Introduction
In a previous article, we talked about the tempdb system database. In this article, we will talk about the msdb database.
The msdb database stores information like the SQL Server Agent information, backup information, log shipping, maintenance plans.
In this article we will describe internal system tables of the msdb database and create some jobs to see the tables used.
Requirements
SQL Server installed (we are using the SQL 2016, but earlier versions are valid).
Getting started
Backup system tables
We will start creating a backup to show how the data is stored in the msdb.
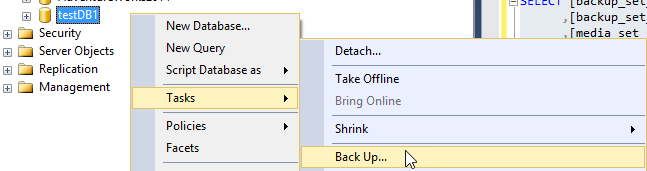
In SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), right click on a database and select the option Tasks>Back up

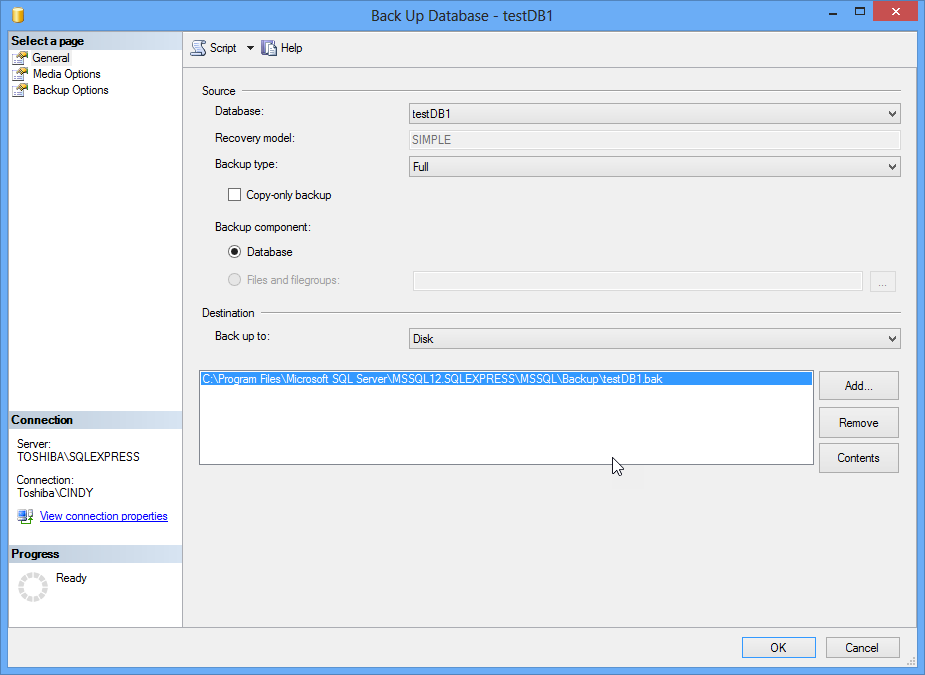
Figure 1. Backup option Press OK to backup with the default values:
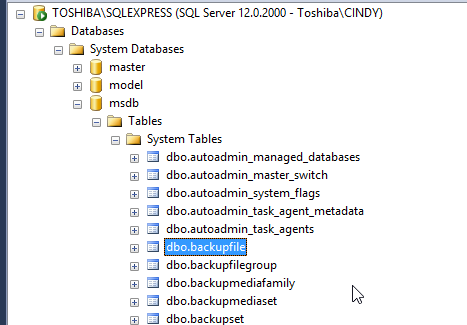
Figure 2. Backup options In the msdb database, you can check the backup information in the backup system tables. For example, you can check the backup file information in the dbo.backupfile:

