This article will explore backup options available in the Azure Cosmos DB service. Backups are very important to safeguard our data in case of data corruption, data deletion, system failure, or any unforeseen circumstances like DR. We have planned, configured, and managed it for our on-prem databases whether it is SQL Server, Oracle, DB2, or system files on various machines. DBAs and Infrastructure admins have ensured to keep a backup of all these systems to safeguard their data. Similarly, we must also secure our data hosted in a cloud environment for any services whether it is Azure VMs, Azure SQL, Cosmos Db accounts, or any other services. Today we will talk about backup options available to secure cosmos DB databases and their contents.
Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed, highly secure, and globally distributed database service that is designed for new-age advanced application development. It automatically runs backup for its databases at regular intervals to ensure data protection in case you need data recovery because of various reasons like corruption, deletion, wrongly data updating, etc. Backups are taken on separate Azure blob storage in the backend without affecting the performance, availability, and provisioned resource units (RUs). These backups are stored locally where you have provisioned your cosmos DB account.
Azure Cosmos DB offers two policies to run backups.
- Periodic backup
- Continuous backup
Let’s discuss both backup policies in detail in the below section.
Periodic backup
This backup mode is the default configuration of any Azure Cosmos DB account. It runs on periodic intervals based on defined configurable periods. You can keep its retention for a month from a data recovery standpoint. It means you can recover any data from its retention time frame by creating a support ticket on the Azure portal to the support team. There is no impact of running this backup on the performance of the cosmos DB account or the provisioned throughput of the cosmos DB account. The backup copies are stored on an Azure storage account which is different than the storage accounts used for Cosmos DB. Backups are copied to the paired region of the Azure region to ensure resiliency.
By default, Periodic backup automatically runs every 4 hours and keeps 2 backup copies at any point of time without any cost. You can change the backup execution interval as well as its retention period to save the backup files on the storage account anytime using the Azure portal. Remember, saving additional backup copies other than 2 copies will be charged additionally.
These configurations need to perform at the cosmos DB account level and then this configuration will apply to all containers stored in that cosmos DB account. Making these changes will cost you additionally so make sure to consider this aspect as well while planning the backups. You cannot control the number of backup copies saved on the storage system rather It depends on the backup interval and backup retention configuration values. You need to find a balance between backup interval and retention so that you don’t need to pay more costs in saving unwanted multiple backup files.
If you have opted for periodic backup as your backup policy for cosmos DB accounts then one thing you must remember is that you cannot restore its backup files, you need to raise an Azure support ticket to restore or recover any data. You need to be aware that data can be restored only if the requested backup copy is from the backup retention period and not outside that retention window.
Continuous backup
This is another option available to configure backups for cosmos DB accounts. This backup policy supports only MongoDB and core (SQL) APIs. You can keep its retention for 30 days, and you can restore any dataset in point in time from the last 30 days using the Azure portal. The continuous backup runs for each replica which is distributed globally to other regions and stores their backup on local redundant storage for their respective replica so it means you will have an equal number of backup copies as you have the number of replicas for your Azure Cosmos DB accounts. If any specific region has availability zones, then the backup copies will be stored on zone redundant storage accounts. If you need to recover your database with the latest possible data, then you should consider the backup copy stored in the write region replica because read region replicas might be a little behind because of the network latency.
The continuous backup supports point-in-time recovery so you can restore your data at a specific point in time as per your need. You don’t need to create a support ticket to restore your data in this mode of backup. One negative side of provisioning Azure Cosmos DB account using continuous backup mode is you can’t move back to periodic backup mode so plan carefully before adopting this mode of backup options.
This backup mode also has some limitations which you must consider or validate whether Azure has overcome this limitation, or this limitation is still there for this backup mode at the time when you are choosing this backup policy. Some of the limitations are given below.
- Continuous backup cannot be configured for other APIs except SQL core and MongoDB APIs. Only MongoDB and SQL core API are supported for this backup.
- If you have multi-region writes enabled, then you cannot use this backup.
- You cannot restore the data outside your source data account region. It means you must restore only to the regions where Azure Cosmos DB accounts exist.
- The point in time recovery is always restoring in the new cosmos DB account. You cannot restore on the same account.
- Azure Cosmos DB account with customer-managed keys is not supported so you cannot use this backup for such accounts.
You must also note pricing because making any changes in backup configuration will charge you the additional cost. If your cosmos DB accounts are configured to use Continuous backup, then you will be charged n times where n is the number of regions you have distributed your cosmos DB account because each region will keep its backup. There will be additional costs in case you are performing a restore based on the size of the data. If you haven’t performed any restore operation, then you don’t need to pay for restore in that month.
The basic formula for backup and restore is as given below.
- Backup cost per month – $0.20 x database size x number of regions
- Restore cost per attempt – $0.15 x database size
Check the backup configuration of the Cosmos DB account
This section will explain how to check the existing backup policy for an Azure Cosmos DB account. Log in to the Azure portal. Type “Azure Cosmos DB” in the search bar and press enter to get the cosmos DB account dashboard page. Here, I have opened a new account creation window to see backup policy options available during its creation. I accessed the Backup Policy tab from the new account creation form and here you can see the default values of backup policy, backup interval, backup retention, and the number of backup copies retained on the storage account in the below image. If you will not make any change then the backup policy will be configured as per the below details. The backup policy option is showing greyed out with the periodic option selected, which means the multi-region write option is enabled under the global distribution tab.
