In this article, we are going to learn how we can copy database objects between two databases of different instances of SQL Server. Sometimes, we receive the request to provide the specific database object to another database. To fulfill this requirement, instead of using Generating the T-SQL script for each object and export data using import-export task, we can use the Transfer SQL Server Object task of SSDT 2017. In this article, we will understand how we can transfer the database objects of a specific schema to another database.
Environment setup
I have created two named instances of SQL Server 2019 named SQL01 and SQL02 on my workstation. I have restored the wideworldimportors database on the SQL01 database. I have created an empty database named SalesDB on SQL02 instance. We want to transfer the tables of the Sales schema to the SalesDB database of SQL02. To do that, we are using the transfer SQL Server of the task of integration services.
Create an integration services project in SSDT 2017.
First, let us create an integration services project named transfer_sales_schema in SSDT 2017. Drag Transfer SQL Server Objects Task from SSIS toolbox and drop it on Control flow designer and rename it to Copy Sales Schema.
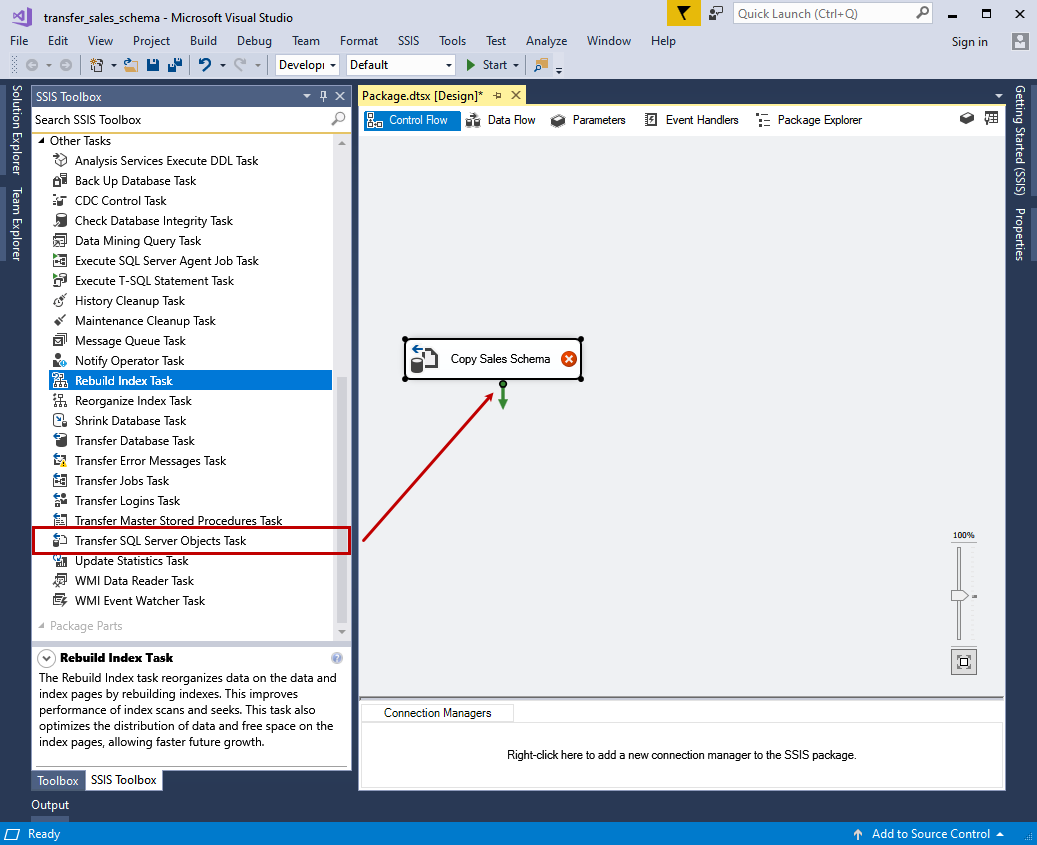
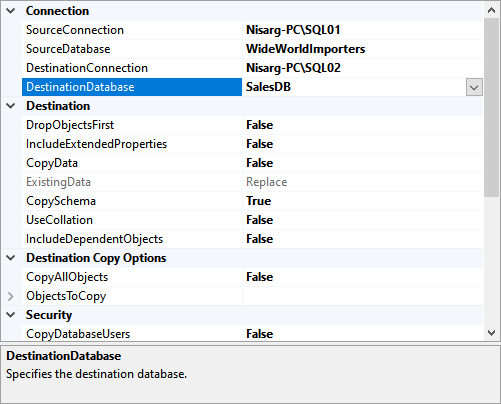
Now, double click on the transfer SQL Server objects task. A dialog Transfer SQL Server objects task editor opens. Click on Source Connection and select the new connection. The SMO Connection Manager opens. Specify the source server name in the dialog box and specify the appropriate credential to connect to it. Click OK to save the source connection.