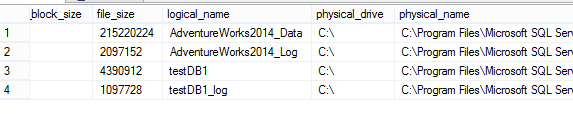
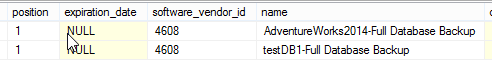
Figure 3. The backupfile system table You can check information like the file size, physical location of the backup, etc:

Figure 4. The backup file information In the dbo.backupset system table you can find the name of the backup and the backup configuration options like the backup size, encryption information and more:

Figure 5. The backupset information As you can see, all the information is stored in the MSDB system views. If you create a backup it is a good practice to backup the MSDB database also to track the changes.
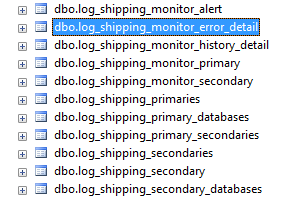
Other tables used in the MSDB database are the Log Shipping system tables. These tables are used to restore the Log Shipping information. Log Shipping is a feature used to have a secondary server ready in case that the primary server fails. This method uses Transaction Logs to replicate the data. For more information about Log Shipping, you can read this related article: How to create SQL Server Log Shipping
You can see the list of system tables in the following picture:

Figure 6. Log Shipping system tables Whenever you change the Log Shipping configuration option it is a good practice to backup the msdb database.
In the demo we will create a Database Backup using PowerShell in the SQL Agent and show the tables used.
-
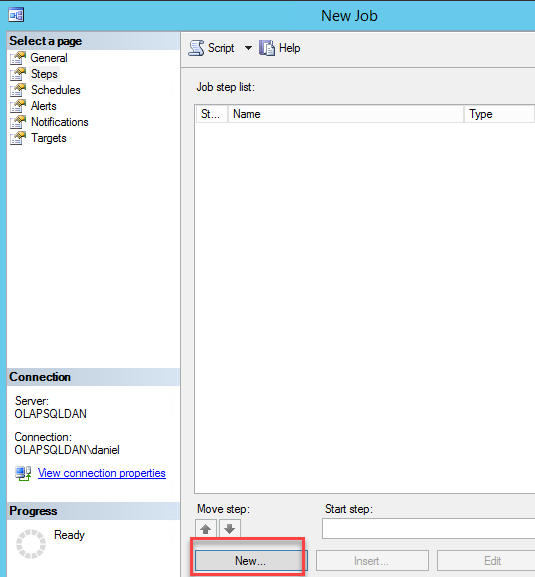
In the SQL Server Agent node right click on Jobs and select new job:

Figure 7. Creating a new job -
Add a name for the job:

Figure 8. General job information In the step page, press the New button:

Figure 9. Job steps -
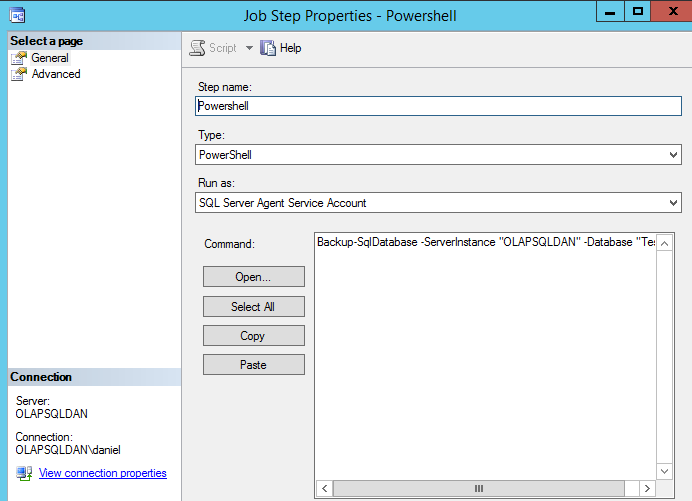
Specify a name. In the type, select Power Shell and in the Command, write the following commands:
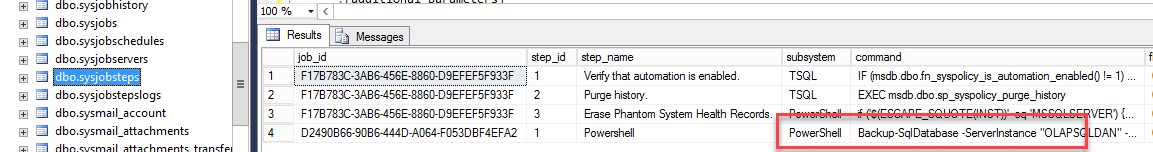
Backup-SqlDatabase –ServerInstance “OLAPSQLDAN” –Database “Test”
The backup-sqlDatabase cmdlet, is used to backup databases. In this example, we are backing up the Test database in the OLAPSQLDAN Server:

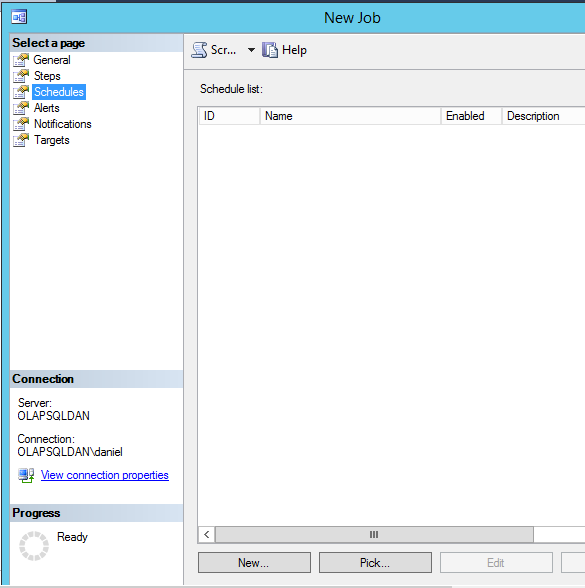
Figure 10. Powershell Backup Cmdlet We can define a Schedule for the job. In the Schedule page, press the new button:

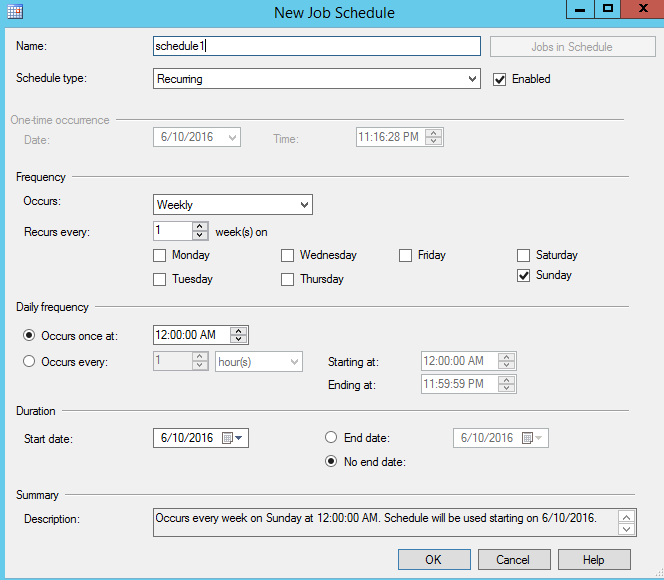
Figure 11. New Schedule Add a name and specify the schedule to run the job:

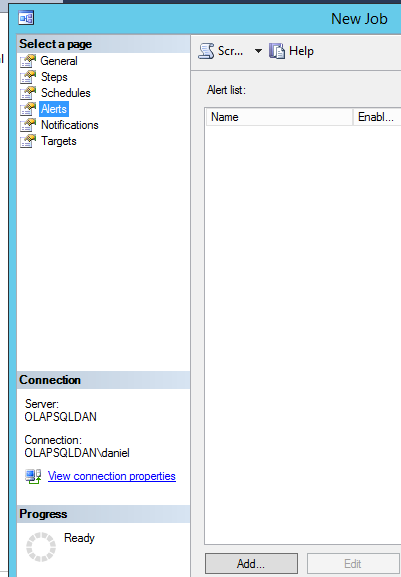
Figure 12. Schedule information In the Alert section, press the Add button:

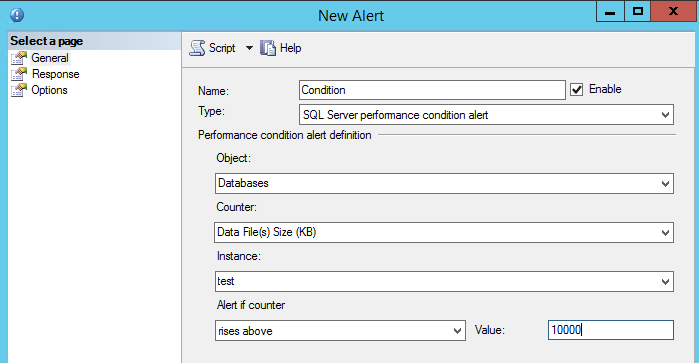
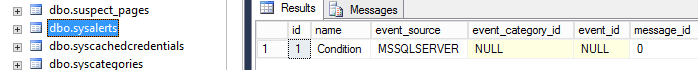
Figure 13. The Alerts page We will generate an alert if the Database file of the test database rises above 10,000 Kb:
Figure 14. Alert options Press OK to save the job. Once the job is create right click the Operators folder and select New Operator:

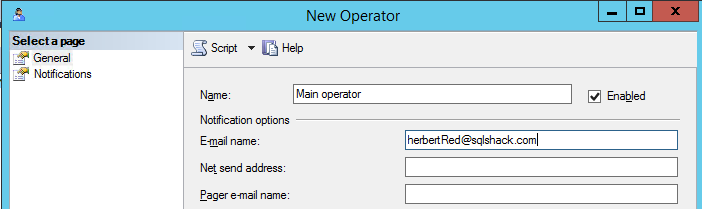
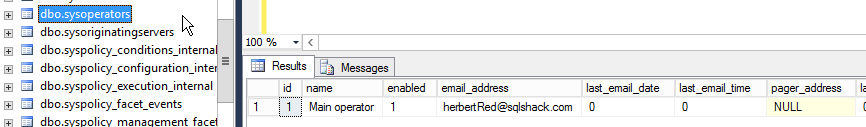
Figure 15. Creating a new operator Add a Name and an email:
Figure 16. New operator properties Save the operator information.
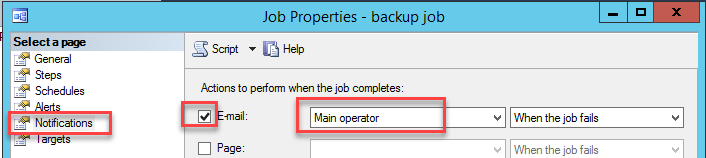
Open the Job created before. Go to the notification page. Check the E-mail and select the operator created on step 11:
Figure 17. Job notification Start the job:

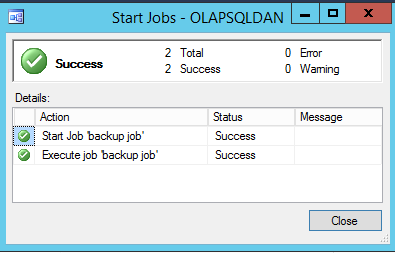
Figure 18. Starting a job You will receive a success message after starting the job:

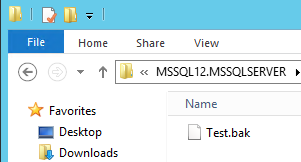
Figure 19. Success job message You can check that the backup was created successfully:

Figure 20. The backup created All the job information is stored in the msdb system tables. For example the execution information is stored in the sysjobactivity:

Figure 21. The job activity table The job activity table contains the information about the executed jobs:

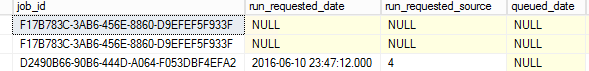
Figure 22. The table information The sysjobhistory contains historical information like the error messages and the execution date and time:

Figure 23. The sysjobhistory table You can also see the success messages and operator information:
Figure 24. The sysjobhistory data The sysjobs table contains the list of jobs available:

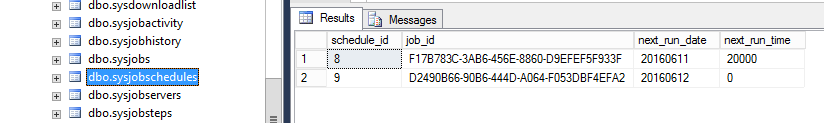
Figure 25. The sysjobs table The sysjobschedules contains the schedules created in figure 12 :
Figure 26. The data in the sysjob table The sysjobschedules contain the schedules created in figure 12:
Figure 27. The sysjobschedules The sysjobsteps table contains the job steps created in figure 10:
Figure 28. The PowerShell job step We can also see the job alerts created on the figure 14 using the sysalerts:
Figure 29. The sysalerts system table In the sysoperators table, you can see the operator created in figure 16
Figure 30. The sysoperators table Make sure to store the MSDB transaction log in a fault tolerant storage device.
Set the recovery model to full (by default it is simple).
- MSDB Database
- SQL Server Agent Tables (Transact-SQL)
- SQL Server Agent Stored Procedures (Transact-SQL)
- PostgreSQL tutorial to create a user - November 12, 2023
- PostgreSQL Tutorial for beginners - April 6, 2023
- PSQL stored procedures overview and examples - February 14, 2023
Log Shipping system tables
SQL Agent System tables
Whenever you make important changes in the SQL Server Agent it is a good practice to backup the msdb database.
How can I restore the msdb database if I do not have a backup?
You can rebuild your msdb database using the instmsdb script included in the MSSQL\Install folder. For more information about restoring system databases, refer to the following link:
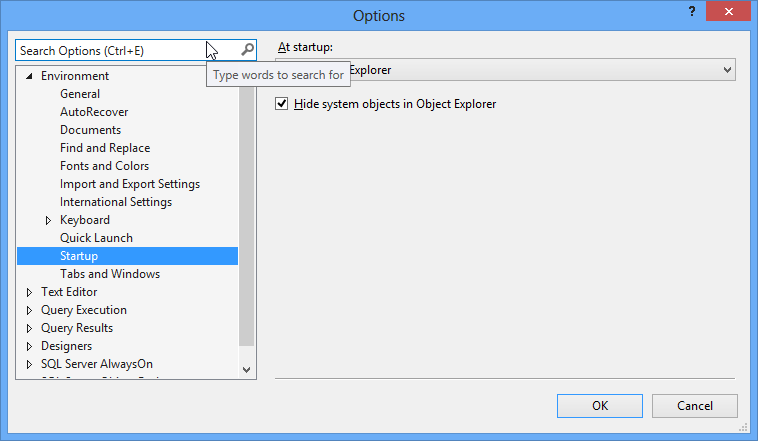
How can I hide the msdb database in the SSMS?
If you want to hide the system database you can do so in SSMS. Go to Tools>Options>Startup and selecting the option Hide system object form Object Explorer:
You will need to close and reopen the SSMS. Once it is done, the system tables including the MSDB will not be visible in the solution explorer:
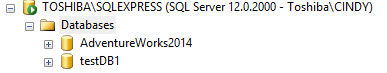
However, you can query the system tables using T-SQL.
Conclusions
The msdb database is an important database used to store backup, Log Shipping and Agent information. Backup your msdb datatabase whenever you create backups, when you change the SQL Agent information or when you change the log shipping information or when you modify information that is stored in the msdb database.
Other recommendations
References
For more information, refer to these links: