetching data from it, it might require different statistics from those statistics that are replicated from Primary replica. The query optimizer cannot create statistics on secondary replica because the database is in read-only mode.
Test Environment:
- Two nodes SQL Always On the replica with synchronous mode
Demo for SQL Server Statistics in Always On Availability Groups
Let’s create a table in Primary replica:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
CREATE TABLE tbltest ( id INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY, NAME NVARCHAR(100), country NVARCHAR(100) ) |
The table does not contain any data as of now. Verify the stats on both primary and secondary replica using the following query:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
SELECT Object_name(s.object_id) AS table_name, s.NAME AS stat_name, s.is_temporary, ds.last_updated, ds.modification_counter, ds.rows, ds.rows_sampled FROM sys.stats AS s (nolock) CROSS apply sys.Dm_db_stats_properties(s.object_id, s.stats_id) AS ds WHERE Object_name(s.object_id) = 'tbltest' |
-
Primary replica SQL Server Statistics output:

-
Secondary replica SQL Server Statistics output:

As highlighted earlier, SQL Server automatically creates the statistics on primary replica as per the query optimizer requirements. Let’s insert a few records into this table.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
DECLARE @Id INT SET @Id = 1 WHILE @Id <= 10000 BEGIN INSERT INTO tbltest VALUES ('Rajendra - ' + Cast(@Id AS NVARCHAR(20)), 'SQLShack - ' + Cast(@Id AS NVARCHAR(10)) + 'Article') SET @Id = @Id + 1 END |
Execute a select statement to create statistics:
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT remarks FROM [adventureworks2014].[dbo].[tbltest] WHERE remarks BETWEEN 'SQLShack - 5674Article' AND 'SQLShack - 9994Article' |
Now execute the query to check SQL Server Statistics on both the primary and secondary replica. We can see new statistics for the name starting from _WA_sys. Primary replica replicates these statistics to the secondary replica, and you can see the same statistics at that end also.
Primary replica output:

Secondary replica output:

SQL Server Statistics in Readable replica in SQL Server Always On
Let’s consider that you are using a secondary replica to serve the read-only workload. As we are not executing these queries on the primary replica, it cannot create new statistics in primary replica and replicates it to the secondary replica.
Let’s see how it works in a readable secondary replica. Execute a command in the secondary replica database:
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT name FROM [adventureworks2014].[dbo].[tbltest] WHERE name BETWEEN 'SQLShack - 5674Article' AND 'SQLShack - 9994Article' |
Primary replica output
Now recheck the statics on both the replicas and see the difference.
-
Primary replica – No change in SQL Server Statistics:

-
Secondary replica – new SQL Server Statistics (temporary) added:

We can see a new statistics _WA_Sys_00000002_405A880E_readonly_database_statistics for tbltest table. Look this row carefully, and we can see a flag is_temporary value to one for these statistics. In the secondary replica, query optimizer creates temporary statistics in the tempdb database. It appends the suffix ‘_readonly_database_statistics’ for these temporary statistics. We need to note here that query optimizer creates statistics in the database itself in primary replica and it gets replicated to the secondary database only. In this case, it cannot generate statistics in a read-only secondary database, so it uses tempdb to create temporary statistics. The query optimizer is smart enough to use these statistics from the tempdb and optimize the workload. SQL Server always On works in primary to secondary replica direction; therefore, these temporary statistics cannot be moved to the primary replica. If we restart the secondary replica due to any issues, these temporary statistics are flushed out. It takes 8 bytes (1 page) of storage in tempdb, and it does not depend upon the table size.
We can use the DBCC Show_Statistics command to check SQL Server Statistics on a particular column. In the following example, we want to check statistics for tbltest table and name column:
|
1 |
DBCC show_statistics('tbltest', 'name') |
We can see the temporary statistics for this column along with its range and density.
Stale SQL Server Statistics in Always On Availability Groups
Consider a scenario in which you are not running any queries on the primary replica. It does not create or update any statistics on primary replica due to no activity on the primary replica. At the same time, we are executing workload on the secondary replica, and it creates, updates statistics as per requirements.
At this point, we have three statistics on the secondary replica:
- Primary key statistics
- Automatic _WA statistics
- Temporary statistics
Insert more records into the primary replica. It makes the statics stale on the primary replica. At this point, execute the following select statement on the secondary replica to retrieve records using primary key column in where condition.
|
1 2 3 |
SELECT remarks FROM [adventureworks2014].[dbo].[tbltest] WHERE id BETWEEN 2000 AND 3000000 |
Check the statistics on the secondary replica, and you can see strange behaviour. In the following screenshot, you can notice it shows primary key statistics also as temporary statistics.