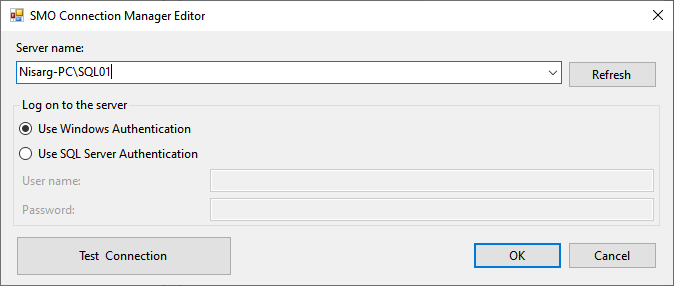
Back to the Transfer database object task, click on Source Database and select Wideworldimportors from the list.
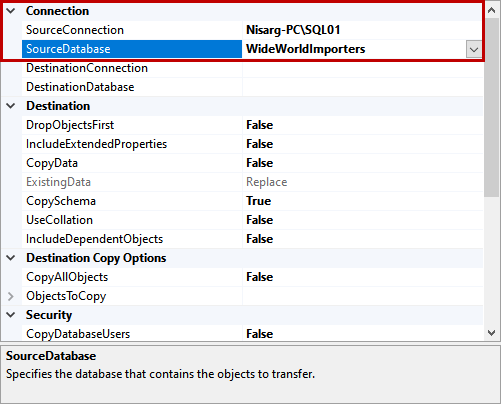
Similarly, click on Destination Connection and select New Connection. On the SMO connection manager, specify the destination server.
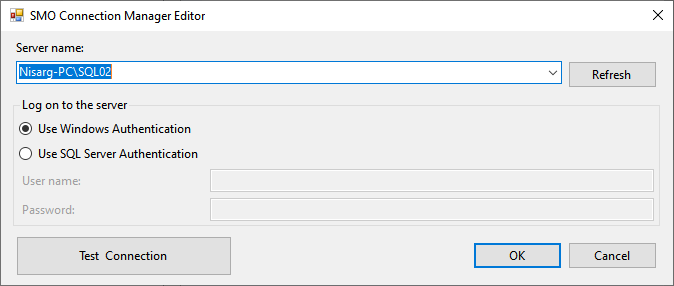
Back to the Transfer database object task, click on Source Database and select SalesDB from the list.
Choose the objects
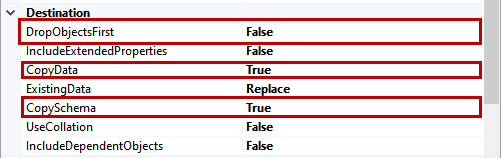
We want to copy the schema and data of the Sales schema to the SalesDB database. So, we will set the following values in the transfer SQL Server database object tasks.
Destination Section
- Drop Objects First: We want to drop and create the tables, so I have set it to TRUE
- Copy Data: We are copying the data so, I have set it to TRUE
Destination Copy Options
Copy All Objects: We are copying specific objects, so I have set their value to FALSE.
Copy All Tables: We are copying specific tables, so I have set it to False.
Tables List: We are copying the tables of Sales schema, so select them from the list.
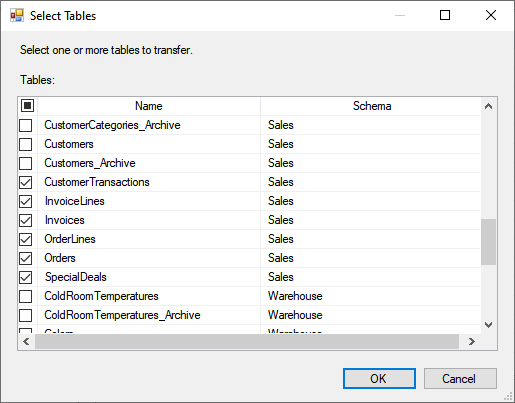
Copy All Schema: We are copying the Sales Schema to set its value to FALSE.