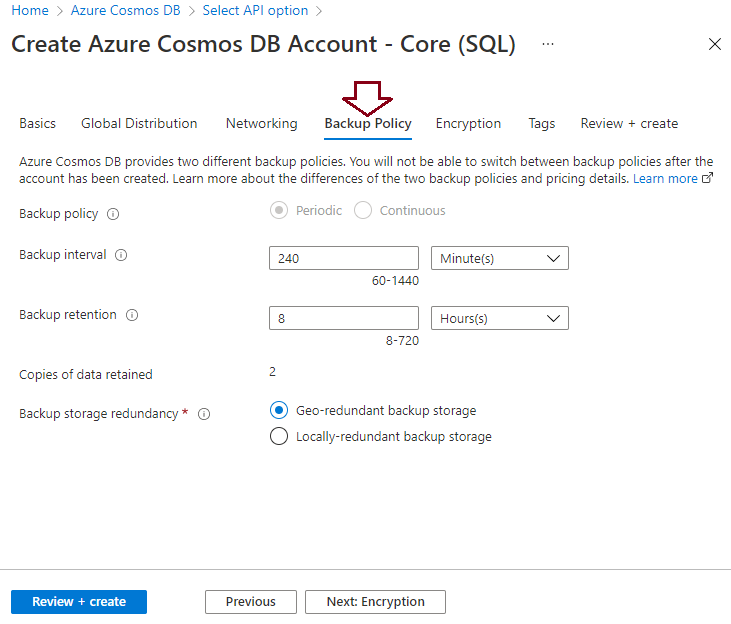
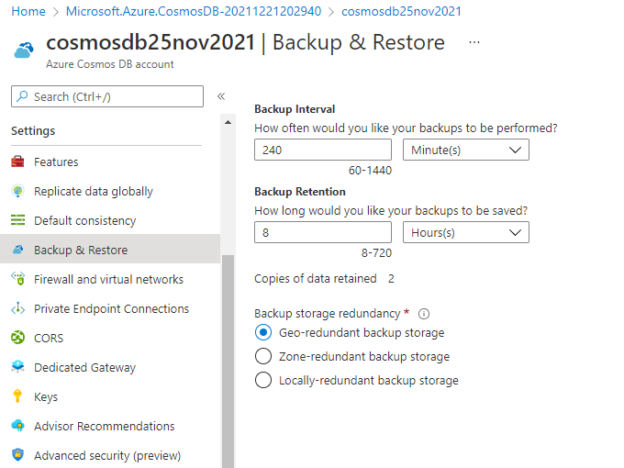
If you want to save more backup copies or want to increase their retention period, then you need to do it by modifying its respective value from the above screen. You can change backup retention as per your desired value with the help of the above screen. You will also note that the number of backup copies will also be changed in the same manner. If you still want to keep only 2 copies, then you need to increase the backup interval accordingly to make it only 2 copies otherwise keeping more than 2 copies of backup files will charge you more cost.
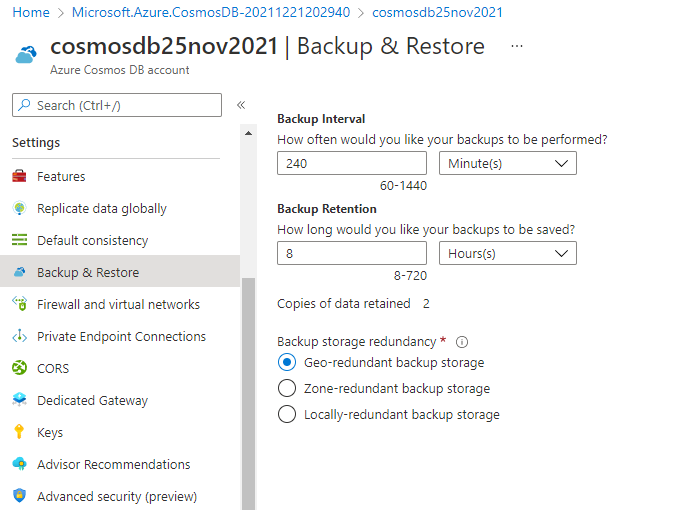
You can also check the backup policy, its retention, and interval of the existing Azure Cosmos DB account by accessing the Backup & Restore tab given under the Settings tab of a cosmos DB account as shown in the below image. The below image shows the backup interval and its retention of the cosmos DB account cosmosdb25nov2021.
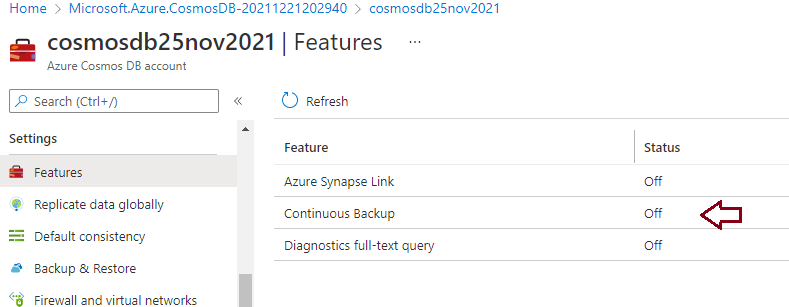
You can also ensure whether another backup policy Continuous backup is enabled for your cosmos DB account or not by accessing the Features options given under the Settings tab of the Azure Cosmos DB account.
Conclusion
I have explored backup options available for Azure Cosmos DB accounts. We learned about the details of both backup options – Periodic and Continuous backups in this article. I have also demonstrated the steps for verifying the existing backup policy configuration of the cosmos DB accounts. Stay tuned for my next articles where I will talk more about these backups and their various how-to topics.
- Configure backup storage redundancy for Azure Cosmos DB account - May 15, 2024
- Difference between SQL SELECT UNIQUE and SELECT DISTINCT - January 16, 2024
- How to do a group by clause - April 12, 2023