It shows that SQL Server has created temporary statistics for this. Since we have not executed the select statement on the primary replica, query optimizer does not update statistics on the primary replica.
It implies that SQL Server has created a temporary SQL Server Statistics. It does not lose the permanent statistics in the secondary replica database. Temporary statistics is still available in tempdb, but query optimizer is intelligent and knows about the temporary statistics is updated statistics than the permanent statistics. It uses it to prepare an execution plan and get the data.
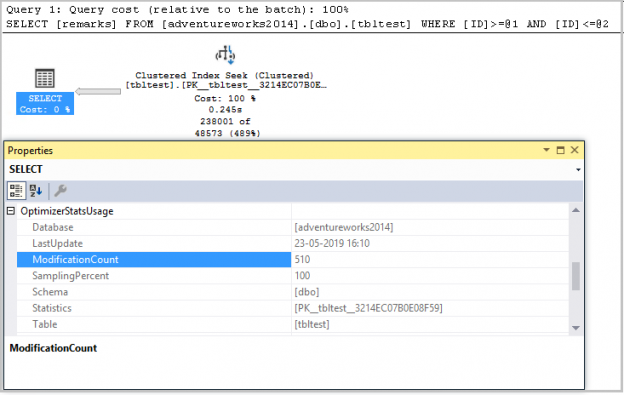
If we look at the execution plan of the select statement, we can see that query optimizer is using PK__tbltest__3214EC07B0E08F59 statistics for executing this query.

Let’s manually update statistics on the primary replica using the Update Statistics command:
|
1 |
Update Statistics tbltest |
It updates statistics on primary replica and replicates the same to the secondary replica. Check the SQL Server Statistics status on the secondary replica.
We do not have temporary statistics for the primary key.

We still have temporary statistics in the secondary replica as _readonly_secondary_status. As you know now that temporary statistics gets created in the tempdb therefore if you restart SQL Services on the secondary replica, it creates a new copy of tempdb, and all temporary statistics are dropped.

Summary of SQL Server Statistics behaviour in SQL Server Always On Availability Group databases
Let’s summarize actions into the following section.
Step No | Step Description | Primary Replica | Secondary Replica |
1 | Create a table with a primary key on Primary | Primary key stat generates on the primary replica – P1 | Secondary replica gets the statistics from primary replica – P1 |
2 | Execute a query on Secondary with a predicate on the remarks column | NA | Temporary statistics gets created – T1 |
3 | Execute the same query on primary ( same as step 2) | It generates a permanent stats S1 on the primary replica | It gets replicated, and Secondary replica has three stats – P1, T1 and S1 at this step |
4 | Restart SQL Service on Secondary | It clears temporary statistics T1 on the secondary replica. | |
5 | Insert records in primary replica and execute the query from step 2 on the e secondary replica. |
| It updates the temporary statistics T1 gets in the secondary replica. |
6 | Insert more records in primary replica and execute a select statement on the Primary replica for another column in the predicate. | It generates a permanent stats S2 on the primary replica | Secondary replica gets the statistics from primary replica – S2 |
7 | Run the same select statement from step 6 on secondary | It creates temporary statistics T2. The secondary replica has three stats – P1, S2 and T2 at this step. The query optimizer uses T2 in the query because it has the latest stats. |
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the behavior of SQL Server Statistics in SQL Server Always On Availability Groups. It is a crucial aspect to take care of performance tuning. If you have any feedback or questions, feel free to leave them in the comments below.
- Understanding PostgreSQL SUBSTRING function - September 21, 2024
- How to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu - July 13, 2023
- How to use the CROSSTAB function in PostgreSQL - February 17, 2023