Schema List: We want to copy the sales schema so, select Sales from the schema list.
Security Section:
- Copy Database Users: We are transferring the database users, so Set it to TRUE
- Copy Database Roles: We are transferring the database roles, so set it to TRUE
- Copy SQL Server Logins: We are transferring the SQL logins, so set it TRUE
- Copy Object Level permission: Set it to TRUE
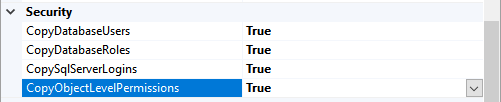
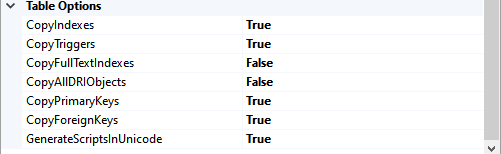
Table Options:
- Copy Indexes: We are copying the indexes, so set it to TRUE
- Copy Triggers: We are copying the triggers, so set it to TRUE
- Copy Primary key: We are copying the Primary keys, so set it to TRUE
- Copy Foreign key: We are copying the foreign keys, so set it to TRUE
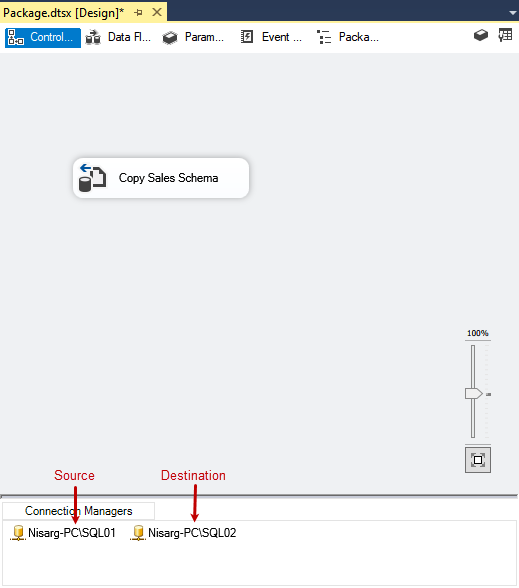
Click OK to save the configuration and close the dialog box. The SSIS package looks like the following image:
Execute the package
Execute the SSIS package by clicking on the Start button from the menu bar.
![]()
The package execution begins. Once the package executes successfully, we will verify that tables have been.
Note: if you are transferring the data of the table that is in the secondary filegroup, then you must create that filegroup in the destination database. Similarly, if the table has a partition scheme and partition function, you must create them on the destination database.
Verify the schema
Now, let us verify whether tables have been copied to the destination server or not. Open SQL Server Management studio 🡪 Connect to Nisarg-PC\SQL02. Run the following queries.
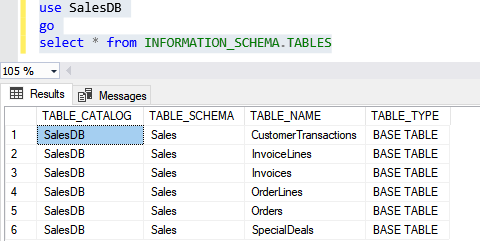
Query to get the tables of sales schema.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
USE salesdb go SELECT * FROM information_schema.tables |
Output
Query to get the list of primary keys
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
SELECT Db_name() AS DatabaseName, Schema_name([tables].schema_id) AS [schema_name], [PrimaryKeys].[name] AS pk_name, Substring(column_names, 1, Len(column_names) - 1) AS [columns], [tables].[name] AS table_name FROM sys.tables [Tables] INNER JOIN sys.indexes [PrimaryKeys] ON [tables].object_id = [PrimaryKeys].object_id AND [PrimaryKeys].is_primary_key = 1 CROSS apply (SELECT [columns].[name] + ', ' FROM sys.index_columns [IndexColumns] INNER JOIN sys.columns [Columns] ON [IndexColumns].object_id = [columns].object_id AND [IndexColumns].column_id = [columns].column_id WHERE [IndexColumns].object_id = [tables].object_id AND [IndexColumns].index_id = [PrimaryKeys].index_id ORDER BY [columns].column_id FOR xml path ('')) D (column_names) ORDER BY Schema_name([tables].schema_id), [PrimaryKeys].[name] |
Output
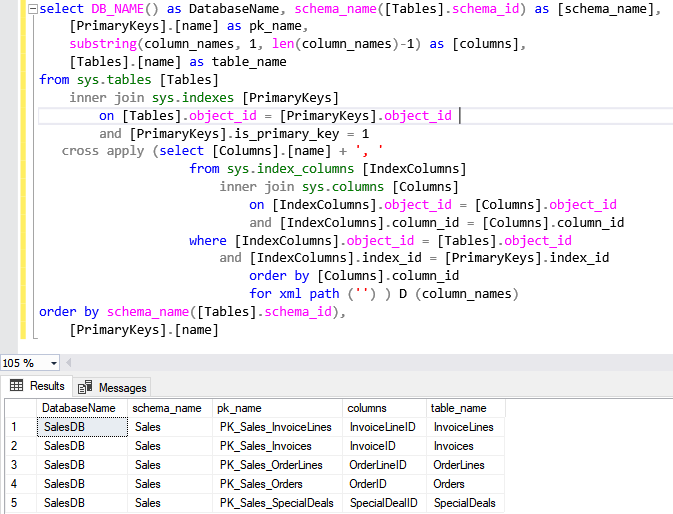
As you can see, the primary keys have been created in the SalesDB database.
Query to get the list of indexes.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
SELECT [indexes].[name] AS index_name, Substring(column_names, 1, Len(column_names) - 1) AS [columns], CASE WHEN [indexes].[type] = 1 THEN 'Clustered index' WHEN [indexes].[type] = 2 THEN 'Nonclustered index' END AS index_type, Schema_name([objects].schema_id) + '.' + [objects].[name] AS table_view, CASE WHEN [objects].[type] = 'U' THEN 'Table' WHEN [objects].[type] = 'V' THEN 'View' END AS [object_type] FROM sys.objects [objects] INNER JOIN sys.indexes [indexes] ON [objects].object_id = [indexes].object_id CROSS apply (SELECT [column].[name] + ', ' FROM sys.index_columns [indexcolumns] INNER JOIN sys.columns [column] ON [indexcolumns].object_id = [column].object_id AND [indexcolumns].column_id = [column].column_id WHERE [indexcolumns].object_id = [objects].object_id AND [indexcolumns].index_id = [indexes].index_id ORDER BY key_ordinal FOR xml path ('')) D (column_names) WHERE [objects].is_ms_shipped <> 1 AND index_id > 0 ORDER BY [indexes].[name] |
Output
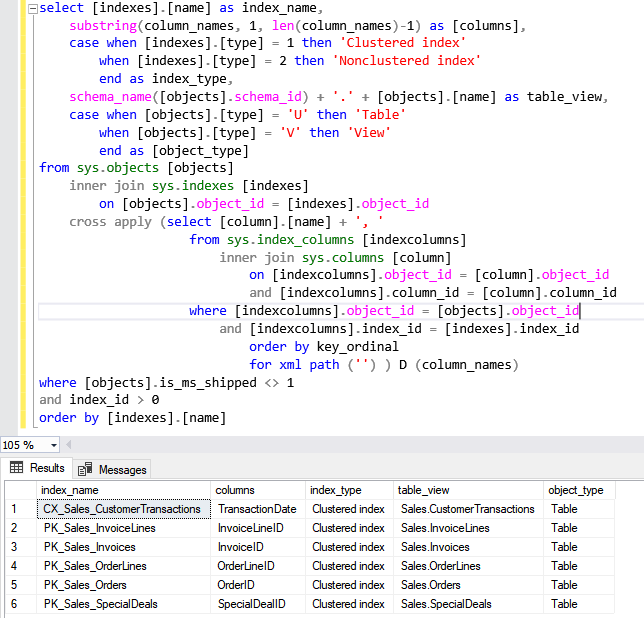
As you can see, the indexes have been created successfully.
Summary
In this article, we learn how to use the Transfer SQL Server object task to export the specific schema and the data from one database to another. To learn the method, we have exported a few tables from the Sales schema of the wideworldimportors database to the SalesDB database using the Transfer SQL Server object task of SSDT 2017.
- Different ways to identify and change compatibility levels in SQL Server - July 22, 2024
- Copy SQL Databases between Windows 10 and CentOS using SQL Server data tools - October 19, 2022
- Changing the location of FILESTREAM data files in SQL Database - October 14, 2022
